Diffuse Cerebral Dysfunction
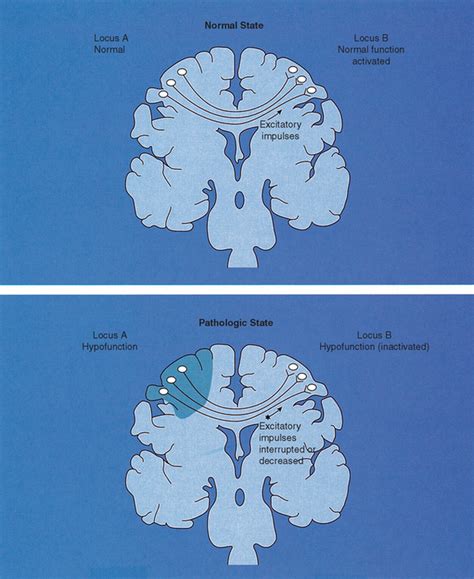
Diffuse cerebral dysfunction, also known as diffuse brain dysfunction, refers to a condition where there is widespread impairment of brain function, affecting multiple cognitive, emotional, and behavioral domains. This condition can result from various factors, including traumatic brain injury, infection, neurodegenerative diseases, and toxic exposures. The manifestations of diffuse cerebral dysfunction can be complex and varied, making diagnosis and treatment challenging.
Historical Evolution of Understanding
The concept of diffuse cerebral dysfunction has evolved over time, with early descriptions dating back to the late 19th century. Initially, it was believed that brain function was highly localized, with specific areas responsible for distinct cognitive and motor tasks. However, as research progressed, it became clear that brain function is more distributed and interconnected. The development of neuroimaging techniques, such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and positron emission tomography (PET), has greatly enhanced our understanding of brain function and the effects of diffuse cerebral dysfunction.
Technical Breakdown of Pathophysiology
Diffuse cerebral dysfunction can arise from various pathophysiological mechanisms, including:
- Axonal Injury: Traumatic brain injury can cause widespread axonal damage, disrupting communication between different brain regions.
- Neuroinflammation: Infection, autoimmune disorders, or other factors can trigger neuroinflammatory responses, leading to diffuse brain dysfunction.
- Neurodegeneration: Conditions like Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and frontotemporal dementia can cause progressive neuronal loss and dysfunction.
- Toxic Exposures: Prolonged exposure to toxins, such as heavy metals or pesticides, can damage brain cells and impair function.
Comparative Analysis of Diagnostic Approaches
Diagnosing diffuse cerebral dysfunction can be challenging, as the symptoms are often nonspecific and can overlap with other conditions. Various diagnostic approaches are used, including:
- Clinical Evaluation: A comprehensive clinical assessment, including medical history, physical examination, and cognitive testing.
- Neuroimaging: Techniques like MRI, CT, and PET scans can help identify structural or functional abnormalities in the brain.
- Electrophysiology: Electroencephalography (EEG) and evoked potentials can assess brain electrical activity and detect abnormalities.
- Neuropsychological Testing: Standardized tests can evaluate cognitive function, including attention, memory, and executive functions.
Expert Perspective: Treatment and Management
According to experts in the field, treatment and management of diffuse cerebral dysfunction depend on the underlying cause and severity of symptoms. A multidisciplinary approach, incorporating neurology, psychiatry, rehabilitation medicine, and neuropsychology, is often necessary. Interventions may include:
- Pharmacological Therapies: Medications to manage symptoms, such as cognitive enhancers, mood stabilizers, or anti-seizure medications.
- Rehabilitation Therapies: Physical, occupational, and speech therapies to improve functional abilities and adapt to cognitive deficits.
- Cognitive Training: Targeted cognitive training programs to enhance attention, memory, and executive functions.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Recommendations for stress management, sleep hygiene, and regular exercise to promote overall brain health.
Future Trends Projection: Advances in Diagnostic and Therapeutic Techniques
Advances in diagnostic and therapeutic techniques are expected to improve our understanding and management of diffuse cerebral dysfunction. Emerging trends include:
- Personalized Medicine: Tailored treatment approaches based on individual genetic profiles and brain function.
- Non-invasive Brain Stimulation: Techniques like transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) and transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) to modulate brain activity.
- Neurofeedback and Neuroplasticity: Training programs to enhance self-regulation of brain function and promote neuroplasticity.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Applications in diagnostic imaging, cognitive analysis, and personalized treatment planning.
Decision Framework for Healthcare Professionals
When encountering patients with suspected diffuse cerebral dysfunction, healthcare professionals should consider the following decision framework:
- Comprehensive Diagnostic Evaluation: Conduct a thorough diagnostic workup to identify underlying causes and rule out other conditions.
- Multidisciplinary Collaboration: Engage a team of specialists, including neurologists, psychiatrists, and rehabilitation experts, to develop a comprehensive treatment plan.
- Individualized Treatment: Tailor treatment approaches to the patient’s specific needs, incorporating pharmacological, rehabilitative, and lifestyle interventions.
- Regular Monitoring and Adjustment: Regularly assess treatment response and adjust the plan as needed to optimize outcomes.
Resource Guide for Patients and Families
For patients and families affected by diffuse cerebral dysfunction, the following resources can provide valuable information and support:
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS): A trusted source for information on brain disorders, including diffuse cerebral dysfunction.
- Brain Injury Association of America (BIAA): An organization providing education, advocacy, and support for individuals with brain injuries and their families.
- American Academy of Neurology (AAN): A professional organization offering resources and guidance on neurological conditions, including diffuse cerebral dysfunction.
- Online Support Groups: Join online forums and support groups to connect with others who are experiencing similar challenges and share experiences.
FAQ Section
What are the common symptoms of diffuse cerebral dysfunction?
+Common symptoms include cognitive impairments, such as difficulties with attention, memory, and executive functions, as well as emotional and behavioral changes, like mood swings, anxiety, and depression.
How is diffuse cerebral dysfunction diagnosed?
+Diagnosis typically involves a comprehensive clinical evaluation, neuroimaging studies, electrophysiology tests, and neuropsychological assessments to identify the underlying cause and extent of brain dysfunction.
What are the treatment options for diffuse cerebral dysfunction?
+Treatment approaches depend on the underlying cause and may include pharmacological therapies, rehabilitation programs, cognitive training, and lifestyle modifications to manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Can diffuse cerebral dysfunction be prevented?
+While some cases of diffuse cerebral dysfunction may not be preventable, reducing risk factors such as traumatic brain injury, infectious diseases, and toxic exposures can help minimize the likelihood of developing this condition.
What is the prognosis for individuals with diffuse cerebral dysfunction?
+Prognosis varies widely depending on the underlying cause, severity of symptoms, and effectiveness of treatment. With appropriate management and support, many individuals can experience significant improvement in their quality of life.
In conclusion, diffuse cerebral dysfunction is a complex condition that requires a comprehensive and multidisciplinary approach to diagnosis, treatment, and management. By understanding the underlying causes, implementing effective treatment strategies, and providing ongoing support, individuals affected by this condition can experience improved quality of life and functional abilities. As research continues to advance, we can expect to see new and innovative approaches to addressing diffuse cerebral dysfunction, ultimately leading to better outcomes for those affected.
