Prolapse Rectal Image
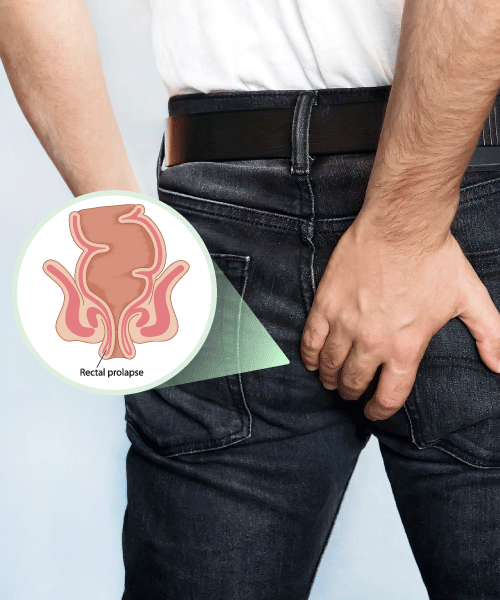
Rectal prolapse is a medical condition where the rectum loses its normal attachments inside the body, allowing it to protrude out through the anus. This condition can cause significant discomfort, difficulty with bowel movements, and emotional distress. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for rectal prolapse is essential for managing the condition effectively.
Causes of Rectal Prolapse
Several factors can contribute to the development of rectal prolapse. These include:
- Chronic Constipation: Straining during bowel movements can weaken the muscles that hold the rectum in place.
- Aging: The muscles and ligaments that support the rectum can weaken with age, making prolapse more likely.
- Pregnancy and Childbirth: The strain of carrying a baby and the physical changes during childbirth can lead to prolapse.
- Previous Pelvic Surgery: Operations in the pelvic area can sometimes lead to weakness in the supportive tissues of the rectum.
- Neurological Conditions: Certain conditions, such as spinal cord injuries, can affect the nerves that control the rectal muscles, leading to prolapse.
Symptoms of Rectal Prolapse
The symptoms of rectal prolapse can vary from person to person but often include:
- Visible Bulge: A noticeable bulge or tissue protruding from the anus, which may be more pronounced after bowel movements or straining.
- Discomfort or Pain: Feeling of discomfort, pain, or pressure in the anal and rectal area, especially when sitting or straining.
- Difficulty with Bowel Movements: Constipation, straining during bowel movements, or the feeling of incomplete evacuation.
- Mucus or Blood Discharge: Presence of mucus or blood from the rectum, which can be a sign of the prolapse.
Diagnosis of Rectal Prolapse
Diagnosing rectal prolapse involves a physical examination and sometimes imaging tests. A healthcare provider may:
- Perform a Physical Examination: Checking for a bulge in the rectum and assessing the strength of the anal muscles.
- Use Imaging Tests: Procedures like a defecography (a special X-ray of the bowel movements), MRI, or ultrasound to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions.
Treatment Options for Rectal Prolapse
Treatment for rectal prolapse depends on the severity of the condition, the patient’s overall health, and their preferences. Options include:
- Lifestyle Changes: Dietary adjustments to prevent constipation, pelvic floor exercises (like Kegel exercises), and avoiding heavy lifting.
- Surgery: Various surgical procedures are available, ranging from repairing the prolapse through the abdomen or using a minimally invasive approach. The choice of surgery depends on the patient’s condition and the surgeon’s expertise.
- Supportive Devices: In some cases, devices like a rectal plug or a supportive garment may be recommended to help manage symptoms before considering surgery.
Prevention of Rectal Prolapse
While not all cases of rectal prolapse can be prevented, certain measures can reduce the risk:
- Maintaining a Healthy Bowel Habit: Eating a balanced diet rich in fiber, staying hydrated, and responding promptly to the urge to have a bowel movement can help prevent constipation.
- Exercising Regularly: Engaging in physical activity can help maintain the strength of pelvic floor muscles.
- Managing Chronic Conditions: Proper management of conditions like diabetes and neurological diseases can reduce the risk of developing prolapse.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the symptoms of rectal prolapse?
+Symptoms can include a visible bulge or tissue protruding from the anus, discomfort or pain, difficulty with bowel movements, and mucus or blood discharge.
Can lifestyle changes alone treat rectal prolapse?
+Lifestyle changes can help manage mild cases of rectal prolapse and are often recommended alongside other treatments. However, for more severe cases, surgery may be necessary.
What are the risks associated with rectal prolapse surgery?
+Risks can include infection, bleeding, bowel obstruction, and the possibility that the prolapse may recur. Discussing these risks with a healthcare provider is crucial before making a decision.
Conclusion
Rectal prolapse is a condition that can significantly impact one’s quality of life, but with the right approach, it can be managed effectively. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and exploring treatment options with a healthcare provider are key steps in addressing rectal prolapse. By combining lifestyle modifications with medical or surgical interventions when necessary, individuals can find relief from the discomfort and distress associated with this condition.
