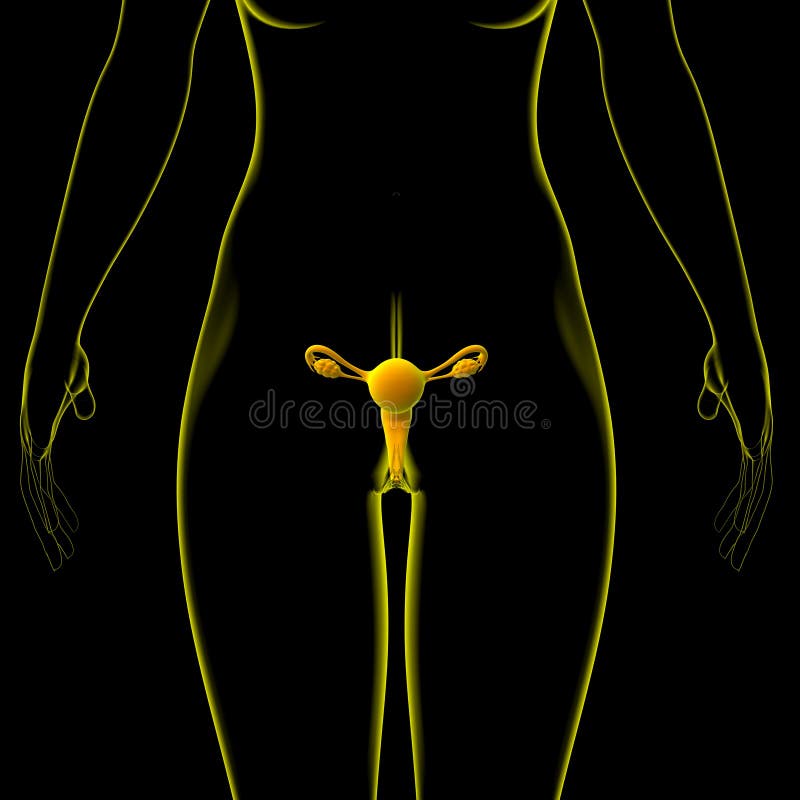
What Is A 3D Female Reproductive System Model?

The 3D female reproductive system model is an advanced educational tool designed to provide a comprehensive and interactive understanding of the female reproductive system. This model utilizes three-dimensional visualization to accurately depict the complex relationships between various organs and structures within the female reproductive system. By allowing users to explore and manipulate the model in a virtual environment, it enhances learning and retention of anatomical knowledge.
One of the primary benefits of a 3D female reproductive system model is its ability to facilitate a deeper understanding of the spatial relationships between different components of the reproductive system. Traditional two-dimensional diagrams and texts often struggle to convey the intricate anatomy of the female body, leading to confusion and misunderstandings. In contrast, 3D models enable learners to visualize how organs such as the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, and vagina are positioned and interconnected, promoting a more intuitive grasp of human anatomy.
Applications in Education and Healthcare
The applications of 3D female reproductive system models are multifaceted, catering to both educational institutions and healthcare settings. In medical schools and anatomy classes, these models serve as invaluable teaching aids. They can be used to explain complex concepts, such as the menstrual cycle, fertilization, and pregnancy, in a way that is engaging and easy to understand. This interactive approach to learning anatomy has been shown to improve student engagement and retention of material compared to traditional teaching methods.
In healthcare, 3D models can be used by medical professionals to communicate more effectively with patients. For example, a gynecologist might use a 3D model to explain a diagnosis or the implications of a surgical procedure, helping patients understand their condition and treatment options more clearly. This enhanced patient education can lead to better health outcomes by ensuring that patients are well-informed and involved in their care.
Technological Advancements
The development of 3D female reproductive system models has been significantly influenced by advancements in technology. The integration of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) into these models has opened up new possibilities for immersive and interactive learning experiences. With VR/AR, users can step into a virtual environment where they can explore the reproductive system from different angles and even participate in simulated procedures. This level of interactivity not only makes learning more enjoyable but also provides a safe space for medical students and professionals to practice and refine their skills without risk to real patients.
Furthermore, 3D printing technology has enabled the creation of physical models that can be handled and examined in detail. These tangible models can be particularly beneficial for learners who prefer a hands-on approach, offering a tactile experience that complements digital tools. The combination of digital and physical 3D models provides a comprehensive learning experience, catering to different learning styles and preferences.
Future Directions
As technology continues to evolve, we can expect 3D female reproductive system models to become even more sophisticated and integrated into medical education and practice. One potential future direction is the development of personalized models based on individual patient data. This could involve using patient-specific imaging data, such as MRI or CT scans, to create customized 3D models that reflect the unique anatomy of each patient. Such personalized models could revolutionize patient care by allowing for more precise diagnosis, treatment planning, and surgical simulation.
Another area of potential growth is the incorporation of real-time data and dynamic simulations into 3D models. This could enable the modeling of physiological processes and the simulation of different scenarios, such as the progression of diseases or the effects of treatments. By bridging the gap between static anatomy and dynamic physiology, these advanced models could further enhance our understanding of the female reproductive system and improve outcomes in women’s health.
Conclusion
3D female reproductive system models represent a significant advancement in the field of medical education and patient care. By providing an interactive, three-dimensional representation of the female reproductive anatomy, these models enhance understanding, improve knowledge retention, and facilitate more effective communication between healthcare providers and patients. As technological capabilities continue to expand, the potential applications of these models will only continue to grow, offering promising avenues for improving education, practice, and outcomes in women’s health.
What are the primary benefits of using 3D models in learning about the female reproductive system?
+The primary benefits include enhanced understanding of spatial relationships between organs, improved retention of anatomical knowledge, and a more engaging learning experience. These models also facilitate better communication between healthcare providers and patients.
How can 3D female reproductive system models be used in healthcare settings?
+In healthcare settings, these models can be used by medical professionals to communicate more effectively with patients about diagnoses, treatment options, and surgical procedures. They can also be used for patient education, helping patients understand their condition and care better.
What role does technology, such as VR and AR, play in the development and use of 3D female reproductive system models?
+Technologies like VR and AR enable the creation of immersive and interactive learning experiences. They allow users to explore the reproductive system in detail, practice procedures in a simulated environment, and engage with the material in a more dynamic way, enhancing learning outcomes.
Implementing 3D Female Reproductive System Models in Education and Practice

- Identify Learning Objectives: Determine what learners need to understand about the female reproductive system, whether it's for educational purposes or patient care.
- Select Appropriate Models: Choose 3D models that align with the identified objectives, considering factors like the level of detail, interactivity, and the technology required to access them.
- Integrate into Curriculum or Practice: Incorporate the 3D models into educational curricula or clinical practice, using them as tools for explanation, demonstration, and interactive learning.
- Monitor and Evaluate Effectiveness: Assess how the use of 3D models impacts learning outcomes, patient understanding, and healthcare providers' ability to communicate complex information effectively.
- Update and Refine Models: As new technologies and anatomical discoveries emerge, update the 3D models to ensure they remain accurate, relevant, and effective tools for education and patient care.
Pros and Cons of 3D Female Reproductive System Models
Pros:
- Enhanced understanding and retention of anatomical knowledge
- Improved patient education and communication
- Interactive and engaging learning experience
- Potential for personalized models based on patient data
Cons:
- Initial investment in technology and model development
- Potential for information overload if not used judiciously
- Need for Update and Maintenance to Reflect Latest Knowledge

