What Causes Diarrhea? Effective Cleanup Solutions
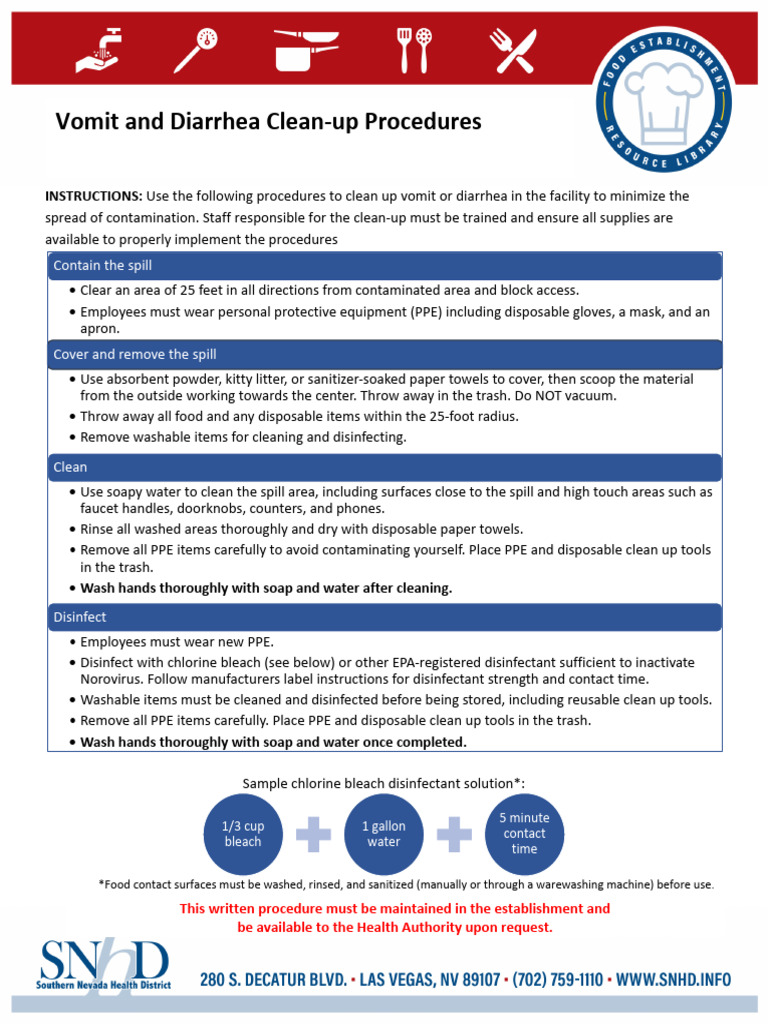
Diarrhea, a condition characterized by loose, watery stools, or a frequent need to have a bowel movement, can be caused by a variety of factors. Understanding the underlying causes of diarrhea is crucial in implementing effective cleanup solutions and preventing the spread of infection. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the common causes of diarrhea, discuss practical cleanup strategies, and provide expert advice on maintaining hygiene and preventing future occurrences.
Viral Gastroenteritis: A Leading Cause of Diarrhea
Viral gastroenteritis, often referred to as the stomach flu, is a major cause of diarrhea. This condition is usually caused by noroviruses or rotaviruses, which can be transmitted through contaminated food, water, or close contact with an infected person. The symptoms of viral gastroenteritis include diarrhea, vomiting, stomach cramps, and fever. Effective cleanup involves thorough disinfection of surfaces, especially in areas where food is prepared, and frequent handwashing to prevent the spread of the virus.
Bacterial Infections: Another Common Cause
Bacterial infections are another common cause of diarrhea. Bacteria such as Salmonella, E. coli, and Campylobacter can contaminate food and water, leading to diarrhea. These infections can be severe and may require medical attention. Cleanup solutions involve cooking food thoroughly, storing it properly, and avoiding cross-contamination. Regularly cleaning and disinfecting food preparation areas and utensils are also essential in preventing bacterial infections.
Food Intolerances and Sensitivities
Food intolerances and sensitivities can also cause diarrhea. Lactose intolerance, gluten sensitivity, and fructose malabsorption are common conditions that can lead to diarrhea after consuming specific foods. Understanding and identifying food triggers is key to managing these conditions. Cleanup solutions involve proper food handling and storage to prevent cross-contamination with allergenic foods.
Medications and Diarrhea
Certain medications, such as antibiotics, can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria, leading to diarrhea. Other medications like laxatives and antacids can also cause diarrhea as a side effect. Managing medication-induced diarrhea involves discussing alternative treatments with a healthcare provider and implementing dietary changes to help stabilize bowel movements.
Practical Cleanup Solutions
Effective cleanup is crucial in preventing the spread of infection and maintaining a hygienic environment. Here are some practical cleanup solutions:
Immediate Cleanup: In case of a diarrhea incident, immediate cleanup is essential. Wear gloves, and using a disposable mop or paper towels, remove as much of the spill as possible. Then, disinfect the area thoroughly with a bleach solution.
Disinfection: Regular disinfection of surfaces, especially in bathrooms and kitchens, can prevent the spread of viruses and bacteria. Pay particular attention to high-touch areas such as doorknobs, faucets, and toilet handles.
Laundry: Soiled clothing and bedding should be washed immediately in hot water to kill bacteria and viruses. Adding a disinfectant to the wash can provide extra protection.
Hand Hygiene: Frequent handwashing with soap and water is one of the most effective ways to prevent the spread of diarrhea-causing viruses and bacteria. Use warm water, soap, and rub hands together for at least 20 seconds, especially after using the bathroom, before eating, and after cleaning up after someone with diarrhea.
Preventing Future Occurrences
Preventing future occurrences of diarrhea involves a combination of good hygiene practices, safe food handling, and a balanced diet. Here are some strategies:
Vaccinations: For certain causes of diarrhea, such as rotavirus, vaccinations are available and can provide protection, especially for young children.
Safe Water: Ensuring access to safe, clean water is crucial. In areas where water quality is a concern, using water purification methods or drinking bottled water can help prevent waterborne illnesses.
Dietary Changes: For individuals with food intolerances or sensitivities, avoiding trigger foods can prevent episodes of diarrhea. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help maintain a healthy gut microbiome.
Regular Health Check-Ups: Regular health check-ups can help identify underlying conditions that may be contributing to diarrhea. Early detection and treatment can prevent complications and improve quality of life.
Conclusion
Diarrhea can be caused by a variety of factors, including viral and bacterial infections, food intolerances, and certain medications. Implementing effective cleanup solutions and maintaining good hygiene practices are key to preventing the spread of infection and promoting a healthy environment. By understanding the causes of diarrhea and taking proactive steps towards prevention, individuals can reduce the incidence of this condition and maintain overall health and well-being.
What are the most common causes of diarrhea?
+The most common causes of diarrhea include viral gastroenteritis, bacterial infections, food intolerances, and certain medications. Viral gastroenteritis, often referred to as the stomach flu, is a leading cause and can be transmitted through contaminated food, water, or close contact with an infected person.
How can I prevent the spread of diarrhea-causing viruses and bacteria?
+Preventing the spread of diarrhea-causing viruses and bacteria involves good hygiene practices, including frequent handwashing with soap and water, especially after using the bathroom, before eating, and after cleaning up after someone with diarrhea. Regular disinfection of surfaces, especially in bathrooms and kitchens, is also crucial.
What dietary changes can help manage diarrhea caused by food intolerances?
+For individuals with food intolerances, avoiding trigger foods is key to managing diarrhea. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help maintain a healthy gut microbiome. Identifying and avoiding foods that cause intolerance, such as lactose for those with lactose intolerance, can significantly reduce episodes of diarrhea.
In conclusion, while diarrhea can be caused by a variety of factors, understanding these causes and implementing effective cleanup solutions and preventive strategies can significantly reduce its incidence. By maintaining good hygiene, practicing safe food handling, and making informed dietary choices, individuals can protect themselves and their communities from the spread of infection and promote overall health and well-being.
