Milk Teeth Xray
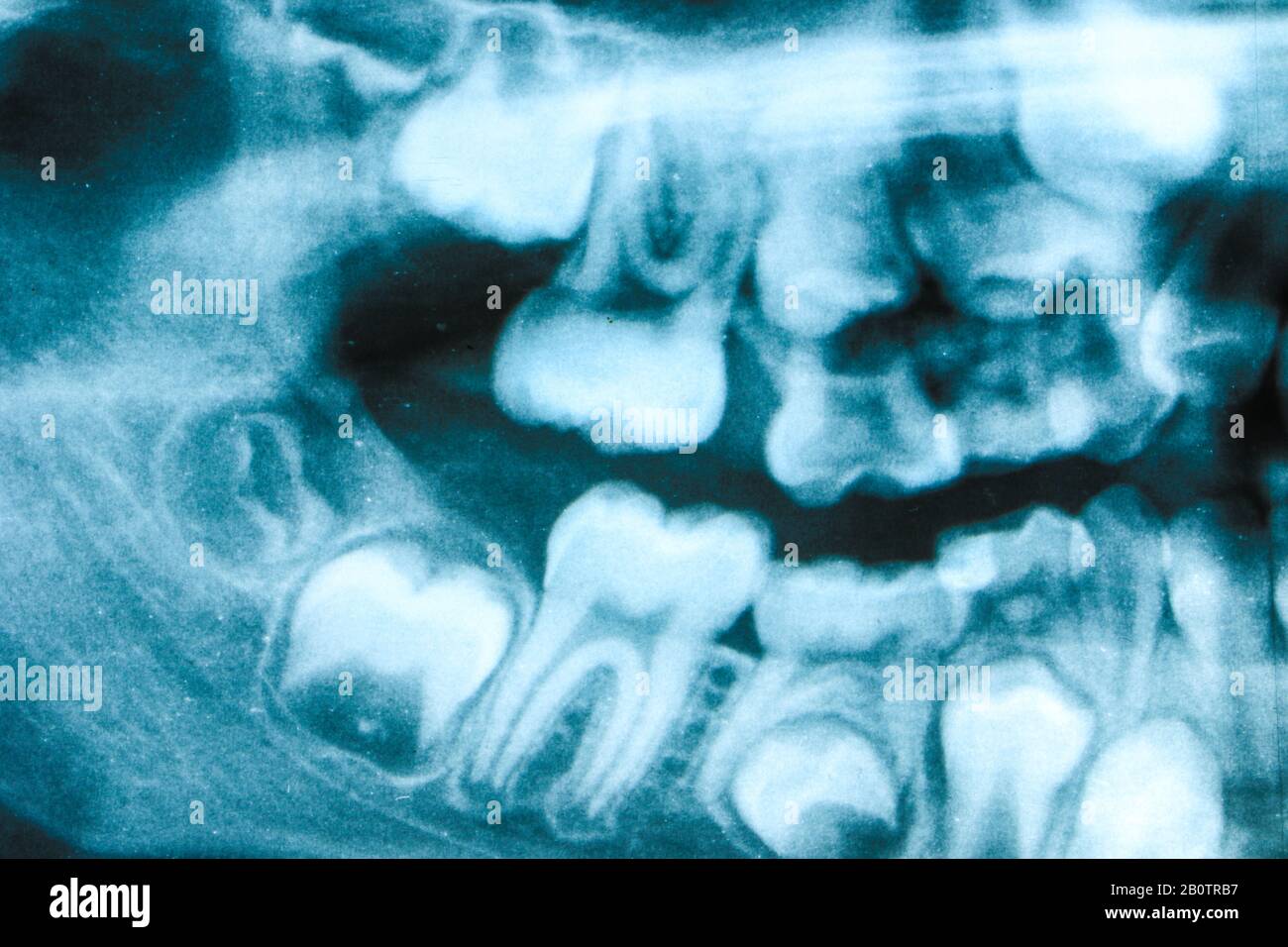
The use of X-rays in dental care has revolutionized the way dentists diagnose and treat various oral health issues, including those related to milk teeth. Milk teeth, also known as primary teeth, are the first set of teeth that erupt in a child’s mouth, typically starting from around six months of age. These teeth play a crucial role in the development of the child’s dental and facial structure, as well as their overall health. Understanding the importance of milk teeth and how X-rays are used in their assessment is essential for parents and dental professionals alike.
Introduction to Milk Teeth
Milk teeth begin to develop in the womb and start coming in when a baby is about six months old. By the time a child is three years old, they usually have a full set of 20 primary teeth. These teeth are smaller and whiter than permanent teeth and are gradually lost and replaced by permanent teeth, starting from around the age of six. The health of milk teeth is vital because they hold space for the permanent teeth to come in properly, help with chewing and speaking, and contribute to the overall health and well-being of the child.
Importance of X-rays for Milk Teeth
X-rays are a valuable diagnostic tool in pediatric dentistry, allowing dentists to assess the health of milk teeth and the underlying structures. There are several reasons why X-rays might be necessary for children:
- Detection of Tooth Decay: X-rays can help identify cavities that are not visible to the naked eye, especially those between the teeth. Early detection of tooth decay is crucial to prevent it from spreading and to avoid more complex treatments.
- Assessment of Tooth Development: X-rays can show the development of the permanent teeth under the gum and the roots of the milk teeth. This information is essential for monitoring the health and development of both the primary and permanent dentition.
- Diagnosis of Tooth Misalignment: If a child’s teeth appear crowded or misaligned, an X-ray can help determine if there are sufficient spaces for all the teeth to come in properly or if orthodontic intervention might be necessary.
- Identification of Abscesses or Infections: In cases of severe tooth decay or trauma, an abscess (a pocket of pus) can form. An X-ray can help locate such infections and guide the dentist in treating them appropriately.
Types of X-rays Used
There are several types of dental X-rays that can be used, depending on the specific diagnostic needs of the child:
- Bitewing X-rays: These are the most common type of X-ray used in children. They show the upper and lower teeth biting down on a special paper or sensor, which helps detect cavities and signs of tooth decay between the teeth.
- Periapical X-rays: These X-rays show the entire tooth, from the crown to the root, and are used to detect any abnormalities in the tooth root or surrounding bone.
- Panoramic X-rays: These provide a broad view of the upper and lower jaw in a single image and are useful for assessing the development of teeth, jaw growth, and the relationship between teeth and jaw.
Safety Concerns and Precautions
While X-rays are an invaluable diagnostic tool, they do involve exposure to ionizing radiation. Therefore, dental professionals follow the ALARA principle (As Low As Reasonably Achievable) to minimize radiation exposure. This means that X-rays are only taken when necessary, and the dosage and frequency are kept as low as possible. Modern digital X-ray systems also emit significantly less radiation compared to traditional film-based systems. Parents should discuss any concerns they have about X-ray safety with their child’s dentist.
Conclusion
The use of X-rays in the examination of milk teeth is an essential part of pediatric dental care. By providing clear images of the teeth and surrounding structures, X-rays help dentists diagnose potential issues early, which can significantly impact the long-term oral health of children. Understanding the benefits and safety precautions of X-rays can reassure parents and help them make informed decisions about their child’s dental health.
Why are X-rays necessary for milk teeth?
+X-rays are necessary for milk teeth to detect tooth decay, assess tooth development, diagnose tooth misalignment, and identify abscesses or infections. They provide crucial information that cannot be seen during a visual examination, helping dentists make accurate diagnoses and develop effective treatment plans.
Are dental X-rays safe for children?
+Dental X-rays are considered safe for children when used appropriately. The amount of radiation exposure from dental X-rays is very low, and modern digital X-ray systems minimize exposure even further. Dentists follow strict guidelines to ensure that X-rays are taken only when necessary and with the lowest possible dose of radiation.
How often should children have dental X-rays?
+The frequency of dental X-rays for children depends on their oral health status and risk factors for dental problems. Children at high risk of tooth decay or with a history of oral health issues may need X-rays more frequently, typically every six months. For children at lower risk, X-rays may be taken less frequently, such as every year or two, as part of their regular dental check-ups.