Ureteral Stent Blood In Urine

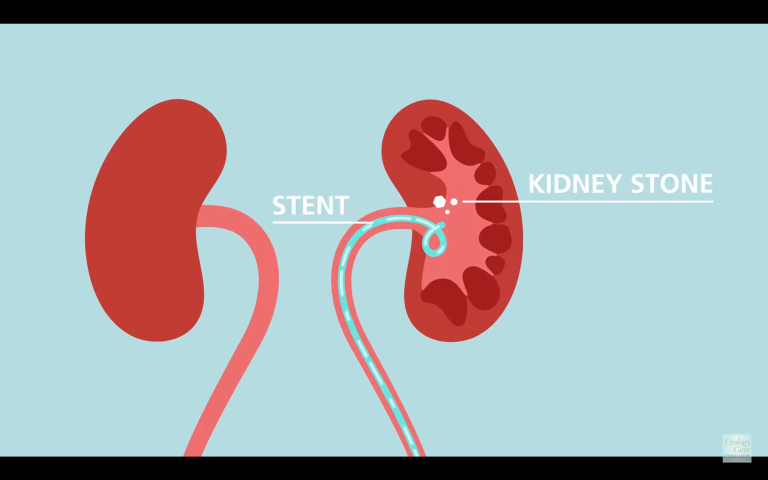
The presence of blood in the urine, also known as hematuria, is a common complication associated with ureteral stents. Ureteral stents are small, hollow tubes made of plastic or metal that are inserted into the ureters to help drain urine from the kidneys to the bladder. They are often used to treat blockages in the ureters, such as kidney stones, tumors, or blood clots.
Blood in the urine can be a disturbing symptom, but it is usually not a cause for concern. In most cases, the bleeding is microscopic, meaning that it can only be detected with a microscope, and it resolves on its own once the stent is removed. However, in some cases, the bleeding can be gross, meaning that it is visible to the naked eye, and it may require medical attention.
There are several reasons why blood may appear in the urine after the insertion of a ureteral stent. One of the most common reasons is irritation of the ureteral lining, which can cause minor bleeding. This irritation can be caused by the stent itself, or by the procedure used to insert it. Another reason for bleeding is the formation of blood clots, which can occur when the stent blocks the flow of urine and causes blood to accumulate in the ureter.
In some cases, the presence of blood in the urine may be a sign of a more serious complication, such as a blockage of the stent, an infection, or a perforation of the ureter. If you experience any of the following symptoms, you should seek medical attention immediately:
- Severe pain or discomfort in the side or back
- Fever or chills
- Cloudy or foul-smelling urine
- Difficulty starting or stopping the flow of urine
- Increased frequency or urgency of urination
To manage the presence of blood in the urine after the insertion of a ureteral stent, your doctor may recommend the following:
- Increase fluid intake to help flush out the system and reduce the risk of blood clots
- Take over-the-counter pain medication, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, to help manage discomfort or pain
- Avoid strenuous activities or heavy lifting, which can exacerbate the bleeding
- Follow a urinary tract infection prevention diet, which may include avoiding certain foods or beverages that can irritate the bladder
It is essential to note that the presence of blood in the urine after the insertion of a ureteral stent is usually a temporary condition that resolves on its own once the stent is removed. However, if you experience any concerning symptoms or if the bleeding persists or worsens over time, you should seek medical attention to rule out any underlying complications.
It's crucial to follow your doctor's instructions and attend all scheduled follow-up appointments to ensure that the stent is functioning correctly and that any potential complications are addressed promptly.
In addition to managing the symptoms, it’s also essential to understand the different types of ureteral stents and their potential effects on the urinary system. There are two main types of ureteral stents: internal and external. Internal stents are inserted directly into the ureter, while external stents are attached to a catheter that drains the urine from the kidney to a bag outside the body.
Each type of stent has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of stent depends on the individual’s specific condition and needs. For example, internal stents are often used for patients with kidney stones or tumors, while external stents may be used for patients with more complex conditions, such as ureteral strictures or blockages.
Pros and Cons of Ureteral Stents
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Relieve blockages and promote urine flow | Can cause irritation, discomfort, or pain |
| Help prevent kidney damage or infection | May require multiple procedures for insertion or removal |
| Can be used to treat a variety of conditions, including kidney stones and tumors | May increase the risk of urinary tract infections or other complications |
Overall, the presence of blood in the urine after the insertion of a ureteral stent is a common complication that usually resolves on its own once the stent is removed. However, it’s essential to follow your doctor’s instructions, attend all scheduled follow-up appointments, and seek medical attention if you experience any concerning symptoms.
What are the common causes of blood in the urine after ureteral stent insertion?
+The common causes of blood in the urine after ureteral stent insertion include irritation of the ureteral lining, formation of blood clots, and blockage or infection of the stent.
How long does it take for the blood in the urine to resolve after ureteral stent removal?
+The blood in the urine usually resolves on its own within a few days to a week after the ureteral stent is removed. However, the exact timeline may vary depending on the individual's condition and the complexity of the procedure.
What are the potential complications of ureteral stents?
+The potential complications of ureteral stents include urinary tract infections, kidney damage, and blockage or perforation of the stent. In rare cases, the stent may also cause irritation or discomfort, which can be managed with medication or other interventions.
By understanding the causes, symptoms, and management of blood in the urine after ureteral stent insertion, patients can better navigate their treatment and recovery. It’s essential to work closely with your healthcare provider to address any concerns or complications that may arise during the treatment process.