Wounds That Require Stitches: Healing Guide
The aftermath of a skin injury can be a daunting experience, with the healing process being just as crucial as the initial treatment. When it comes to wounds that require stitches, understanding the intricacies of the healing process is vital for optimal recovery. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of wound healing, exploring the types of wounds that necessitate stitches, the stitching process itself, and the subsequent care required to ensure a seamless recovery.
Types of Wounds That Require Stitches
Not all wounds require stitches, but those that are deep, large, or have jagged edges often do. The primary goal of stitches, also known as sutures, is to bring the edges of the wound closer together, promoting faster healing and minimizing the risk of infection. Wounds that typically require stitches include:
- Deep Cuts: Any cut that goes beyond the top layer of skin may need stitches to close the wound properly and prevent infection.
- Large Cuts: The size of the cut is a significant factor. Larger cuts are more likely to require stitches to ensure the wound heals correctly and to reduce the risk of scar formation.
- Cuts with Jagged Edges: Smooth edges are easier to close and heal faster. Jagged edges, on the other hand, may require stitches to align the skin properly.
- Cuts on the Face: Due to the face’s visibility and the potential for significant scarring, cuts here often receive stitches, even if they might not require them based on size or depth alone.
- Cuts That Won’t Stop Bleeding: If a cut continues to bleed after applying pressure for a few minutes, it might need stitches, as this could indicate a deeper wound.
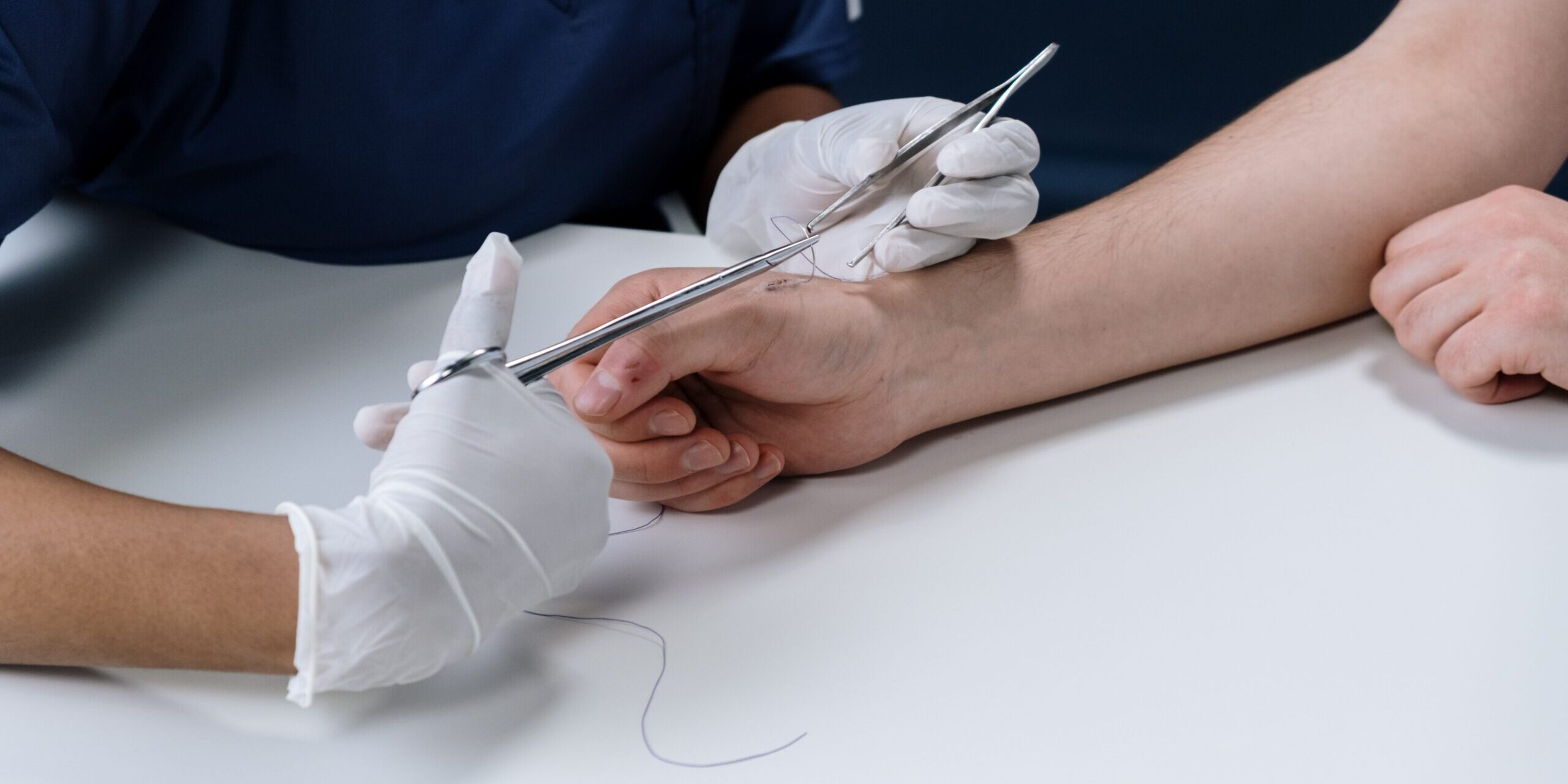
The Stitching Process
The process of getting stitches is relatively straightforward but requires precision and care. Here’s what you can expect:
- Preparation: The area around the wound is cleaned, and you might be given a local anesthetic to numb the pain.
- Stitching: The healthcare provider then uses a needle and thread to sew the edges of the wound together. The type of thread used can vary; sometimes, it’s absorbable and doesn’t need to be removed, while other times, it’s non-absorbable and requires a follow-up visit for removal.
- Aftercare Instructions: You’ll be given instructions on how to care for your wound, including keeping it clean, applying antibiotic ointment, and covering it with a bandage.
Caring for Your Stitches
Proper care of your stitches is crucial for healing and preventing complications. Here are some key points to remember:
- Keep It Clean: Gently wash the wound with soap and water. Avoid using harsh soap, hydrogen peroxide, or iodine.
- Apply Antibiotic Ointment: This can help prevent infection and promote healing.
- Cover the Wound: Use a bandage to protect the wound and keep it clean.
- Follow Up: Attend your follow-up appointments to have your stitches removed and to check on the healing progress.
Potential Complications
While stitches are generally safe, there are potential complications to watch out for, including:
- Infection: Signs of infection include increased redness, swelling, warmth, or pus around the wound, and fever.
- Allergic Reaction: Some people may be allergic to the materials used in stitches.
- Scarring: The appearance of the scar can vary based on the wound’s location, size, and how well you care for it during healing.
Preventing Wounds
Prevention is always better than cure. Here are some tips to reduce your risk of getting wounds that might require stitches:
- Wear Protective Gear: When engaging in activities that could lead to cuts or abrasions, wear appropriate protective gear, such as gloves or safety glasses.
- Be Cautious with Sharp Objects: Always handle sharp objects with care, and keep them out of the reach of children.
- Maintain a Safe Environment: Ensure your home is free from hazards that could cause falls or cuts.
Conclusion
Wounds that require stitches can be a significant health concern, but with the right care and understanding, the healing process can be smooth and effective. Remember, each wound is unique, and the specific care required can vary. Always follow the instructions provided by your healthcare provider and seek medical attention if you notice any signs of infection or other complications. By taking the right steps, you can ensure your wound heals well, minimizing the risk of long-term damage or scarring.
How long do stitches typically take to heal?
+The healing time for stitches can vary depending on the location and depth of the wound, as well as the overall health of the individual. Generally, it can take anywhere from a few days to a couple of weeks for the wound to heal enough for the stitches to be removed.
Can I take a bath or shower with stitches?
+It’s generally recommended to avoid submerging the wound in water until it’s fully healed, which usually means avoiding baths. However, showers are often okay, provided you keep the wound covered and avoid getting soap or shampoo directly on it. It’s best to consult with your healthcare provider for specific advice based on your situation.
How can I minimize scarring from stitches?
+To minimize scarring, it’s crucial to follow the aftercare instructions provided by your healthcare provider diligently. This includes keeping the wound clean, applying topical treatments as recommended, and protecting the area from the sun. Silicone gel or sheeting can also be used to help flatten and soften the scar tissue as it forms.