Infantile Tongue Thrust
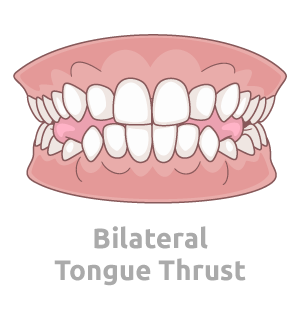
Infantile tongue thrust, also known as orofacial myofunctional disorder, is a condition where the tongue rests against the teeth or moves forward in an exaggerated way during swallowing, speaking, or at rest. This can lead to a range of issues, including difficulties with feeding, speech development, and dental alignment. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for infantile tongue thrust is essential for parents, caregivers, and healthcare professionals to provide appropriate support and intervention.
Causes of Infantile Tongue Thrust
Several factors can contribute to the development of infantile tongue thrust. These include:
- Genetic predisposition: Family history can play a role, with some children being more likely to develop tongue thrust due to inherited traits.
- Oral motor skills: Difficulty with coordination and control of the tongue, lips, and jaw can lead to abnormal tongue movements.
- Breathing patterns: Mouth breathing, rather than nasal breathing, can cause the tongue to adapt and move forward.
- Feeding habits: Bottle-feeding or pacifier use can influence the development of the oral cavity and contribute to tongue thrust.
- Tongue-tie: A condition where the tongue is anchored to the floor of the mouth, restricting its movement and potentially leading to tongue thrust.
Symptoms of Infantile Tongue Thrust
Infantile tongue thrust can manifest in different ways, depending on the age and individual characteristics of the child. Common symptoms include:
- Abnormal swallowing pattern: The tongue may move forward or to the side during swallowing, rather than moving back and up.
- Difficulty with speech: Tongue thrust can affect articulation, leading to challenges with pronouncing certain sounds or words.
- Dental issues: The constant pressure of the tongue against the teeth can cause misalignment, gaps, or other orthodontic problems.
- Feeding difficulties: Infants with tongue thrust may experience trouble latching, sucking, or swallowing during feeding.
- Mouth breathing: Children with tongue thrust may breathe through their mouth instead of their nose, potentially leading to respiratory issues.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Infantile Tongue Thrust
Early identification and intervention are crucial in addressing infantile tongue thrust. Diagnosis typically involves a comprehensive evaluation by a multidisciplinary team, including:
- Pediatricians: To rule out underlying medical conditions and assess overall health.
- Orthodontists: To evaluate dental alignment and provide guidance on orthodontic treatment.
- Speech-language pathologists: To assess speech development and provide therapy to address articulation and communication challenges.
- Orofacial myologists: To evaluate and treat oral motor skills and myofunctional disorders.
Treatment for infantile tongue thrust may involve a combination of:
- Oral motor therapy: Exercises and activities to improve tongue movement, coordination, and control.
- Speech therapy: Targeted interventions to address speech development and articulation challenges.
- Orthodontic treatment: Braces, retainers, or other appliances to correct dental alignment and promote proper oral function.
- Myofunctional therapy: Exercises and techniques to improve the function and coordination of the muscles involved in swallowing, speaking, and breathing.
Prevention and Prognosis
While some cases of infantile tongue thrust may be unavoidable, certain preventive measures can reduce the risk of developing this condition. These include:
- Exclusive breastfeeding: Breastfeeding can help promote proper oral development and reduce the risk of tongue thrust.
- Proper feeding techniques: Avoiding bottle-feeding and pacifier use can help minimize the risk of tongue thrust.
- Regular dental check-ups: Early identification of dental issues can help prevent more severe problems from developing.
With proper diagnosis, treatment, and support, children with infantile tongue thrust can learn to manage their condition and develop proper oral function, speech, and breathing habits. Prognosis is generally favorable, especially when intervention occurs at a young age.
What are the most common symptoms of infantile tongue thrust?
+Common symptoms of infantile tongue thrust include abnormal swallowing patterns, difficulty with speech, dental issues, feeding difficulties, and mouth breathing.
How is infantile tongue thrust diagnosed?
+Diagnosis typically involves a comprehensive evaluation by a multidisciplinary team, including pediatricians, orthodontists, speech-language pathologists, and orofacial myologists.
What are the treatment options for infantile tongue thrust?
+Treatment may involve a combination of oral motor therapy, speech therapy, orthodontic treatment, and myofunctional therapy.
Can infantile tongue thrust be prevented?
+While some cases may be unavoidable, exclusive breastfeeding, proper feeding techniques, and regular dental check-ups can help reduce the risk of developing infantile tongue thrust.
What is the prognosis for children with infantile tongue thrust?
+Prognosis is generally favorable, especially when intervention occurs at a young age. With proper diagnosis, treatment, and support, children with infantile tongue thrust can learn to manage their condition and develop proper oral function, speech, and breathing habits.
In conclusion, infantile tongue thrust is a condition that requires attention and intervention to prevent long-term consequences on oral function, speech development, and dental alignment. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, parents, caregivers, and healthcare professionals can provide the necessary support and guidance to help children overcome this condition and develop proper oral habits.
