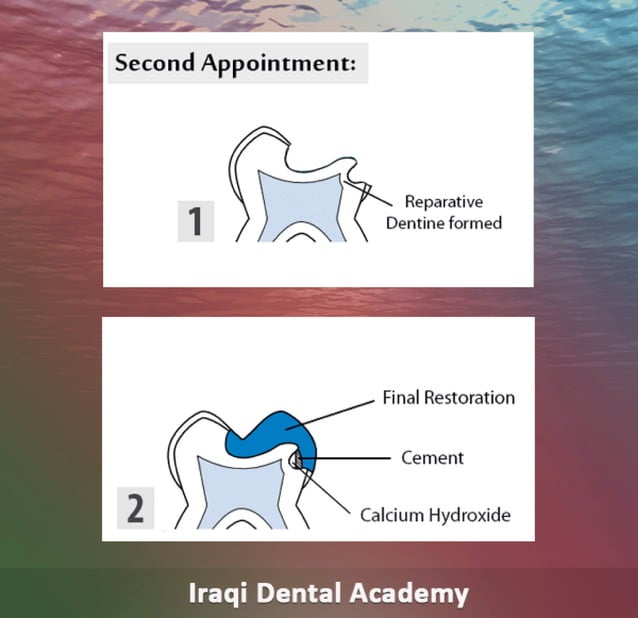
What Is Dds In Dentistry? Your Career Guide
The field of dentistry has undergone significant transformations over the years, with advances in technology, techniques, and educational pathways. One such development is the Doctor of Dental Surgery (DDS) degree, which has become a cornerstone of dental education. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of DDS in dentistry, exploring its history, curriculum, career prospects, and what it takes to become a successful dentist.
To begin with, let’s define what a DDS is. The Doctor of Dental Surgery degree is a professional degree that qualifies individuals to practice dentistry. It is awarded upon completion of a four-year undergraduate program in dental surgery, which includes both theoretical and clinical training. The DDS degree is equivalent to the Doctor of Dental Medicine (DMD) degree, with the difference being largely historical and regional.
History of the DDS Degree
The DDS degree has its roots in the mid-19th century, when the first dental schools were established in the United States. The Baltimore College of Dental Surgery, founded in 1840, was the first institution to offer a formal dental education program. Initially, the program was a two-year course, but it was later extended to three years, and eventually, to four years. Today, the DDS degree is recognized as the standard qualification for dental practice in many countries around the world.
Curriculum and Training
The DDS program is designed to provide students with a comprehensive education in the theoretical and clinical aspects of dentistry. The curriculum typically includes:
- Basic Sciences: Courses in anatomy, biochemistry, physiology, pharmacology, and microbiology lay the foundation for understanding the biological and chemical principles of dental practice.
- Clinical Sciences: Students learn about various aspects of clinical dentistry, including diagnosis, treatment planning, and patient management.
- Clinical Practice: Under the supervision of experienced dentists, students participate in clinical rotations, where they gain hands-on experience in treating patients.
- Elective Courses: Students can choose from a range of elective courses, such as pediatric dentistry, orthodontics, or oral surgery, to develop specialized skills and interests.
Throughout the program, students are also taught essential skills, such as:
- Communication: Effective communication with patients, colleagues, and other healthcare professionals.
- Critical Thinking: Analyzing complex cases, evaluating evidence, and making informed decisions.
- Problem-Solving: Developing creative solutions to clinical problems.
- Professionalism: Understanding the ethical, legal, and social responsibilities of dental practice.
Career Prospects and Specializations
A DDS degree opens up a wide range of career opportunities in dentistry. Some of the most common specializations include:
- General Dentistry: Providing routine dental care, including exams, fillings, crowns, and extractions.
- Pediatric Dentistry: Specializing in the care of children’s teeth and oral health.
- Orthodontics: Focusing on the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of dental and facial irregularities.
- Oral Surgery: Performing surgical procedures, such as extractions, implants, and bone grafting.
- Periodontics: Treating gum diseases and other conditions affecting the supporting structures of the teeth.
In addition to these specializations, DDS graduates can also pursue careers in:
- Academia: Teaching and researching at dental schools or universities.
- Research: Conducting studies and developing new treatments or technologies.
- Public Health: Working in government agencies, non-profits, or private organizations to promote oral health and prevent disease.
- Private Practice: Establishing their own dental practices or joining existing ones.
Key Skills and Traits
To succeed as a dentist, you will need to possess certain skills and traits, including:
- Manual Dexterity: Good hand-eye coordination and fine motor skills for performing precise procedures.
- Attention to Detail: Carefully examining patients’ teeth and oral tissues to diagnose and treat conditions.
- Communication: Effectively interacting with patients, explaining treatment options, and providing instructions.
- Empathy: Understanding and addressing patients’ concerns, fears, and anxieties.
- Business Acumen: Managing a dental practice, including staff, finances, and marketing.
Real-World Applications and Case Studies
To illustrate the practical aspects of dentistry, let’s consider a few case studies:
- Case 1: A patient presents with a severe toothache and requires an emergency extraction. The dentist must quickly assess the situation, administer anesthesia, and perform the extraction while ensuring the patient’s comfort and safety.
- Case 2: A child patient requires orthodontic treatment to correct a misaligned bite. The dentist must evaluate the child’s growth and development, create a customized treatment plan, and monitor progress over several years.
These cases demonstrate the importance of staying up-to-date with the latest techniques, technologies, and research in dentistry.
Staying Current in the Field
The field of dentistry is constantly evolving, with new technologies, materials, and techniques being developed. To stay current, dentists must commit to ongoing education and professional development. This can include:
- Continuing Education Courses: Participating in workshops, conferences, and online courses to enhance skills and knowledge.
- Professional Memberships: Joining dental associations and organizations to stay informed about industry developments and network with peers.
- Research and Publications: Staying up-to-date with the latest research and publications in dental journals and textbooks.
Frequently Asked Questions
For those considering a career in dentistry, here are some frequently asked questions:
What is the difference between a DDS and a DMD degree?
+The difference between a DDS and a DMD degree is largely historical and regional. Both degrees qualify individuals to practice dentistry, but the DDS degree is more commonly used in the United States, while the DMD degree is used in other countries.
How long does it take to complete a DDS program?
+A DDS program typically takes four years to complete, although some programs may offer combined undergraduate and graduate degree options.
What are the admission requirements for a DDS program?
+Admission requirements for a DDS program typically include a bachelor's degree, completion of prerequisite courses, and satisfactory scores on the Dental Acceptance Test (DAT).
What are the job prospects for DDS graduates?
+Job prospects for DDS graduates are excellent, with a high demand for dental services and a wide range of career opportunities in private practice, academia, research, and public health.
What are the key skills and traits required to succeed as a dentist?
+To succeed as a dentist, you will need to possess good manual dexterity, attention to detail, communication skills, empathy, and business acumen.
In conclusion, a DDS degree is a rewarding and challenging career path that requires a strong foundation in science, clinical skills, and communication. With a wide range of specializations and career prospects, dentistry offers a fulfilling and dynamic profession that can make a significant difference in people’s lives. Whether you are just starting your educational journey or are a seasoned professional, the field of dentistry has much to offer.