Old Root Canal Infection Symptoms
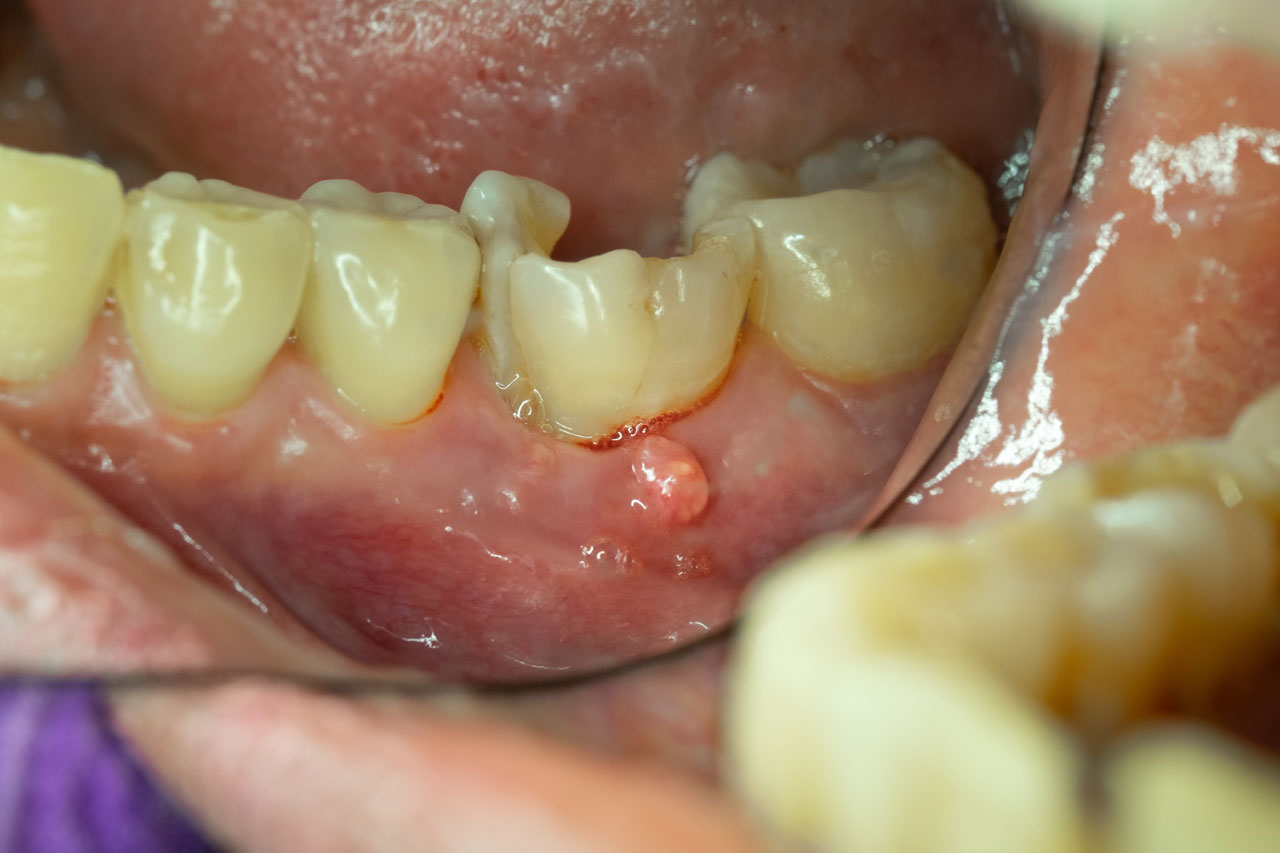
When a root canal treatment is performed, the goal is to remove infected tissue from within the tooth, thereby eliminating the source of pain and infection. However, in some cases, an old root canal can become re-infected, leading to a variety of uncomfortable and potentially serious symptoms. Understanding these symptoms is crucial for seeking timely dental care to prevent further complications.
One of the most common signs of an old root canal infection is persistent or recurring pain. This pain can range from a dull ache to a sharp, stabbing sensation and may be exacerbated by pressure, temperature changes, or even simple activities like chewing. The pain associated with a re-infected root canal can be localized to the affected tooth or may radiate to other areas of the face, such as the cheek or jaw. It’s not uncommon for individuals to experience pain that wakes them up at night, significantly impacting their quality of life.
Another symptom that may indicate an old root canal infection is swelling or abscesses in the gums or face. An abscess is a pocket of pus that forms as a result of the infection, and it can cause significant swelling, redness, and pain. In severe cases, the swelling can be so pronounced that it affects the ability to open the mouth or swallow. The presence of an abscess is a serious sign that the infection has progressed and requires immediate attention to prevent it from spreading to other parts of the body.
Sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures is another common symptom of an old root canal infection. Normally, after a root canal, the tooth may be sensitive for a short period, but this sensitivity should resolve once the tooth has healed. However, if the sensitivity persists or returns after a period of being asymptomatic, it could be a sign that the tooth has become re-infected. This sensitivity can make eating and drinking uncomfortable, affecting the individual’s ability to enjoy certain foods or beverages.
Bad breath (halitosis) that persists despite good oral hygiene practices can also be a symptom of an underlying infection, including one related to an old root canal. The bacteria causing the infection can release volatile sulfur compounds, leading to a bad taste in the mouth and unpleasant breath. This symptom can be particularly distressing, affecting an individual’s confidence and social interactions.
In addition to these symptoms, some individuals may notice a foul taste in their mouth. This foul taste is often associated with the discharge of pus from the infected tooth, which can drain into the mouth, leaving a bad taste. The presence of pus is a clear indication of an active infection that requires professional dental care.
Furthermore, an old root canal infection can lead to swelling of the lymph nodes in the neck or face. The body’s immune response to the infection can cause these nodes to become enlarged and tender, which can be uncomfortable and may indicate that the infection is spreading beyond the tooth.
In severe cases, an untreated root canal infection can lead to more serious complications, such as osteomyelitis (an infection of the bone) or the spread of infection to other parts of the body, potentially leading to life-threatening conditions like sepsis. It’s crucial, therefore, to seek dental care at the first sign of symptoms to prevent such outcomes.
Upon visiting a dentist, a thorough examination will be conducted, which may include radiographs (x-rays) to assess the extent of the infection and the condition of the tooth and surrounding bone. Based on the findings, the dentist may recommend a series of treatments to address the infection, which could include antibiotics to control the infection, drainage of any abscesses, and possibly a surgical procedure to remove any infected tissue.
In some cases, it may be necessary to re-treat the root canal, a procedure known as endodontic re-treatment. This involves re-accessing the canal system of the tooth, removing any existing filling material, and then re-cleaning and shaping the canals before refilling them with a new inert material. The success rate of re-treatment is generally high, offering relief from symptoms and a return to oral health.
The key to managing old root canal infections is early detection and intervention. Regular dental check-ups can help identify potential issues before they become severe, and maintaining good oral hygiene practices, including brushing, flossing, and using mouthwash, can help prevent infections from occurring in the first place. If symptoms persist or recur after a root canal treatment, it’s essential to consult a dental professional without delay to address the issue and restore oral health.
What are the common symptoms of an old root canal infection?
+Common symptoms include persistent or recurring pain, sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures, swelling or abscesses, bad breath, and a foul taste in the mouth. These symptoms indicate that the tooth has become re-infected and requires immediate dental care.
Why does an old root canal infection need urgent dental care?
+An untreated root canal infection can lead to severe complications, including the spread of infection to other parts of the body, potentially causing life-threatening conditions like sepsis. Timely intervention is crucial to prevent such outcomes and restore oral health.
What is involved in the treatment of an old root canal infection?
+Treatment may include antibiotics to control the infection, drainage of any abscesses, and possibly a surgical procedure to remove infected tissue. In some cases, endodontic re-treatment may be necessary, involving the re-cleaning and re-filling of the tooth's canal system.
Can an old root canal infection be prevented?
+While not all infections can be prevented, regular dental check-ups and good oral hygiene practices can significantly reduce the risk of developing an infection. Early detection and intervention are key to managing any dental issues before they become severe.
What is the prognosis for teeth treated for old root canal infections?
+The success rate for treating old root canal infections, especially with re-treatment, is generally high. Most teeth can be saved and returned to full function, provided that the infection is addressed promptly and properly. Regular follow-up care is essential to ensure the tooth remains healthy.
In conclusion, recognizing the symptoms of an old root canal infection is crucial for seeking the necessary dental care to prevent complications and restore oral health. Through timely intervention and proper treatment, individuals can find relief from symptoms and enjoy improved well-being. Regular dental care and good hygiene practices play a significant role in preventing such infections, underlining the importance of proactive oral health management.