What Are Surgical Drains After Mastectomy? Expert Guidance
Surgical drains are a common aspect of the recovery process for many patients undergoing mastectomy, a surgical procedure to remove one or both breasts, often performed to treat breast cancer. These drains play a crucial role in managing the aftermath of surgery, ensuring that the patient heals properly and reducing the risk of complications. Understanding what surgical drains are, how they work, and their importance in the postoperative care of mastectomy patients is essential for both healthcare providers and patients to navigate the recovery period effectively.
What Are Surgical Drains?
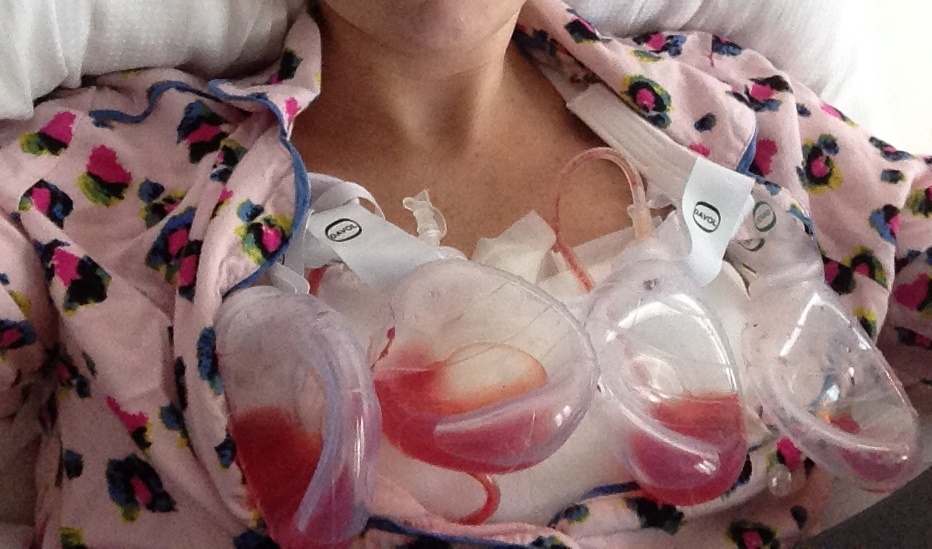
Surgical drains, also known as suction drains, are medical devices placed within the surgical site to remove fluid, such as blood, serum, or other liquids that might accumulate during and after surgery. In the context of mastectomy, these drains are typically inserted at the time of surgery and remain in place for several days or weeks, depending on the individual’s healing progress.
Types of Surgical Drains
There are several types of surgical drains that might be used after a mastectomy, each with its specific features and purposes. The most common types include:
- Jackson-Pratt (JP) Drain: A type of closed-suction drain, it consists of a flexible tube with a bulb at the end that creates negative pressure when compressed, drawing out fluid from the surgical site.
- Bulb Drain: Similar to the JP drain but might have slight variations in design, such as a softer bulb for easier compression.
- Flat Drains: These are thin, flexible drains designed for insertion under the skin to remove fluid from the surgical site, often used in procedures where less fluid accumulation is expected.
How Do Surgical Drains Work?
The principle behind surgical drains is to create a conduit for excess fluid to escape the surgical site, thereby reducing swelling, promoting healing, and minimizing the risk of infection or hematoma (a collection of blood outside of blood vessels). Here’s a simplified overview of their operation:
- Insertion: During the mastectomy, the surgeon carefully places the drain in the surgical cavity.
- Fluid Collection: The drain collects fluid that accumulates at the surgical site, preventing it from building up and causing unnecessary pressure or discomfort.
- Expression: The bulb or collection chamber of the drain is squeezed periodically to create negative pressure, drawing fluid out of the body.
- Monitoring and Removal: Healthcare providers monitor the amount and character of the fluid drained to assess the healing process. Once the fluid output diminishes to a certain level, usually indicating that significant healing has occurred, the drain is removed.
Importance of Surgical Drains After Mastectomy
The use of surgical drains following a mastectomy is critical for several reasons:
- Reduces Complications: By minimizing fluid accumulation, drains help reduce the risk of seroma (a collection of fluid under the skin) and hematoma, which can lead to infection or necessitate further surgical intervention.
- Promotes Healing: Drains facilitate a conducive environment for wound healing by reducing pressure and preventing fluid buildup, which can impede the healing process.
- Enhances Patient Comfort: By controlling swelling and reducing the risk of complications, surgical drains can make the recovery period more comfortable for patients.
Care and Management of Surgical Drains
Proper care and management of surgical drains are vital to ensure they function effectively and minimize the risk of complications. Patients should follow specific guidelines provided by their healthcare team, which typically include:
- Monitoring Drain Output: Keeping a log of the fluid drained can help in assessing the healing progress.
- Maintaining Drain Patency: Ensuring the drain remains unobstructed to allow for continuous fluid drainage.
- Preventing Infection: Following proper hygiene techniques and potentially using antimicrobial solutions to clean the drain site.
- Scheduling Follow-Up Appointments: Regular visits to the healthcare provider for assessment of healing and potential drain removal.
FAQs
How long do surgical drains stay in after a mastectomy?
+The duration for which surgical drains remain in place can vary significantly depending on the individual's healing progress, typically ranging from a few days to several weeks.
Can I shower with my surgical drains in place?
+Yes, but it's crucial to follow your healthcare provider's instructions carefully. Typically, patients are advised to keep the drain site dry for a certain period or use specific techniques to protect the site during showering.
What are the signs of complications with surgical drains that I should look out for?
+Signs of potential complications include increased redness or swelling around the drain site, fever, pus or foul odor from the drain, and significant pain that is not relieved by pain medication. If you experience any of these symptoms, contact your healthcare provider immediately.
Conclusion
Surgical drains are an integral component of the postoperative care plan for patients undergoing mastectomy, serving to minimize complications, promote healing, and enhance patient comfort. Understanding their role, proper care, and potential signs of complications is essential for a smooth and effective recovery process. As with any aspect of medical care, following the specific guidance of your healthcare team and staying informed can significantly contribute to a successful outcome.