Dental Impression For Crown
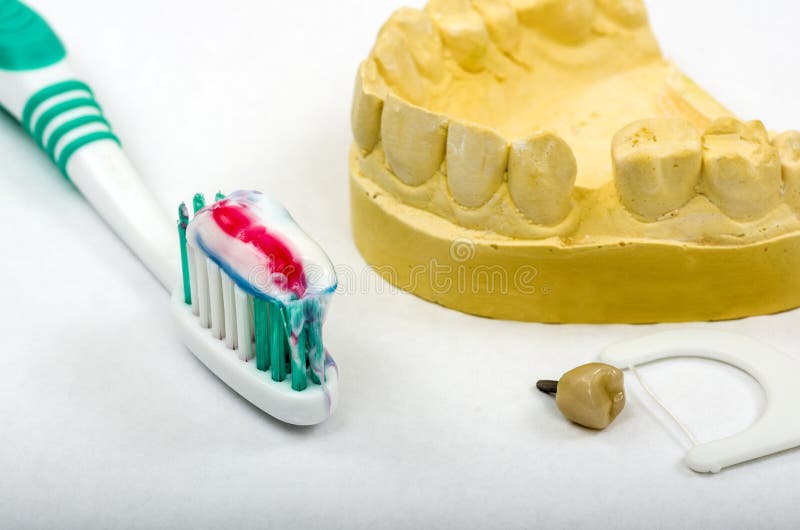
Achieving an accurate dental impression is a critical step in the creation of a well-fitting dental crown. The process involves creating a negative replica of the patient’s mouth, which includes the teeth and surrounding tissues, to capture the precise details necessary for crown fabrication. This article delves into the importance, techniques, and materials used in dental impressions for crowns, discussing the evolution of impression materials and the integration of digital technologies in modern dentistry.
Introduction to Dental Impressions
Dental impressions are a cornerstone of restorative dentistry, enabling dentists to create prosthetic devices that are tailored to the individual patient’s dental anatomy. For crown fabrication, an impression must accurately capture the details of the tooth to be crowned, as well as the opposing teeth and the bite relationship. This information is crucial for creating a crown that fits perfectly, functions correctly, and meets aesthetic expectations.
Materials Used for Dental Impressions
Over the years, the materials used for dental impressions have evolved significantly, from traditional plaster and dental stone to more advanced elastomeric impression materials. Today, the most commonly used materials include:
Alginate: A hydrocolloid material that is widely used for preliminary impressions due to its ease of use and cost-effectiveness. Alginate impressions are not as accurate as those made with elastomeric materials and are typically used for study models or as a means to communicate the overall dental anatomy to the patient.
Elastomeric Impression Materials: These are the gold standard for making precise impressions required for crowns. They include polyether and polysulfide materials, which offer high accuracy and are used for final impressions. Each has its unique properties, such as dimensional stability and flexibility, making them ideal for capturing the fine details necessary for crown fabrication.
Digital Impressions: The advent of intraoral scanners has revolutionized the impression process, allowing for the direct digital capture of the dental anatomy. This technology eliminates the need for physical impression materials, reducing chair time and increasing patient comfort. Digital impressions also enable immediate verification of the captured data, reducing the likelihood of errors.
Techniques for Taking Dental Impressions
The technique used for taking dental impressions can significantly impact the accuracy of the final crown. Key considerations include:
Tray Selection: The impression tray should be sufficiently large to capture all relevant dental structures but not so large that it causes discomfort or interferes with the patient’s ability to close their mouth.
Impression Material Mixing and Loading: The mixing of impression material must be done accurately to achieve the correct consistency, and the material should be loaded into the tray in a way that ensures complete coverage of the dental arch.
Insertion and Removal Techniques: The tray is inserted into the mouth gently to avoid compressing or displacing the soft tissues. Removal should also be done carefully to prevent distortion of the impression.
Digital Impressions and Crown Fabrication
Digital impression systems, such as those offered by companies like Align Technology (Itero) and Dentsply Sirona (CEREC), are increasingly popular due to their ability to streamline the dental restoration process. These systems allow for the creation of digital models of the patient’s mouth, which can then be used to design and fabricate crowns using computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM) technology. This integration of digital impressions with CAD/CAM fabrication can significantly reduce the time required for crown fabrication, improve fit accuracy, and enhance patient satisfaction.
Future Trends in Dental Impressions for Crowns
The field of dental impressions is evolving rapidly, with advancements in digital technologies expected to play a pivotal role in shaping the future. Innovations such as improved intraoral scanner accuracy, increased accessibility of digital impression systems to more dental practices, and advancements in CAD/CAM technologies are anticipated. Furthermore, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in the design and fabrication process could lead to even more precise and aesthetically pleasing crowns, setting new standards for dental restorations.
FAQ Section
What is the most accurate material for dental impressions for crowns?
+Elastomeric impression materials, such as polyether and polysulfide, are considered the most accurate for capturing the fine details necessary for crown fabrication.
How do digital impressions compare to traditional methods in terms of accuracy and patient comfort?
+Digital impressions offer high accuracy, reduce the need for retakes, and are generally more comfortable for patients, as they eliminate the need for bulky impression trays and materials.
Can digital impressions be used for all types of dental restorations?
+While digital impressions can be used for a wide range of dental restorations, including crowns, bridges, and dentures, their application may be limited by the specific requirements of each case and the capabilities of the digital system being used.
In conclusion, dental impressions for crowns represent a critical juncture in restorative dentistry, where accuracy, comfort, and technology converge. As dental practices continue to adopt digital impression systems and CAD/CAM technologies, the future of crown fabrication promises to be more efficient, accurate, and patient-centric than ever before.