Tmj Causing Ear Pressure
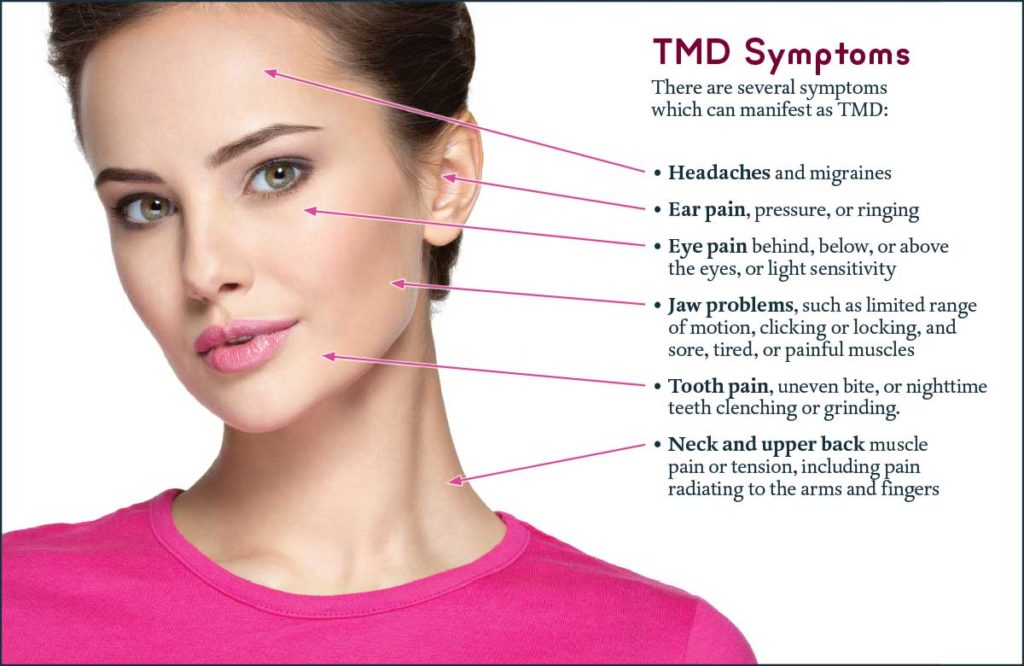
Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders are a common issue affecting millions of people worldwide. One of the lesser-known symptoms of TMJ disorders is ear pressure, which can be both confusing and concerning for those experiencing it. The relationship between TMJ and ear pressure is multifaceted, involving anatomical, neurological, and functional connections between the jaw, the ear, and the surrounding structures.
The TMJ is a complex joint that connects the mandible (lower jawbone) to the temporal bone of the skull. This joint plays a crucial role in movements such as opening and closing the mouth, chewing, and even supporting the lower jaw in its correct position. The proximity of the TMJ to the ear and the shared nerve pathways contribute to the possibility of referred pain and pressure in the ear when the TMJ is dysfunctional.
Anatomical Connection
The anatomical connection between the TMJ and the ear explains why issues with the TMJ can lead to ear pressure. The TMJ is located very close to the ear, and several structures, including the auriculotemporal nerve, connect the two areas. The auriculotemporal nerve, a branch of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve, supplies sensory innervation to both the TMJ and parts of the ear. When the TMJ is inflamed or irritated, it can cause pain and pressure sensations that are referred to the ear via this nerve.
Functional Connection
From a functional perspective, the movement and alignment of the jaw can affect the Eustachian tube’s function, which is responsible for regulating air pressure within the ear. When the jaw is misaligned due to a TMJ disorder, it can indirectly affect the functioning of the Eustachian tube. This can lead to issues with equalizing the air pressure on both sides of the eardrum, resulting in feelings of fullness, pressure, or even hearing changes.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Symptoms of TMJ-related ear pressure can vary but often include a feeling of fullness or pressure in one or both ears, which may worsen with jaw movements. Some individuals may also experience ear pain, tinnitus (ringing in the ears), or changes in hearing. It’s essential to differentiate these symptoms from other ear-related issues, as the treatment approach for TMJ-induced ear pressure is distinct from that for primary ear conditions.
Diagnosing TMJ disorders as the cause of ear pressure involves a comprehensive evaluation, including a detailed medical history, a physical examination focusing on the jaw and facial muscles, and possibly imaging studies to assess the TMJ and surrounding structures.
Treatment and Management
Treatment for TMJ disorders causing ear pressure aims to address the underlying issue with the TMJ, thereby alleviating the referred symptoms. This can include:
- Physical Therapy: Jaw exercises and physical therapy can help in strengthening the jaw muscles and improving the alignment of the jaw.
- Splints and Oral Appliances: Custom-made splints or oral appliances can be worn to help stabilize the jaw and reduce strain on the TMJ.
- Pain Management: Medications may be prescribed to manage pain and reduce inflammation.
- Lifestyle Changes: Avoiding chewing gum, taking soft diets, and practicing relaxation techniques to reduce stress and jaw clenching can also be beneficial.
- Surgical Intervention: In severe cases where conservative treatments are ineffective, surgery may be considered to repair or replace the TMJ.
Preventive Measures
While not all TMJ disorders can be prevented, certain measures can reduce the risk of developing TMJ issues and, by extension, ear pressure related to TMJ dysfunction. These include maintaining good oral health, avoiding excessive jaw movements or strains, managing stress, and ensuring proper bite alignment through orthodontic treatment if necessary.
In conclusion, the connection between TMJ disorders and ear pressure is more than coincidental; it involves complex anatomical and functional relationships. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of TMJ-induced ear pressure is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management. By addressing the root cause of the issue—namely, the dysfunction within the TMJ—it is possible to alleviate not just the ear pressure but also other associated symptoms, leading to significant improvements in quality of life.
What are the common symptoms of TMJ disorders that can be mistaken for ear problems?
+Common symptoms include ear pressure, pain in the ear, tinnitus (ringing in the ears), and hearing changes. These symptoms can mimic primary ear conditions but are actually referred from the TMJ.
How is TMJ-related ear pressure diagnosed?
+Diagnosis involves a comprehensive medical history, a physical examination of the jaw and facial muscles, and possibly imaging studies like MRI or CT scans to evaluate the TMJ and surrounding structures.
Can TMJ disorders causing ear pressure be treated without surgery?
+Yes, most cases of TMJ disorders can be treated conservatively with treatments such as physical therapy, splints or oral appliances, pain management medications, and lifestyle changes. Surgery is considered in severe cases where these treatments are not effective.
How can I prevent TMJ disorders and related ear pressure?
+Preventive measures include maintaining good oral health, avoiding excessive jaw movements, managing stress through relaxation techniques, and ensuring proper bite alignment. Early recognition and treatment of TMJ issues can also prevent progression to more severe symptoms.
Are there any home remedies that can help relieve TMJ-induced ear pressure?
+Yes, certain home remedies such as applying warm compresses to the affected area, practicing gentle jaw stretches, and following a soft diet can provide temporary relief from symptoms. However, consulting a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan is essential for long-term relief.
In addressing TMJ disorders and their impact on ear pressure, it’s crucial to adopt a comprehensive approach that considers both the immediate symptoms and the underlying causes. By doing so, individuals can find effective relief from the discomfort and disturbances caused by TMJ-induced ear pressure, improving their overall quality of life.



