Where Should My Tongue Rest
The ideal position of the tongue is a topic of interest in various fields, including dentistry, orthodontics, and even speech therapy. The placement of the tongue when at rest can have implications for oral health, breathing, and overall comfort. So, where should your tongue rest?
To understand the optimal tongue position, let’s first explore the anatomy and functions of the tongue. The tongue is a muscular organ that plays a crucial role in activities such as eating, speaking, and swallowing. It is composed of intrinsic and extrinsic muscles that work together to facilitate these functions. The tongue’s position and movement are controlled by the lingual frenulum, a small fold of tissue that connects the tongue to the floor of the mouth.
The Neutral Position
When the tongue is at rest, it should be in a neutral position, meaning it should not be pushing against the teeth or the roof of the mouth. This position allows for a balanced and relaxed state of the oral cavity. So, where exactly is this neutral position?
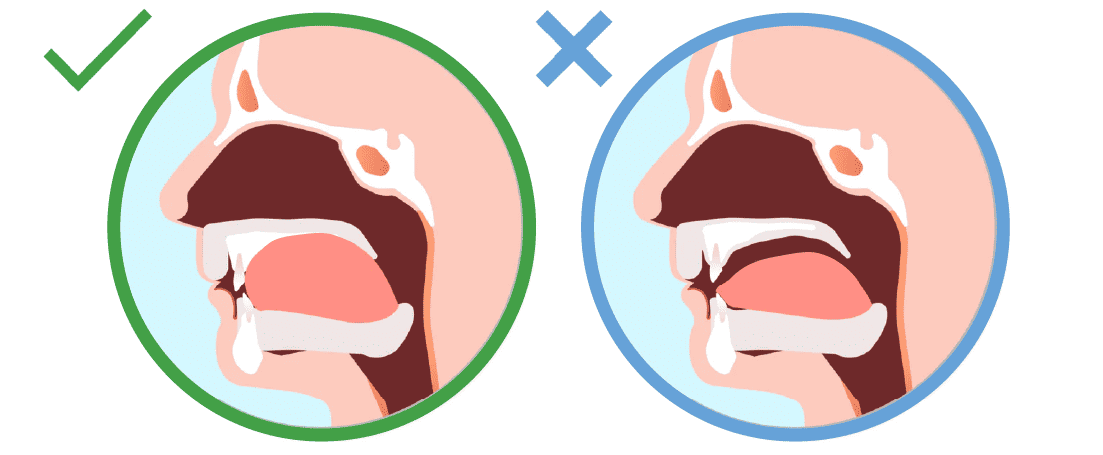
Research suggests that the ideal resting position of the tongue is against the palate, with the tongue’s surface lightly touching the roof of the mouth. This position is often referred to as the “palatal position.” When the tongue is in this position, it should be relaxed, with the tip of the tongue gently touching the area just behind the upper front teeth.
Why is the Palatal Position Important?
The palatal position is essential for maintaining proper oral posture and preventing various oral health issues. When the tongue rests against the palate, it:
- Supports proper breathing: The tongue’s position helps keep the airway open, allowing for unobstructed breathing.
- Maintains oral posture: The tongue’s resting position helps maintain the alignment of the teeth and jaws, reducing the risk of orthodontic issues.
- Prevents teeth grinding and clenching: The relaxed tongue position reduces the likelihood of teeth grinding and clenching, which can lead to TMJ disorders and tooth wear.
- Facilitates proper swallowing: The tongue’s position helps coordinate the swallowing process, ensuring that food and liquids are properly directed down the esophagus.
What Happens if the Tongue Doesn’t Rest in the Palatal Position?
If the tongue doesn’t rest in the palatal position, it can lead to various issues, including:
- Orthodontic problems: A tongue that rests against the teeth or the floor of the mouth can exert pressure on the teeth, leading to misalignment and orthodontic issues.
- Breathing difficulties: A tongue that obstructs the airway can lead to breathing difficulties, such as mouth breathing or sleep apnea.
- TMJ disorders: A tongue that rests in an abnormal position can lead to TMJ disorders, including pain and clicking in the jaw joint.
- Tooth wear and erosion: A tongue that rests against the teeth can lead to tooth wear and erosion, particularly on the upper front teeth.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the ideal resting position of the tongue is against the palate, with the tongue’s surface lightly touching the roof of the mouth. Maintaining this position is essential for proper oral posture, breathing, and overall oral health. If you’re unsure about your tongue’s resting position or experience any oral health issues, consult with a dental professional or orthodontist for personalized guidance.
What is the ideal resting position of the tongue?
+The ideal resting position of the tongue is against the palate, with the tongue’s surface lightly touching the roof of the mouth.
Why is the palatal position important for oral health?
+The palatal position is essential for maintaining proper oral posture, supporting proper breathing, preventing teeth grinding and clenching, and facilitating proper swallowing.
What happens if the tongue doesn’t rest in the palatal position?
+If the tongue doesn’t rest in the palatal position, it can lead to orthodontic problems, breathing difficulties, TMJ disorders, and tooth wear and erosion.
