What Is Furcation In Dentistry
Furcation in dentistry refers to the area where the roots of multi-rooted teeth diverge or split. This anatomical region is of significant importance in dental diagnosis, treatment planning, and oral hygiene practices. The complexity of furcation areas can pose challenges for dental professionals and patients alike, as these areas can be difficult to clean and are susceptible to various pathological conditions.
Anatomy and Classification
Multi-rooted teeth, such as molars, have more than one root. The furcation is essentially the point at which these roots separate. The classification of furcation involvements is typically based on the extent of bone loss in the furcation area, which can be observed during radiographic examination or through direct visualization during surgical procedures.
- Class I Furcation Involvement: This is the initial stage where there is a slight bone loss, but it does not extend beyond the furcation roof.
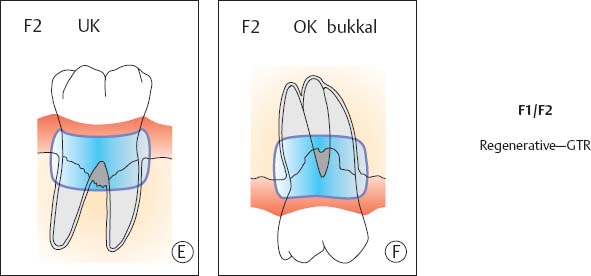
- Class II Furcation Involvement: Bone loss is more pronounced, extending into the furcation but not beyond the level of the root trunk.
- Class III Furcation Involvement: This stage represents significant bone loss where the furcation is through-and-through, allowing for probing or visual inspection from one side of the tooth to the other.
- Class IV Furcation Involvement: The most advanced stage, characterized by severe bone loss and possible disintegration of the root structure.
Clinical Significance
The clinical significance of furcation involvements is multifaceted:
- Periodontal Disease: Furcation areas are prone to periodontal disease due to their anatomy, which can trap plaque, bacteria, and debris, leading to inflammation and infection.
- Treatment Challenges: The anatomy of the furcation area makes it difficult for patients to maintain good oral hygiene and for dental professionals to access for cleaning and treatment.
- Prognosis: Teeth with advanced furcation involvements may have a poorer prognosis, potentially requiring more complex and aggressive treatments, including surgical interventions or extraction in severe cases.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis of furcation involvements involves a combination of clinical examination, radiographic evaluation, and, in some cases, probing under anesthesia to assess the extent of bone loss accurately.
Treatment options vary based on the extent of the involvement and the overall health of the tooth and surrounding tissues:
- Non-surgical Periodontal Therapy: Deep cleaning, including root planing and scaling, may be effective for early stages of furcation involvement.
- Surgical Interventions: For more advanced cases, surgical procedures such as root resection, hemisection, or tunnel preparation may be indicated to eliminate the diseased furcation area or to facilitate better access for oral hygiene.
- Regenerative Procedures: In some instances, regenerative techniques can be employed to regenerate lost bone and periodontal tissue in the furcation area.
Prevention and Maintenance
Prevention of furcation involvements focuses on meticulous oral hygiene practices and regular dental check-ups to catch and treat periodontal disease early. For patients with existing furcation involvements, tailored oral hygiene instructions, possibly including the use of interdental brushes or specialized floss, and regular follow-up appointments are crucial for maintaining periodontal health and preventing further deterioration.
In conclusion, furcation in dentistry represents a critical aspect of periodontal health and disease. Understanding the anatomy, classification, and clinical implications of furcation involvements is essential for dental professionals to provide appropriate diagnosis, treatment, and preventive care to patients with multi-rooted teeth.
What is the primary challenge posed by furcation areas in teeth?
+The primary challenge posed by furcation areas is their susceptibility to plaque, bacteria, and debris accumulation due to their anatomical complexity, leading to periodontal disease and difficulties in cleaning and treatment.
How are furcation involvements classified in dentistry?
+Furcation involvements are classified based on the extent of bone loss, ranging from Class I, which is the initial stage with slight bone loss, to Class IV, representing severe bone loss with possible disintegration of the root structure.
What are the treatment options for furcation involvements?
+Treatment options for furcation involvements include non-surgical periodontal therapy for early stages, surgical interventions such as root resection or hemisection for more advanced cases, and regenerative procedures to regenerate lost bone and tissue.
The complexities of furcation involvements underscore the importance of preventive dental care and early intervention in periodontal diseases. By understanding the nuances of furcation anatomy and pathology, dental professionals can provide targeted treatments and educate patients on the most effective strategies for maintaining oral health and preventing the progression of periodontal disease in teeth with furcation involvements.
