Mouth Ulcers Coeliac

The presence of mouth ulcers in individuals with coeliac disease is a phenomenon that has garnered significant attention in the medical community. Coeliac disease, an autoimmune disorder, is characterized by the body’s adverse reaction to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. This reaction leads to inflammation and damage in the small intestine, impairing the absorption of essential nutrients. The manifestation of mouth ulcers in coeliac patients introduces a complex interplay of factors, including malabsorption, immune system dysregulation, and the potential for other autoimmune conditions.
Malabsorption and Nutritional Deficiencies
One of the primary concerns in coeliac disease is the malabsorption of nutrients. The damage to the small intestine’s villi, which are crucial for absorption, can lead to deficiencies in vitamins and minerals. Mouth ulcers, also known as oral ulcers or aphthous ulcers, can be a symptom of underlying nutritional deficiencies, particularly in vitamin B12, iron, and folate. These nutrients are essential for maintaining healthy mucous membranes and their deficiency can impair the healing process of ulcers.
Immune System Dysregulation
Coeliac disease is characterized by an abnormal immune response to gluten. This immune dysregulation can lead to the production of autoantibodies that not only target the small intestine but can also affect other parts of the body, including the mouth. The inflammation caused by this immune response can contribute to the development of mouth ulcers.
Associated Autoimmune Conditions
Individuals with coeliac disease are at an increased risk of developing other autoimmune conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, type 1 diabetes, and autoimmune thyroid disease. Some of these conditions, like Behçet’s disease (a form of vasculitis), can directly cause mouth ulcers. The connection between coeliac disease and other autoimmune conditions suggests that the presence of mouth ulcers could be indicative of a broader immune system issue.
Diagnosis and Management
Diagnosing coeliac disease involves a combination of blood tests to detect the presence of certain autoantibodies and an intestinal biopsy to assess the damage to the small intestine. The management of coeliac disease primarily involves a strict gluten-free diet, which can also help in reducing the frequency and severity of mouth ulcers. However, treating mouth ulcers in the context of coeliac disease may require additional approaches, including nutritional supplements to address deficiencies and topical treatments to facilitate ulcer healing.
Prevention and Future Directions
Preventing mouth ulcers in individuals with coeliac disease involves maintaining a rigorous gluten-free diet and ensuring adequate nutrition. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers can help in early detection and treatment of nutritional deficiencies. Future research directions may include exploring the specific immune mechanisms that lead to mouth ulcers in coeliac patients and developing targeted therapies to address these underlying issues.
Comparison of Dietary Approaches
| Dietary Approach | Description | Potential Benefit for Coeliac Disease and Mouth Ulcers |
|---|---|---|
| Gluten-Free Diet | Complete avoidance of gluten | Essential for managing coeliac disease, can help reduce mouth ulcers by reducing immune system activation |
| Nutrient-Rich Diet | Focus on foods high in vitamins and minerals (e.g., vitamin B12, iron, folate) | Can help address nutritional deficiencies that contribute to mouth ulcers |
| Exclusion Diets | Temporarily removing and then reintroducing certain foods to identify sensitivities | May help identify other food sensitivities that could contribute to mouth ulcers |
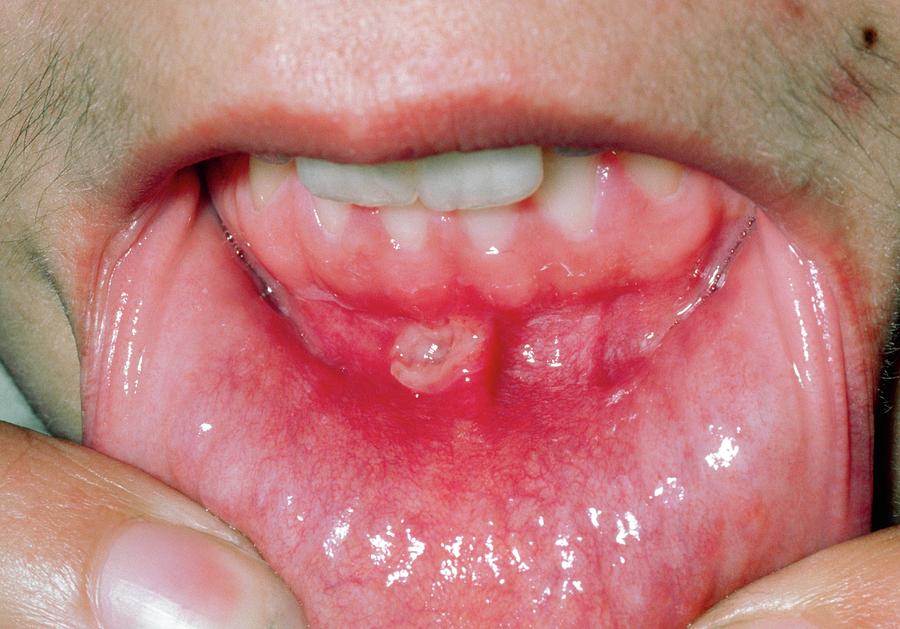
What is the relationship between coeliac disease and mouth ulcers?
+Mouth ulcers in coeliac disease can be related to malabsorption of essential nutrients and immune system dysregulation. Addressing these underlying issues through a gluten-free diet and ensuring adequate nutrition can help in managing mouth ulcers.
Can mouth ulcers be a symptom of untreated coeliac disease?
+How can individuals with coeliac disease prevent mouth ulcers?
+Preventing mouth ulcers involves adhering to a strict gluten-free diet, ensuring adequate intake of essential nutrients, and maintaining good oral hygiene. Regular health check-ups can also help in early detection and management of any underlying issues.
In conclusion, the presence of mouth ulcers in individuals with coeliac disease underscores the complex nature of this autoimmune disorder. Managing coeliac disease through a gluten-free diet and addressing potential nutritional deficiencies are crucial steps in reducing the occurrence of mouth ulcers. Further research into the immune mechanisms and nutritional aspects of coeliac disease will provide valuable insights into the prevention and treatment of associated symptoms like mouth ulcers.