Dental Vs Medicine
The age-old debate between dental and medicine has sparked intense discussions among healthcare professionals and students alike. While both fields are crucial components of the healthcare system, they require distinct skill sets, knowledge bases, and approaches to patient care. In this comprehensive analysis, we will delve into the differences between dental and medicine, exploring the historical context, educational requirements, scope of practice, and the future of these two interconnected fields.
Historical Evolution
The separation between dental and medicine dates back to the 18th century, when dental care began to emerge as a distinct profession. Prior to this, medical practitioners were responsible for treating dental ailments, often with limited success. The establishment of the first dental school in Baltimore in 1840 marked the beginning of a new era in dental education and training. Since then, dentistry has evolved into a specialized field, with its own set of principles, techniques, and technologies.
In contrast, the field of medicine has a longer and more complex history, with roots dating back to ancient civilizations. The development of modern medicine has been shaped by countless discoveries, innovations, and advancements, resulting in a vast and diverse range of specialties. From cardiology to neurology, each medical specialty requires unique expertise and training, often involving years of study and practice.
Educational Requirements
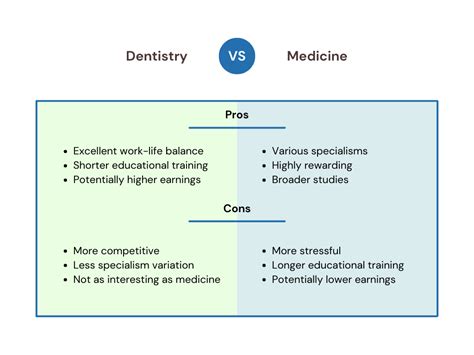
The educational pathways for dental and medical professionals differ significantly. In the United States, for example, aspiring dentists typically complete four years of undergraduate study, followed by four years of dental school, resulting in a Doctor of Dental Surgery (DDS) or Doctor of Dental Medicine (DMD) degree. Dental students undergo rigorous training in subjects such as anatomy, biochemistry, and pharmacology, as well as clinical practice in diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of oral diseases.
Medical students, on the other hand, typically complete four years of undergraduate study, followed by four years of medical school, resulting in a Doctor of Medicine (M.D.) or Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine (D.O.) degree. Medical students receive comprehensive training in a wide range of subjects, including anatomy, physiology, biochemistry, and pharmacology, as well as clinical rotations in various specialties.
Scope of Practice
The scope of practice for dental and medical professionals is largely distinct, although there is some overlap. Dentists are trained to diagnose, treat, and prevent diseases and conditions affecting the oral cavity, including teeth, gums, and related structures. They perform a range of procedures, from routine cleanings and fillings to complex surgical interventions, such as root canals and implants.
Medical professionals, by contrast, are trained to diagnose and treat a vast array of conditions and diseases affecting the entire body. Their scope of practice encompasses everything from primary care and preventive medicine to specialized fields like surgery, cardiology, and oncology. While some medical specialties, such as oral and maxillofacial surgery, may overlap with dentistry, the two fields generally require different expertise and approaches.
Comparison of Dental and Medical Specialties
| Specialty | Dental | Medical |
|---|---|---|
| Orthodontics | Focus on teeth alignment and bite correction | Focus on overall facial aesthetics and reconstruction |
| Oral Surgery | Performs surgical procedures on the teeth, gums, and jaw | Performs surgical procedures on the entire body |
| Periodontology | Focus on gum health and disease prevention | Focus on overall health and disease prevention |
| Prosthodontics | Focus on dental prosthetics and restorations | Focus on medical prosthetics and reconstruction |

Future Trends and Interconnections
As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, the relationship between dental and medicine is becoming increasingly interconnected. The recognition of the oral-systemic connection, which highlights the links between oral health and overall well-being, has led to greater collaboration and integration between the two fields.
Advances in technology, such as digital dentistry and personalized medicine, are also blurring the lines between dental and medical care. The rise of interdisciplinary approaches, such as implantology and oral medicine, is creating new opportunities for professionals from both fields to work together and share knowledge.
Sideline: Interdisciplinary Approaches
Interdisciplinary approaches, which combine the expertise of dental and medical professionals, are becoming increasingly popular. These approaches recognize the complexity of human health and the need for comprehensive, integrated care. Some examples of interdisciplinary approaches include:
- Implantology: Combines dental and medical expertise to restore teeth and oral function
- Oral Medicine: Combines dental and medical expertise to diagnose and treat oral diseases and conditions
- Orofacial Pain: Combines dental and medical expertise to diagnose and treat pain and dysfunction of the jaw and face
Conclusion
In conclusion, while dental and medicine are distinct fields with unique requirements and scopes of practice, they are interconnected and interdependent. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, it is essential for professionals from both fields to recognize the value of collaboration, shared knowledge, and integrated care. By working together and embracing the complexity of human health, we can provide more effective, comprehensive, and patient-centered care.
FAQ Section
What is the difference between a DMD and a DDS degree?
+A DMD (Doctor of Dental Medicine) and a DDS (Doctor of Dental Surgery) degree are equivalent and indicate that the holder has completed the required education and training to become a licensed dentist.
Can medical doctors perform dental procedures?
+In general, medical doctors are not trained or licensed to perform dental procedures. However, some medical specialties, such as oral and maxillofacial surgery, may overlap with dentistry.
What is the oral-systemic connection?
+The oral-systemic connection refers to the links between oral health and overall well-being. Research has shown that there is a significant relationship between gum disease and an increased risk of heart disease, diabetes, and other systemic conditions.
Reference List
- American Dental Association. (2022). Dental Education.
- American Medical Association. (2022). Medical Education.
- National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research. (2022). Oral-Systemic Connection.