X Ray Of Childs Teeth
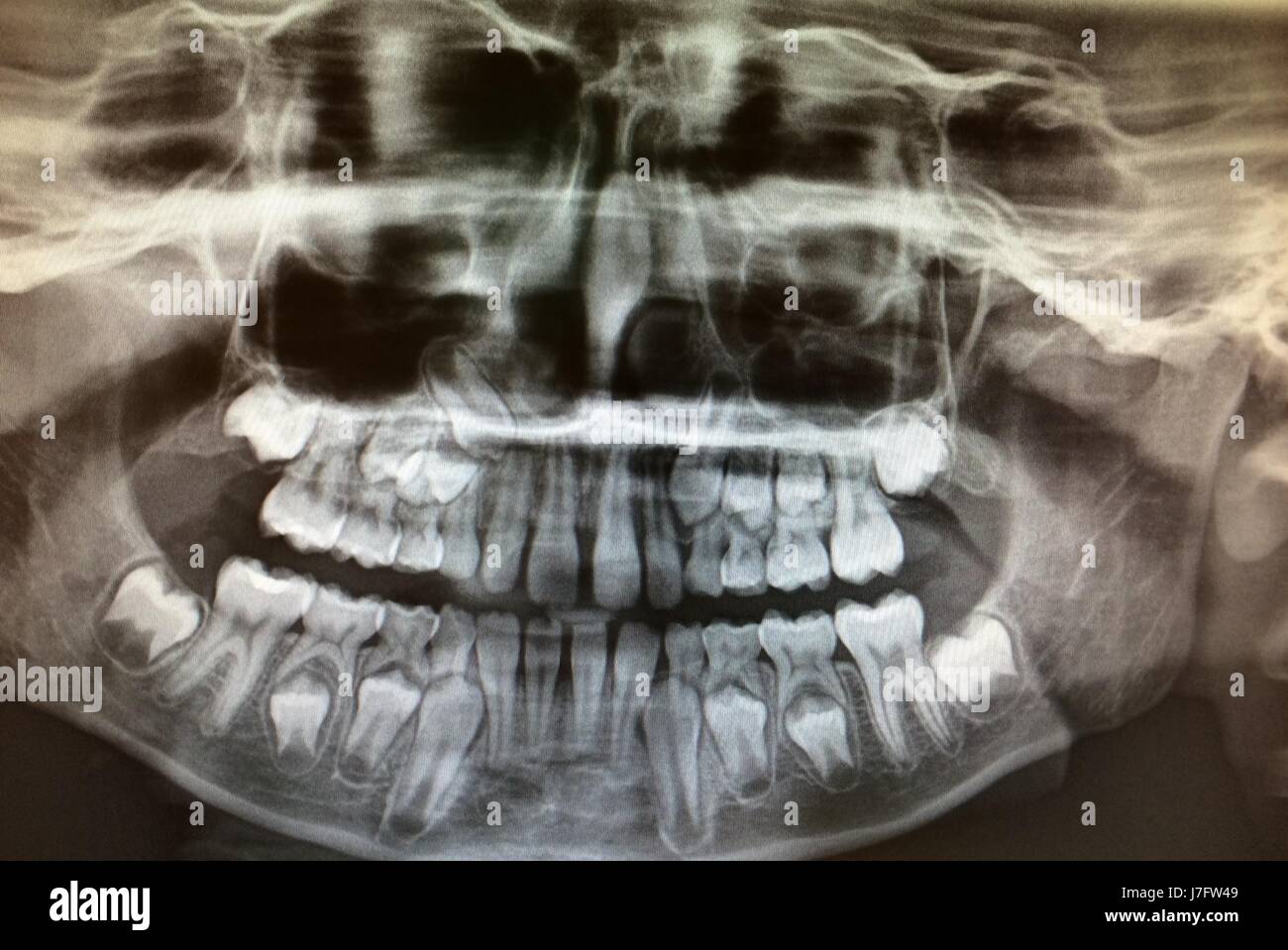
When it comes to the oral health of children, one of the most valuable diagnostic tools available to dentists is the X-ray. An X-ray of a child’s teeth can provide a wealth of information that is not visible during a routine visual examination. This includes the presence of cavities, the development and positioning of teeth, and the health of the bone surrounding the teeth.
Why Are X-Rays Necessary for Children?
X-rays are an essential part of pediatric dental care because they allow dentists to assess the health of a child’s teeth and surrounding tissues in a way that is not possible through a visual examination alone. Children are more susceptible to tooth decay due to various factors, including inadequate brushing habits, a diet high in sugars, and the presence of bacteria in the mouth. An X-ray can help identify cavities in their early stages, even before they become visible on the surface of the tooth. This early detection is crucial because it can prevent the progression of decay and the potential need for more extensive treatments, such as fillings or extractions.
Types of X-Rays Used in Pediatric Dentistry
There are several types of X-rays that can be used in pediatric dentistry, each serving a different purpose and offering unique advantages:
Bitewing X-Rays: These are the most common type of X-ray used in pediatric dentistry. They are taken with the child biting down on a piece of film or a digital sensor, which captures the crowns of the teeth. Bitewing X-rays are excellent for detecting cavities between the teeth and assessing the height of the bone supporting the teeth.
Periapical X-Rays: These X-rays show the entire tooth, from the crown to the root, as well as the surrounding bone. They are useful for detecting problems with the root of the tooth and the periapical region, which is the area around the root tip.
Panoramic X-Rays: Also known as panorex, these X-rays provide a wide view of the upper and lower jaw in a single image. They are particularly useful for assessing the development of wisdom teeth, the relationship of teeth to the jaw, and the presence of any abnormalities in the jawbone.
Digital X-Rays: These are similar to traditional X-rays but use digital technology to capture the images. Digital X-rays have several advantages, including lower radiation exposure, immediate image availability, and the ability to enhance the image for better diagnosis.
The Process of Taking X-Rays
The process of taking X-rays of a child’s teeth is relatively quick and painless. For bitewing and periapical X-rays, the dentist or dental assistant will place a film or digital sensor in the child’s mouth and then take the X-ray using an X-ray machine. For panoramic X-rays, the child stands still for a few seconds while the machine rotates around their head, capturing the full view of their jaw and teeth.
Safety Concerns and Radiation Exposure
One of the primary concerns parents have about X-rays is the exposure to radiation. While it is true that X-rays involve radiation, the amount used in dental X-rays is very small. Modern dental X-ray machines are designed to minimize radiation exposure, and digital X-rays use even less radiation than traditional film X-rays. Additionally, the American Dental Association (ADA) and the American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry (AAPD) have established guidelines to ensure that X-rays are used judiciously and only when necessary.
Interpreting X-Ray Results
After the X-rays are taken, the dentist will review them carefully to look for any signs of dental problems. If cavities are detected, the dentist will discuss the appropriate treatment options with the parent. If the X-rays show that the child’s teeth and surrounding tissues are healthy, the dentist may simply recommend continuing with regular dental check-ups and good oral hygiene practices to prevent future problems.
Conclusion
X-rays are a critical tool in pediatric dentistry, offering dentists a way to diagnose and treat dental problems early on. By understanding the types of X-rays used, the process of taking them, and addressing safety concerns, parents can feel more at ease when their child undergoes this diagnostic procedure. Remember, the goal of using X-rays in pediatric dentistry is to ensure the long-term health and integrity of a child’s teeth and to prevent potential issues from becoming more serious problems.
What is the purpose of taking X-rays of a child’s teeth?
+The purpose of taking X-rays of a child’s teeth is to detect any dental problems that are not visible during a routine visual examination, such as cavities between the teeth, the development and positioning of teeth, and the health of the surrounding bone.
Are dental X-rays safe for children?
+Yes, dental X-rays are safe for children. The radiation exposure from dental X-rays is minimal, especially with the use of digital X-ray technology, which uses significantly less radiation than traditional film X-rays.
How often should a child have dental X-rays?
+The frequency of dental X-rays for children depends on their individual oral health needs and risk factors for dental problems. The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry recommends that children have X-rays taken based on their specific needs, which could range from every 6 months for children at high risk of dental problems to every 2-3 years for children at lower risk.