Human Muscle Model

The human muscle model is a complex system that has fascinated scientists and researchers for centuries. It is a vital component of the human body, responsible for movement, posture, and overall physical function. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the human muscle model, exploring its structure, function, and the various factors that influence its performance.
Introduction to Muscle Structure
The human muscle is composed of several layers, each with its unique characteristics and functions. The outermost layer is the epimysium, a thin layer of connective tissue that surrounds the entire muscle. Beneath the epimysium lies the perimysium, a layer of connective tissue that separates the muscle into smaller bundles called fascicles. The fascicles are further divided into individual muscle fibers, which are the building blocks of the muscle.
Each muscle fiber is a long, multinucleated cell that contains the contractile units known as sarcomeres. The sarcomeres are composed of actin and myosin filaments, which slide past each other to produce muscle contraction. The muscle fibers are surrounded by a network of blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissue, which provide the necessary nutrients, oxygen, and support for muscle function.
Muscle Fiber Types
There are several types of muscle fibers, each with its unique characteristics and functions. The two main types of muscle fibers are slow-twitch (ST) and fast-twitch (FT) fibers. Slow-twitch fibers are designed for endurance and are responsible for low-intensity, long-duration activities such as distance running or cycling. They are rich in myoglobin, which stores oxygen for energy production, and have a high concentration of mitochondria, which are the energy-producing structures within the cell.
Fast-twitch fibers, on the other hand, are designed for speed and power and are responsible for high-intensity, short-duration activities such as sprinting or weightlifting. They have a lower concentration of myoglobin and mitochondria than slow-twitch fibers but have a higher concentration of glycolytic enzymes, which are involved in the production of energy from glucose.
Muscle Function
Muscle function is a complex process that involves the coordinated effort of multiple muscle groups. When a muscle is stimulated by a nerve impulse, the actin and myosin filaments within the sarcomeres slide past each other, producing muscle contraction. The force of contraction depends on the number of muscle fibers activated and the frequency of stimulation.
Muscle function can be influenced by a variety of factors, including muscle length, joint angle, and the presence of fatigue. Muscle length, for example, can affect the force of contraction, with muscles generating more force when they are at their optimal length. Joint angle can also influence muscle function, with muscles generating more force when they are at a 90-degree angle to the joint.
Factors Influencing Muscle Performance
Muscle performance can be influenced by a variety of factors, including genetics, training, nutrition, and overall health. Genetics, for example, can play a significant role in determining muscle fiber type and overall muscle function. Some people may be naturally more endowed with slow-twitch fibers, making them more suited to endurance activities, while others may have a higher concentration of fast-twitch fibers, making them more suited to power-based activities.
Training is also a critical factor in muscle performance, with regular exercise leading to increases in muscle strength, endurance, and size. Resistance training, in particular, can lead to significant increases in muscle mass and strength, as well as improvements in bone density and overall health.
Nutrition also plays a critical role in muscle performance, with inadequate nutrition leading to decreased muscle function and overall health. A diet rich in protein, complex carbohydrates, and healthy fats is essential for muscle growth and repair, while adequate hydration is necessary to maintain muscle function and overall health.
Injury and Disease
Muscle injury and disease can have a significant impact on muscle function and overall health. Muscle strains, for example, can occur when a muscle is stretched or torn, leading to pain, inflammation, and decreased muscle function. Muscle strains can be treated with rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), as well as physical therapy and rehabilitation.
Muscle disease, such as muscular dystrophy, can have a more profound impact on muscle function and overall health. Muscular dystrophy is a group of genetic disorders that lead to progressive muscle weakness and degeneration, with symptoms ranging from mild to severe. Treatment for muscular dystrophy typically involves a combination of physical therapy, medication, and surgery, with the goal of slowing disease progression and improving overall quality of life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the human muscle model is a complex system that plays a vital role in overall physical function and health. Understanding the structure, function, and factors that influence muscle performance can help us better appreciate the importance of regular exercise, proper nutrition, and overall health. By taking care of our muscles, we can improve our overall quality of life, reduce our risk of injury and disease, and maintain optimal physical function throughout our lives.
What are the different types of muscle fibers?
+There are several types of muscle fibers, including slow-twitch (ST) and fast-twitch (FT) fibers. Slow-twitch fibers are designed for endurance and are responsible for low-intensity, long-duration activities, while fast-twitch fibers are designed for speed and power and are responsible for high-intensity, short-duration activities.
What factors influence muscle performance?
+Muscle performance can be influenced by a variety of factors, including genetics, training, nutrition, and overall health. Genetics can play a significant role in determining muscle fiber type and overall muscle function, while training can lead to increases in muscle strength, endurance, and size. Nutrition also plays a critical role, with inadequate nutrition leading to decreased muscle function and overall health.
How can I improve my muscle function?
+Improving muscle function requires a combination of regular exercise, proper nutrition, and overall health. Engaging in resistance training can lead to significant increases in muscle mass and strength, while a diet rich in protein, complex carbohydrates, and healthy fats can provide the necessary nutrients for muscle growth and repair. Adequate hydration is also essential to maintain muscle function and overall health.
| Muscle Fiber Type | Characteristics | Functions |
|---|---|---|
| Slow-Twitch (ST) | Rich in myoglobin, high concentration of mitochondria | Endurance, low-intensity, long-duration activities |
| Fast-Twitch (FT) | Low concentration of myoglobin and mitochondria, high concentration of glycolytic enzymes | Speed, power, high-intensity, short-duration activities |
Understanding the human muscle model is essential for appreciating the importance of regular exercise, proper nutrition, and overall health. By taking care of our muscles, we can improve our overall quality of life, reduce our risk of injury and disease, and maintain optimal physical function throughout our lives.
Steps to Improve Muscle Function
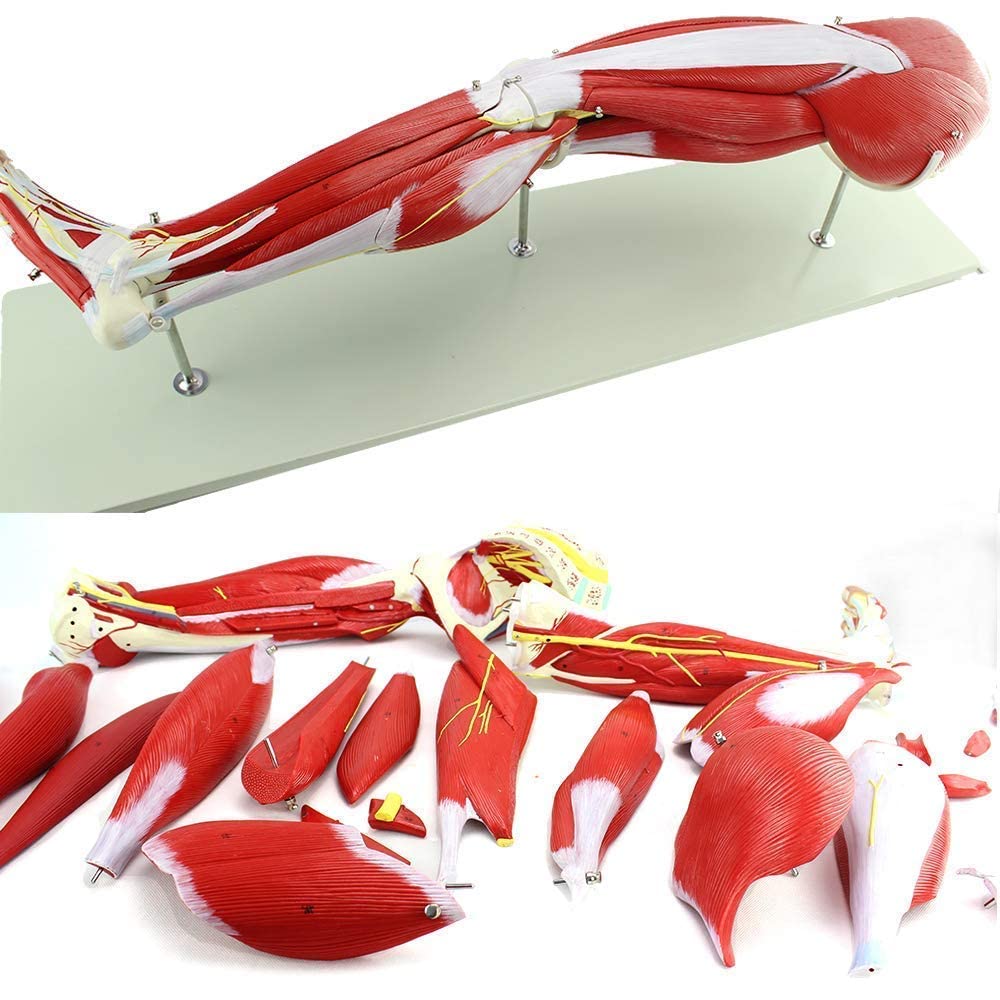

- Engage in regular resistance training to increase muscle mass and strength
- Eat a diet rich in protein, complex carbohydrates, and healthy fats to provide necessary nutrients for muscle growth and repair
- Stay hydrated to maintain muscle function and overall health
- Get adequate rest and recovery to allow muscles to repair and rebuild
The human muscle model is a complex system that plays a vital role in overall physical function and health. Understanding the structure, function, and factors that influence muscle performance can help us better appreciate the importance of regular exercise, proper nutrition, and overall health.


