What Causes Decayed Wisdom Tooth? Relief Options
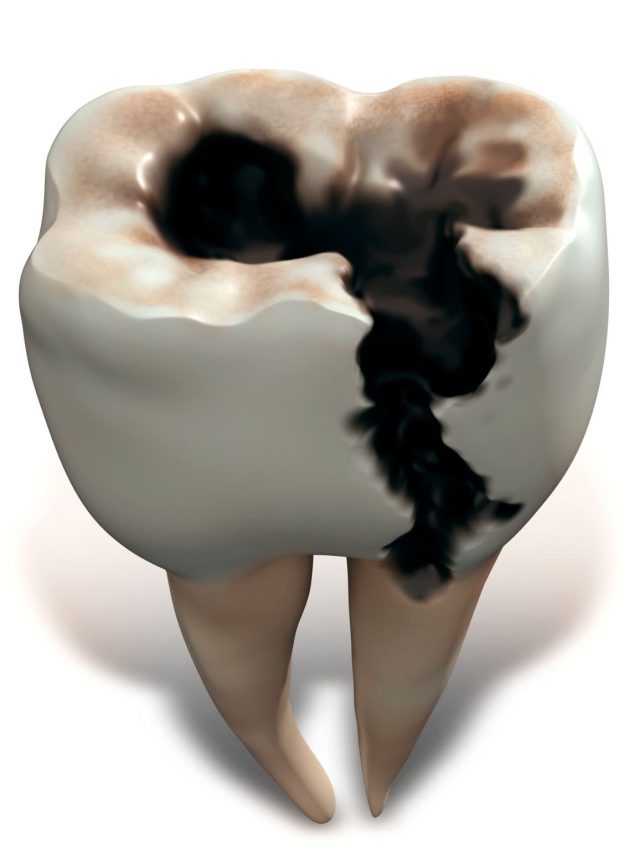
The presence of decayed wisdom teeth can be a significant source of discomfort and potential health issues for many individuals. Wisdom teeth, which typically emerge between the ages of 17 and 25, can become problematic due to their late emergence, often resulting in inadequate space in the jaw. This can lead to a variety of complications, including decay, due to the difficulty in cleaning these teeth properly.
One of the primary causes of decayed wisdom teeth is the inability to maintain good oral hygiene in the area surrounding these teeth. Because of their position at the back of the mouth, wisdom teeth are more challenging to brush and floss compared to other teeth. This difficulty in cleaning can lead to the accumulation of plaque and bacteria, which, over time, can cause tooth decay. Furthermore, the partially erupted nature of some wisdom teeth can create a haven for bacteria, as food particles can become trapped, fostering an environment conducive to decay.
Another factor contributing to the decay of wisdom teeth is the potential for overcrowding. When there is not enough space in the jaw for wisdom teeth to emerge properly, they can become impacted. Impacted wisdom teeth can be fully or partially submerged in the gum and bone, leading to swelling, pain, and increased susceptibility to infection and decay. The overcrowding also makes it harder for the teeth to be properly cleaned, increasing the risk of decay.
Symptoms of a decayed wisdom tooth can range from mild to severe and may include persistent toothache, swelling of the gums around the tooth, sensitivity to hot and cold foods, and bad breath. In some cases, if the decay progresses without intervention, it can lead to more serious complications such as abscesses, which are pockets of pus that can form at the tip of the root, or even cysts, which are fluid-filled sacs that can develop around the impacted tooth.
For relief from the discomfort and potential health risks associated with decayed wisdom teeth, several options are available. The most common recommendation is the removal of the affected tooth. This is particularly advised if the decay is extensive or if the tooth is impacted, as removing the tooth can prevent further complications. The procedure for removing a wisdom tooth can vary depending on the complexity of the case. Simple extractions can be performed by a general dentist, while more complex cases might require the expertise of an oral surgeon.
Before the extraction, the dentist or surgeon will typically review the patient’s medical history, take X-rays to assess the tooth’s position, and discuss anesthesia options to ensure the procedure is as painless as possible. Post-extraction care instructions are crucial to follow to minimize the risk of dry socket, a condition where the blood clot is dislodged from the socket, and to promote healing.
In cases where the decay is not extensive and the tooth can be saved, a dentist might recommend a filling or a crown, depending on the extent of the decay. However, given the common difficulties associated with wisdom teeth, such as their hard-to-reach location and potential for recurring problems, extraction is often the preferred solution.
Preventive care is crucial in minimizing the risk of wisdom teeth decay. Regular dental check-ups can help in early detection of potential issues. Additionally, practicing good oral hygiene, including brushing at least twice a day and flossing once a day, can significantly reduce the risk of decay. It’s also important to monitor the development of wisdom teeth, typically through X-rays during routine dental visits, to anticipate and manage any potential complications early on.
In conclusion, decayed wisdom teeth are a common dental issue that arises due to factors such as poor oral hygiene and overcrowding. Recognizing the symptoms and seeking professional dental advice is crucial to prevent further complications. Whether through extraction or restoration, there are effective relief options available for managing decayed wisdom teeth and preventing future oral health issues.
What are the common symptoms of a decayed wisdom tooth?
+The common symptoms include persistent toothache, swelling of the gums around the tooth, sensitivity to hot and cold foods, and bad breath. In some cases, more severe symptoms like abscesses or cysts can develop.
Can a decayed wisdom tooth be saved, or is removal always necessary?
+While removal is often recommended due to the potential for further complications, a decayed wisdom tooth can sometimes be saved with a filling or crown, depending on the extent of the decay. However, the decision to save or remove the tooth should be made under the guidance of a dental professional.
How can I prevent wisdom teeth decay?
+Practicing good oral hygiene, including regular brushing and flossing, and attending routine dental check-ups can significantly reduce the risk of wisdom teeth decay. Early monitoring of wisdom teeth development can also help in anticipating and managing potential complications.