Penetrating Ulcer Symptoms
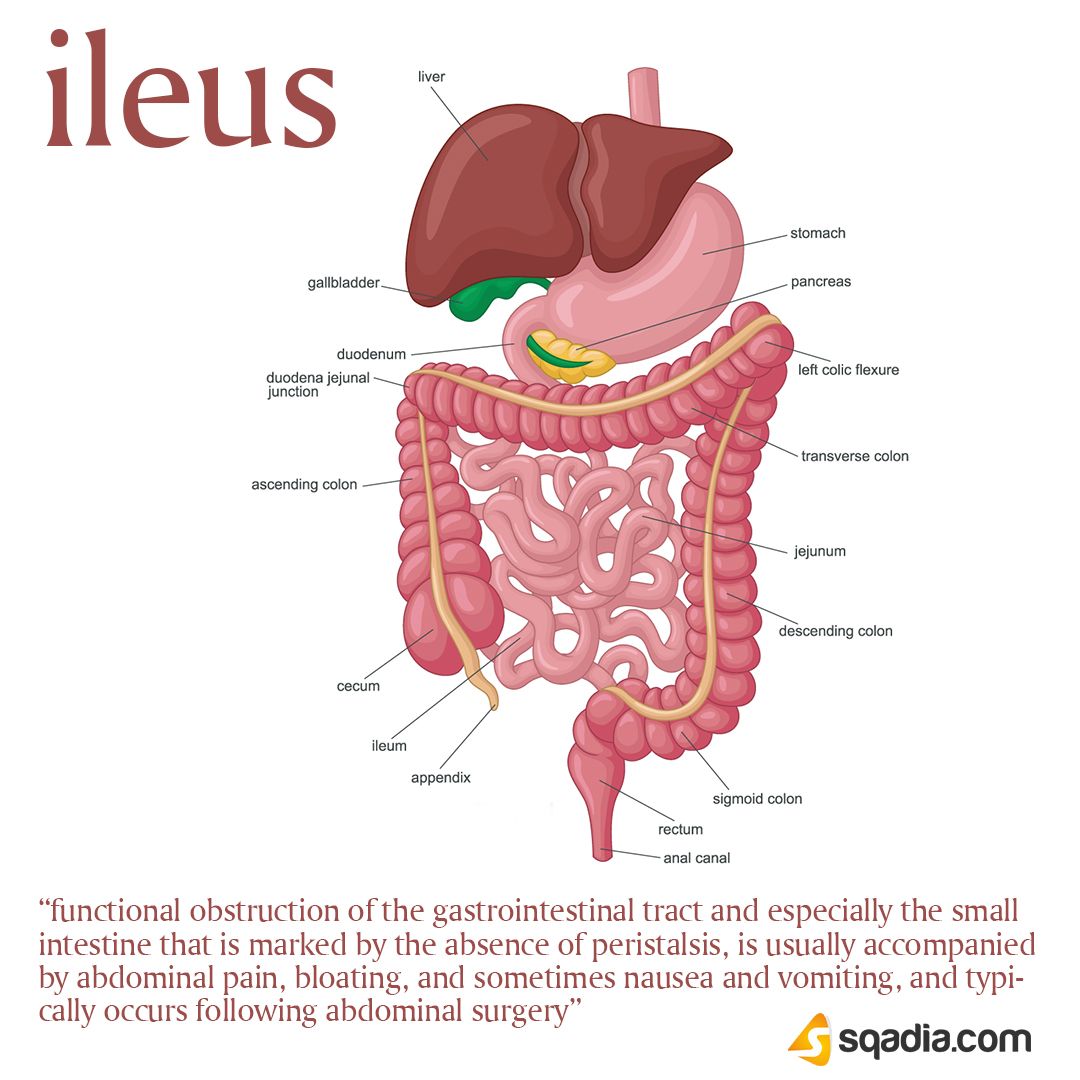
A penetrating ulcer is a serious medical condition that can have severe consequences if left untreated. It is characterized by a deep sore or crater-like lesion that extends through the wall of an organ, such as the stomach or intestine, and into the surrounding tissue. This can lead to perforation, peritonitis, and potentially life-threatening complications. The symptoms of a penetrating ulcer can vary depending on the location and severity of the condition, but there are several common warning signs that individuals should be aware of.
One of the primary symptoms of a penetrating ulcer is severe, persistent abdominal pain. This pain can be diffuse, radiating to the back, or localized to a specific area, such as the upper abdomen. The pain may worsen over time and can be exacerbated by eating, drinking, or movement. In some cases, the pain may be accompanied by tenderness or guarding, which is the involuntary contraction of the abdominal muscles in response to pressure or touch.
Another common symptom of a penetrating ulcer is nausea and vomiting. As the ulcer penetrates deeper into the tissue, it can cause irritation and inflammation of the surrounding organs, leading to stomach upset and vomiting. In some cases, the vomit may contain blood or coffee ground-like material, which is a sign of gastrointestinal bleeding.
Individuals with a penetrating ulcer may also experience changes in bowel habits, such as diarrhea or constipation. The ulcer can cause obstruction or narrowing of the intestinal lumen, leading to alterations in bowel movements. Additionally, the condition can cause fatigue, weight loss, and loss of appetite, as the body’s ability to absorb nutrients is impaired.
In severe cases, a penetrating ulcer can lead to perforation, which is a life-threatening complication. Perforation occurs when the ulcer ruptures through the wall of the organ, allowing bacteria and other contents to spill into the abdominal cavity. This can cause peritonitis, a severe inflammatory response that can lead to sepsis, organ failure, and death. The symptoms of perforation include sudden, severe abdominal pain, tenderness, and guarding, as well as fever, chills, and rigors.
It is essential to seek medical attention immediately if you are experiencing any of the above symptoms. A penetrating ulcer can be diagnosed using a combination of imaging studies, such as X-rays, CT scans, and endoscopy, as well as laboratory tests, such as blood work and stool analysis.
To understand the condition better, let’s delve into the comparative analysis of different types of ulcers. A penetrating ulcer is distinct from other types of ulcers, such as peptic ulcers, which are shallow sores that occur in the lining of the stomach or duodenum. While peptic ulcers can be painful and cause discomfort, they are generally less severe than penetrating ulcers and can be treated with medications and lifestyle modifications.
In contrast, penetrating ulcers require more aggressive treatment, including hospitalization, antibiotics, and surgery in some cases. The treatment approach depends on the severity of the condition, the location of the ulcer, and the presence of complications, such as perforation or peritonitis.
- Hospitalization: Individuals with a penetrating ulcer require close monitoring and care in a hospital setting.
- Antibiotics: Broad-spectrum antibiotics are administered to treat bacterial infections and prevent sepsis.
- Pain management: Pain relief medications, such as opioids, are used to manage severe abdominal pain.
- Fluid replacement: Intravenous fluids are administered to replace lost fluids and electrolytes.
- Nutritional support: Nutritional supplements, such as total parenteral nutrition, may be provided to support the body's nutritional needs.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair the damaged tissue, remove infected material, or close the perforation.
In addition to medical treatment, there are several lifestyle modifications that can help alleviate symptoms and promote healing. These include:
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can provide essential nutrients, fiber, and antioxidants that can help reduce inflammation and promote tissue repair. Avoiding spicy, fatty, or acidic foods can also help reduce irritation and discomfort.
Additionally, managing stress through relaxation techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing, can help reduce symptoms and promote healing. Stress can exacerbate symptoms and worsen the condition, so it is essential to find healthy coping mechanisms.
What are the common symptoms of a penetrating ulcer?
+The common symptoms of a penetrating ulcer include severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, changes in bowel habits, and fatigue.
How is a penetrating ulcer diagnosed?
+A penetrating ulcer can be diagnosed using a combination of imaging studies, such as X-rays, CT scans, and endoscopy, as well as laboratory tests, such as blood work and stool analysis.
What is the treatment approach for a penetrating ulcer?
+The treatment approach for a penetrating ulcer typically involves hospitalization, antibiotics, pain management, fluid replacement, nutritional support, and surgery in some cases.
In conclusion, a penetrating ulcer is a severe medical condition that requires prompt attention and treatment. The symptoms can be severe and debilitating, and if left untreated, can lead to life-threatening complications. By understanding the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment approach, individuals can seek medical attention early and prevent long-term damage. Remember, early diagnosis and treatment are critical in preventing the complications associated with penetrating ulcers. If you are experiencing any symptoms, do not hesitate to seek medical attention.