How Accurate Is Ovarian Cancer Screening? Get Tested
Ovarian cancer is one of the most deadly forms of cancer in women, with a high mortality rate due to late-stage diagnosis. Early detection is crucial for improving survival rates, which has led to an increased focus on ovarian cancer screening methods. However, the accuracy of these screening tests is a topic of ongoing debate.
Understanding Ovarian Cancer Screening Methods
There are several methods used for ovarian cancer screening, including:
- Transvaginal Ultrasound (TVUS): This imaging test uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of the ovaries and detect any abnormalities.
- Cancer Antigen 125 (CA-125) Blood Test: This test measures the level of CA-125, a protein that can be elevated in women with ovarian cancer.
- Combination of TVUS and CA-125: This approach combines the results of both tests to improve detection accuracy.
Accuracy of Ovarian Cancer Screening Tests
Studies have shown that the accuracy of ovarian cancer screening tests varies. A 2018 meta-analysis published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) found that:
- TVUS had a sensitivity of 47.1% and a specificity of 95.4% for detecting ovarian cancer.
- CA-125 had a sensitivity of 54.5% and a specificity of 94.5%.
- The combination of TVUS and CA-125 had a sensitivity of 75.5% and a specificity of 94.2%.
These results indicate that while the combination of TVUS and CA-125 is the most accurate approach, it still misses approximately 25% of ovarian cancer cases.
Limitations and Challenges
There are several limitations and challenges associated with ovarian cancer screening:
- False Positives: Screening tests can produce false-positive results, leading to unnecessary anxiety, additional testing, and potential harm from invasive procedures.
- Overdiagnosis: Screening may detect slow-growing, benign tumors that would never cause harm, leading to overtreatment.
- Lack of Standardization: There is currently no standardized approach to ovarian cancer screening, making it challenging to compare results and develop effective screening programs.
Recommendations for Ovarian Cancer Screening
Based on the current evidence, the following recommendations have been made:
- Women at Average Risk: The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends against routine screening for ovarian cancer in women at average risk.
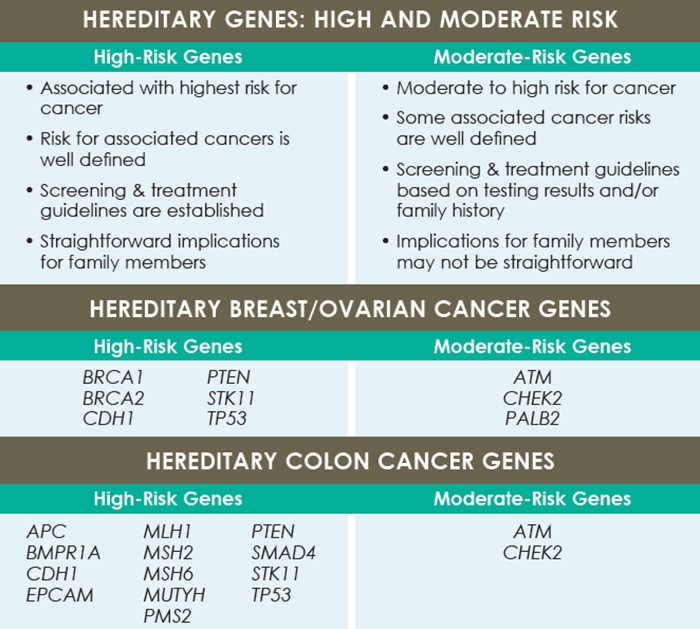
- Women at High Risk: Women with a family history of ovarian cancer or those with a known genetic mutation (e.g., BRCA1 or BRCA2) should discuss their risk with their healthcare provider and consider more frequent screening or preventive measures.
The Importance of Symptom Awareness
While screening tests are not foolproof, it is essential for women to be aware of the symptoms of ovarian cancer, which can include:
- Persistent abdominal bloating
- Pelvic pain or discomfort
- Difficulty eating or feeling full quickly
- Urinary frequency or urgency
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is crucial to consult with your healthcare provider to rule out ovarian cancer or other underlying conditions.
Early detection of ovarian cancer is critical for improving survival rates. While screening tests have limitations, being aware of your risk factors and symptoms can help you take proactive steps towards protecting your health.
Conclusion
Ovarian cancer screening is a complex and multifaceted issue. While current screening methods have limitations, ongoing research and advancements in technology are expected to improve detection accuracy. It is essential for women to be aware of their risk factors, symptoms, and screening options to make informed decisions about their health.
What are the most common symptoms of ovarian cancer?
+The most common symptoms of ovarian cancer include persistent abdominal bloating, pelvic pain or discomfort, difficulty eating or feeling full quickly, and urinary frequency or urgency.
Who should consider ovarian cancer screening?
+Women with a family history of ovarian cancer or those with a known genetic mutation (e.g., BRCA1 or BRCA2) should discuss their risk with their healthcare provider and consider more frequent screening or preventive measures.
What are the limitations of current ovarian cancer screening methods?
+Current ovarian cancer screening methods have limitations, including false positives, overdiagnosis, and a lack of standardization, which can lead to unnecessary anxiety, additional testing, and potential harm from invasive procedures.

