Urinary Stent Pain
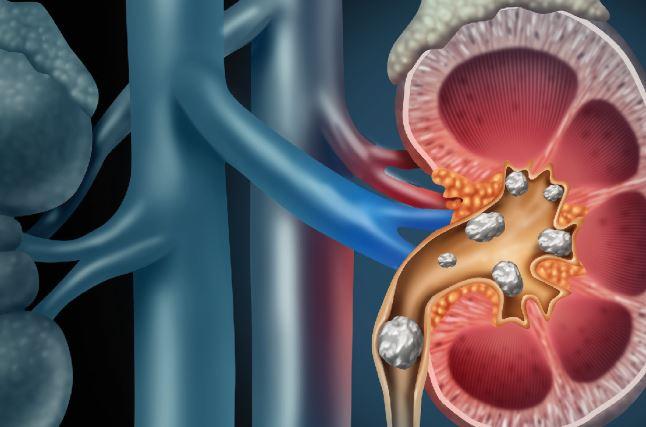
Urinary stent pain is a common issue faced by many individuals who undergo ureteral stent placement, a medical procedure aimed at relieving blockages in the urinary tract. The ureteral stent, a small, hollow tube made of plastic or metal, is inserted into the ureter to facilitate the flow of urine from the kidney to the bladder. While the stent is generally effective in addressing urinary tract blockages, it can cause discomfort and pain for some patients.
The severity and duration of urinary stent pain vary from person to person, with some individuals experiencing mild discomfort and others facing significant pain. Several factors contribute to the development of pain after ureteral stent placement, including the size and material of the stent, the location of the stent within the ureter, and individual differences in pain tolerance.
One of the primary causes of urinary stent pain is irritation of the bladder and ureteral lining. The stent can rub against the walls of the urinary tract, leading to inflammation and discomfort. Additionally, the stent can cause spasms in the ureter, which can be painful. In some cases, the stent may also cause an increase in urinary frequency and urgency, as the body tries to expel the foreign object.
Symptoms of urinary stent pain may include:
- Dull ache or sharp pain in the side or back
- Pain or discomfort during urination
- Increased urinary frequency or urgency
- Blood in the urine
- Fever or chills
To manage urinary stent pain, several strategies can be employed. Over-the-counter pain medications, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can help alleviate discomfort. Additionally, alpha-blockers, which relax the muscles in the urinary tract, may be prescribed to reduce pain and spasms. In some cases, anticholinergic medications may be used to reduce bladder spasms.
Lifestyle modifications can also play a crucial role in managing urinary stent pain. Drinking plenty of fluids, avoiding caffeine and spicy foods, and taking regular breaks to empty the bladder can help reduce discomfort. Applying heat to the affected area, such as with a warm bath or heating pad, may also provide relief.
It is essential to note that while some discomfort is common after ureteral stent placement, severe pain or other concerning symptoms should be reported to a healthcare provider promptly. In rare cases, the stent may need to be repositioned or removed to alleviate pain.
In terms of prevention, several steps can be taken to minimize the risk of urinary stent pain. Choosing a stent made from a biocompatible material, such as silicone or polyurethane, may reduce the risk of irritation and discomfort. Additionally, ensuring proper placement of the stent and following post-procedure instructions carefully can help prevent complications.
While urinary stent pain can be a significant issue for some individuals, it is generally a temporary condition that can be managed with proper care and attention. By understanding the causes and symptoms of urinary stent pain, individuals can take steps to alleviate discomfort and promote a smooth recovery.
What are the common causes of urinary stent pain?
+The common causes of urinary stent pain include irritation of the bladder and ureteral lining, spasms in the ureter, and individual differences in pain tolerance.
What are the symptoms of urinary stent pain?
+Symptoms of urinary stent pain may include dull ache or sharp pain in the side or back, pain or discomfort during urination, increased urinary frequency or urgency, blood in the urine, and fever or chills.
How can urinary stent pain be managed?
+Urinary stent pain can be managed with over-the-counter pain medications, alpha-blockers, anticholinergic medications, and lifestyle modifications such as drinking plenty of fluids, avoiding caffeine and spicy foods, and taking regular breaks to empty the bladder.
To further understand urinary stent pain, it is essential to explore the various treatment options available. In addition to medications and lifestyle modifications, alternative therapies such as acupuncture and physical therapy may be beneficial in managing pain and discomfort.
In conclusion, urinary stent pain is a common issue faced by many individuals who undergo ureteral stent placement. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available, individuals can take steps to alleviate discomfort and promote a smooth recovery. It is crucial to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop an effective management plan and address any concerns or complications that may arise.
While urinary stent pain can be a challenging issue to navigate, there are many resources available to support individuals throughout the recovery process. From online support groups to educational materials, individuals can access a wealth of information to help them better understand their condition and make informed decisions about their care.
Ultimately, the key to managing urinary stent pain lies in a comprehensive approach that addresses the physical, emotional, and psychological aspects of the condition. By taking a proactive and informed approach to care, individuals can reduce their risk of complications, alleviate discomfort, and promote a smooth and successful recovery.
