How Long Do Ganglion Cysts Last After Surgery? Treatment Options
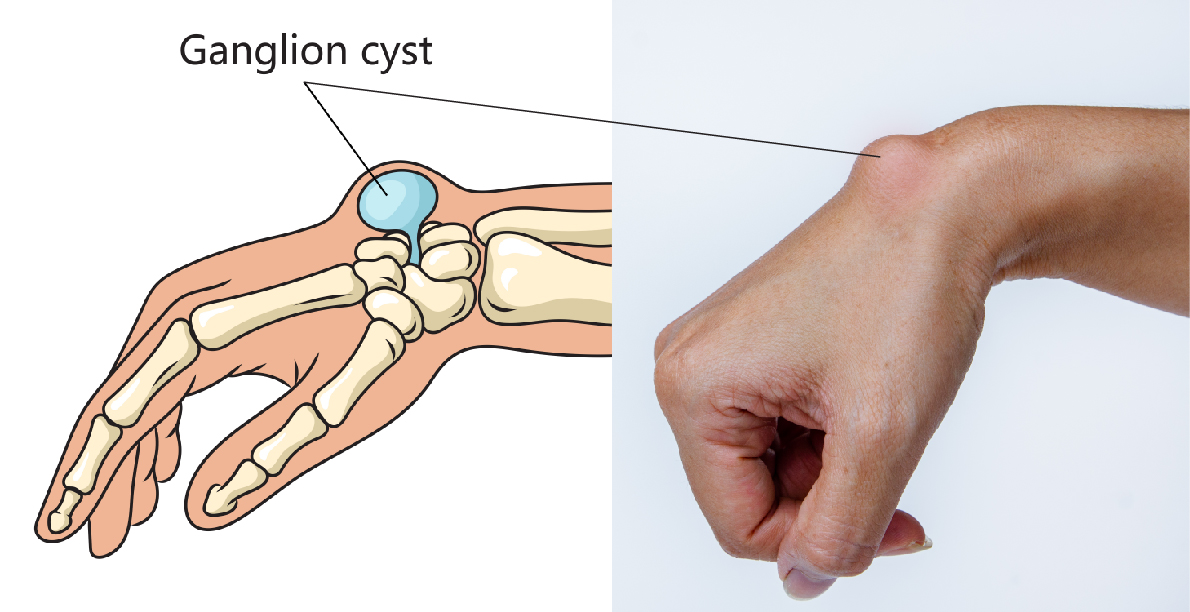
Ganglion cysts are among the most common types of lumps that can develop on the hand or wrist, posing a range of challenges for those affected, from mild aesthetic concerns to significant pain and functional impairment. While surgical removal is often considered the most definitive treatment for ganglion cysts, there are several factors to consider regarding the duration and effectiveness of this approach, including the potential for recurrence, postoperative recovery time, and alternative treatment options.
Introduction to Ganglion Cysts
Before delving into the specifics of surgical treatment and its outcomes, it’s essential to understand what ganglion cysts are. These cysts are benign lumps that most commonly appear on the wrist but can also be found on the fingers or the base of the fingers. They are filled with a jelly-like fluid and are usually attached to a tendon or joint by a stalk. The exact cause of ganglion cysts is not fully understood, but they are thought to arise from the tissue that surrounds joints or tendons, possibly as a result of repetitive injury or irritation.
Surgical Treatment for Ganglion Cysts
Surgical removal of a ganglion cyst is typically recommended when the cyst is causing significant pain, limiting joint movement, or when other treatments have not been effective. The procedure involves removing the cyst as well as the stalk that attaches it to the joint or tendon. This is usually done under local anesthesia, meaning the patient remains awake but does not feel pain in the area being operated on.
Recurrence Rates After Surgery
One of the critical factors in assessing the success of surgical treatment for ganglion cysts is the recurrence rate. Historically, surgical excision has been shown to have a lower recurrence rate compared to aspiration (draining the fluid from the cyst with a needle). However, recurrences can still occur, and the rates vary in the literature. On average, it’s estimated that between 5% to 20% of ganglion cysts can recur after surgical removal. This variability can be due to several factors, including the technique used, the completeness of the cyst removal, and individual patient factors.
Postoperative Recovery
The duration of recovery after ganglion cyst surgery can vary but generally follows a predictable course. Most patients can expect some degree of pain, swelling, and stiffness in the affected area immediately after surgery. Pain is usually manageable with over-the-counter pain medications, and swelling can be reduced with ice and elevation of the affected limb. Stitches are typically removed 7-10 days after surgery, and most patients can return to their normal activities within a few weeks. However, it may take several months for the strength and range of motion in the wrist to return to normal.
Treatment Options Beyond Surgery
While surgery is often considered for ganglion cysts that are symptomatic or large, there are other treatment options available, especially for those who wish to avoid surgery or whose cysts are not significantly bothersome.
Aspiration: This involves using a needle to drain the fluid from the cyst. While simpler and less invasive than surgery, aspiration has a higher recurrence rate, sometimes as high as 50-60%.
Immobilization: For ganglion cysts that are causing pain, immobilizing the affected area with a splint may help alleviate symptoms, though this does not address the underlying issue and is more of a temporary measure.
Observation: If the cyst is not causing any symptoms, some healthcare providers may recommend simply monitoring it over time to see if it changes in size or becomes problematic.
Alternative Therapies: Some patients may seek alternative therapies such as acupuncture or homeopathic remedies, though the evidence supporting the effectiveness of these treatments for ganglion cysts is limited.
Conclusion
Ganglion cysts can pose a significant challenge for those affected, impacting both the aesthetic appearance of the hand or wrist and, in some cases, causing considerable discomfort or functional impairment. Surgical removal represents a definitive treatment option, offering a relatively low recurrence rate and the potential for full recovery of wrist function. However, as with any surgical procedure, there are factors to consider, including postoperative recovery time and the small chance of recurrence. For those seeking alternatives to surgery, other treatments are available, each with its own set of considerations regarding effectiveness, invasiveness, and potential for recurrence.
What is the average recurrence rate for ganglion cysts after surgical removal?
+The average recurrence rate for ganglion cysts after surgical removal is between 5% to 20%, though this can vary based on several factors, including the surgical technique and individual patient characteristics.
How long does it take to recover from ganglion cyst surgery?
+Recovery from ganglion cyst surgery can vary, but most patients can expect to return to their normal activities within a few weeks. It may take several months, however, for full strength and range of motion in the wrist to be restored.
What are the alternatives to surgical removal of a ganglion cyst?
+Alternatives to surgical removal include aspiration (draining the cyst with a needle), immobilization of the affected area, observation (if the cyst is not causing symptoms), and alternative therapies such as acupuncture or homeopathic remedies, though the effectiveness of these latter options is less well-established.

