Dental Implant Abutments
The concept of dental implant abutments has revolutionized the field of dentistry, providing a highly effective solution for individuals seeking to restore their oral function and aesthetics. At the forefront of this innovation is the understanding that dental implants are not solely about replacing missing teeth, but about recreating the natural harmony of the mouth. This involves not just the implant itself, but also the abutment that connects the implant to the prosthetic tooth.
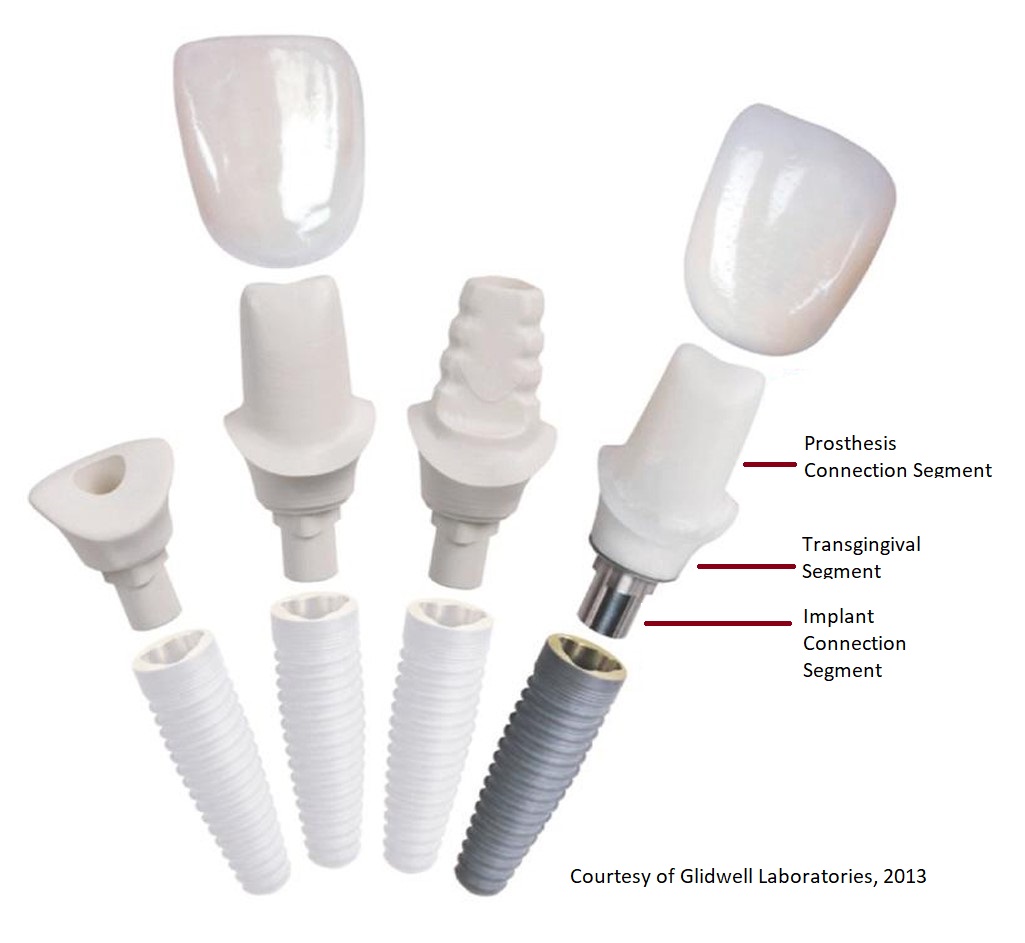
To grasp the significance of dental implant abutments, it’s essential to delve into their role within the broader context of dental implants. A dental implant is essentially a titanium post that is surgically placed into the jawbone beneath the gum line. This post serves as the anchor for a prosthetic tooth, which is secured to the implant via an abutment. The abutment is a small connector that is attachable to the implant and provides the necessary foundation for the prosthetic tooth.
The Evolution of Dental Implant Abutments
The development of dental implant abutments has undergone significant transformations over the years. Initially, abutments were considered mere accessories to the dental implant itself. However, as dental implantology progressed, the importance of abutments became more apparent. Today, abutments are recognized as crucial components that significantly influence the success and longevity of dental implants.
One of the key advancements in abutment technology is the introduction of customized abutments. Unlike standard abutments, which are pre-fabricated to fit a range of implant sizes, customized abutments are specifically designed to match the unique contours of each patient’s mouth. This personalization allows for a more precise fit, enhancing the stability and aesthetic appeal of the prosthetic tooth.
Materials Used for Dental Implant Abutments
The materials used for dental implant abutments have also seen considerable improvement. Traditionally, abutments were made from titanium, given its biocompatibility and strength. While titanium remains a popular choice, other materials such as zirconia have gained prominence due to their durability and aesthetic benefits. Zirconia abutments, for instance, offer a more natural look, as they can be colored to match the surrounding teeth, thereby enhancing the overall aesthetic outcome of the dental implant.
The Impact of Digital Technology on Dental Implant Abutments
The integration of digital technology into dental implantology has profoundly impacted the design, manufacture, and placement of abutments. Computer-aided design (CAD) software and 3D printing technologies enable the creation of highly precise and customized abutments. This precision not only improves the fit of the prosthetic tooth but also reduces the time required for the procedure, making the overall experience more efficient for both the dentist and the patient.
Moreover, digital impressions and guided surgery have significantly improved the accuracy of abutment placement. By utilizing these technologies, dentists can now predictably achieve optimal positioning of the abutment, which is critical for the long-term success of the dental implant.
Considerations for Selecting Dental Implant Abutments
When selecting dental implant abutments, several factors must be considered. The material of the abutment, as mentioned earlier, is crucial for both functional and aesthetic reasons. Additionally, the design of the abutment, including its shape and size, should be carefully chosen to ensure it adequately supports the prosthetic tooth and promotes easy maintenance.
The compatibility of the abutment with the specific dental implant system being used is also of paramount importance. Different implant systems may have unique characteristics that require abutments designed specifically for those systems. Ensuring compatibility is vital for achieving a secure and durable connection between the implant and the prosthetic tooth.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the advancements in dental implant abutments, challenges still exist. One of the primary concerns is the potential for abutment screw loosening over time, which can compromise the stability of the prosthetic tooth. Ongoing research focuses on developing abutment designs and materials that minimize this risk, ensuring the long-term viability of dental implants.
Furthermore, the increasing demand for more aesthetically pleasing outcomes has driven innovation in abutment design. Future directions include the development of abutments that not only provide superior functional support but also enhance the natural appearance of the prosthetic tooth, blending seamlessly with the surrounding dentition.
Conclusion
Dental implant abutments play a pivotal role in the success of dental implant procedures. From their evolution over time to the current advancements in materials and technology, abutments have become a cornerstone of modern dentistry. As research and development continue to push the boundaries of what is possible, it is likely that dental implant abutments will become even more sophisticated, offering patients improved functional outcomes and more natural-looking results.
What is the primary function of a dental implant abutment?
+The primary function of a dental implant abutment is to connect the dental implant to the prosthetic tooth, thereby serving as a critical link that supports the restoration and facilitates oral function.
What materials are commonly used for dental implant abutments?
+Titanium and zirconia are among the most commonly used materials for dental implant abutments. Each material has its advantages, with titanium offering strength and biocompatibility, and zirconia providing durability and aesthetic benefits.
How has digital technology impacted the field of dental implant abutments?
+Digital technology has significantly impacted the field by enabling the creation of highly customized and precise abutments. Technologies such as CAD software and 3D printing allow for tailored designs that enhance the fit and aesthetic appeal of prosthetic teeth. Additionally, digital impressions and guided surgery have improved the accuracy of abutment placement.