Deep Pockets Teeth: Fix Receding Gums Easily
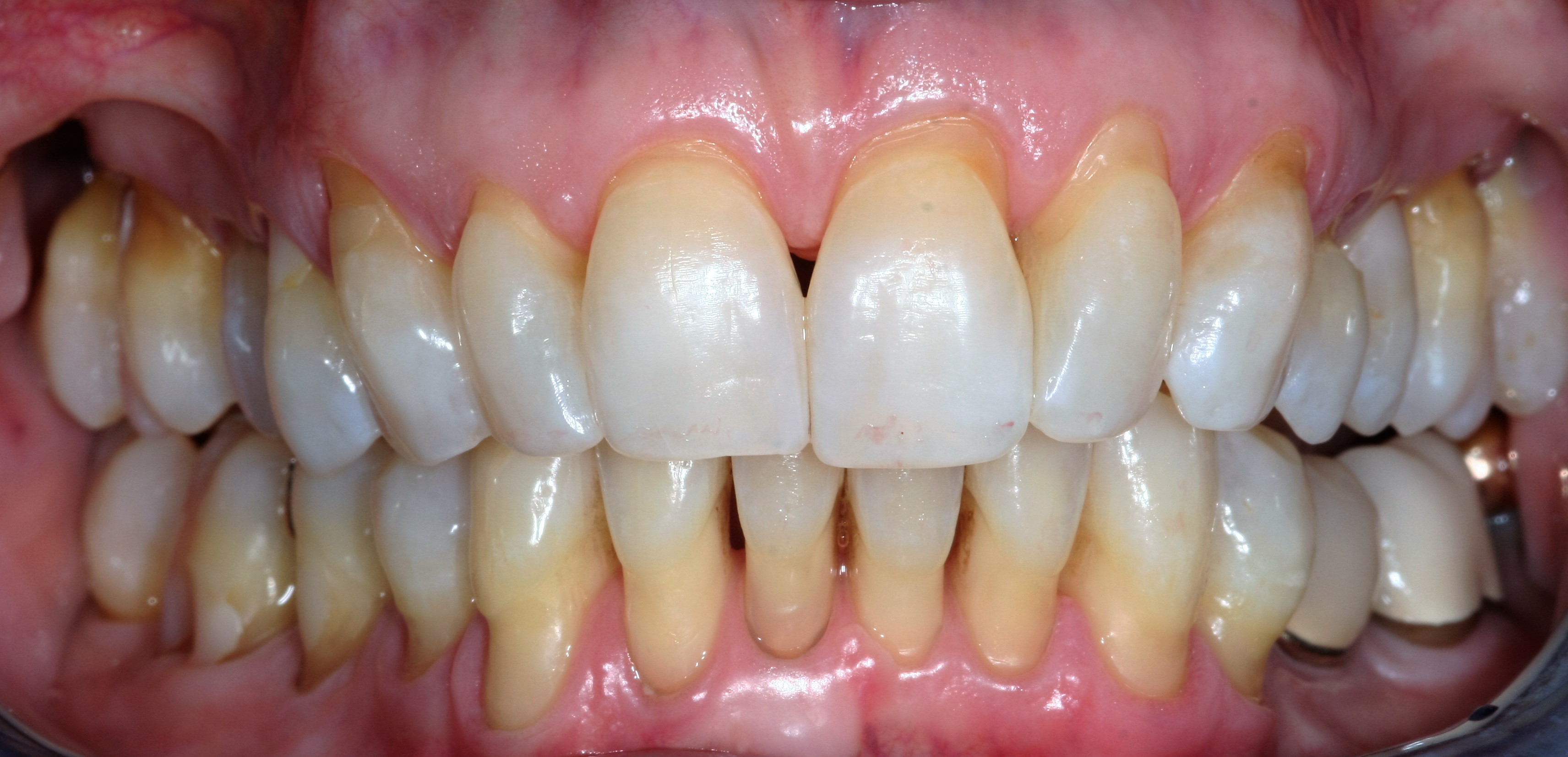
Receding gums, a condition where the gum tissue surrounding the teeth pulls back, exposing more of the tooth and its root, can be a source of both aesthetic concern and health issues. While it’s often associated with aging, receding gums can affect anyone, regardless of age, due to various factors such as poor oral hygiene, aggressive brushing, genetic predisposition, and certain medical conditions. One of the key challenges in addressing receding gums is finding effective and minimally invasive treatments that can restore the health and appearance of the gums without requiring extensive surgical procedures. The concept of “deep pockets” in dentistry refers to the spaces between the teeth and gums that have become deeper due to gum recession, potentially harboring bacteria and leading to further complications. Fixing receding gums, therefore, involves not just restoring the gum line but also addressing these deep pockets to prevent future issues.
Understanding Receding Gums and Deep Pockets
Receding gums are often a gradual process, and symptoms may not be immediately noticeable. However, as the condition progresses, it can lead to increased sensitivity of the teeth, especially to hot and cold temperatures, changes in the appearance of the teeth, making them seem longer, and in severe cases, loose teeth due to the loss of support from the gums. The presence of deep pockets is a significant concern because these spaces can trap food particles and plaque, leading to infections and further recession if not properly cleaned.
Causes and Risk Factors
Before diving into the solutions, it’s crucial to understand the causes and risk factors associated with receding gums. These include:
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque to build up, leading to gum inflammation (gingivitis) and, if left untreated, gum recession.
- Aggressive Brushing: Brushing too hard or using a hard-bristled toothbrush can wear away the gum tissue.
- Genetics: Some people are more prone to gum disease and recession due to their genetic makeup.
- Tobacco Use: Smoking and chewing tobacco increase the risk of gum recession.
- Grinding and Clenching Teeth: This can put additional stress on the gums, making them more susceptible to recession.
- Certain Medical Conditions: Diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and hormonal changes can increase the risk of gum recession.
Treatment Options for Receding Gums and Deep Pockets
The good news is that receding gums and deep pockets can be treated, and the approach often depends on the severity of the condition. Here are some of the treatment options available:
1. Deep Cleaning (Scaling and Root Planing):
This is a non-surgical method used to treat mild to moderate gum recession. A dental professional will remove plaque and tartar both above and below the gum line, smoothing the root of the tooth to prevent future plaque buildup.
2. Gum Grafting:
For more advanced gum recession, gum grafting may be necessary. This involves taking healthy gum tissue from another part of the mouth and attaching it to the affected area. The goal is to cover the exposed roots and restore the natural gum line.
3. Pinhole Surgical Technique (PST):
A minimally invasive procedure that involves making a small pinhole in the gum tissue above the receded area. Through this pinhole, special instruments are used to gently loosen and reposition the gum tissue over the receded area, covering the exposed roots without the need for incisions or sutures.
4. Regenerative Procedures:
These include the use of grafts and other materials to help regenerate lost bone and tissue. This approach is often used in conjunction with other treatments.
5. Laser Treatment:
Laser therapy can be used to remove diseased gum tissue and promote healing. It’s less invasive than traditional surgery and can reduce bleeding, discomfort, and recovery time.
Preventive Measures
While these treatments can address existing receding gums and deep pockets, prevention remains key. Adopting good oral hygiene practices can significantly reduce the risk of developing gum recession:
- Brush Gently: Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and gentle circular motions.
- Floss Daily: Clean between teeth once a day to remove plaque.
- Regular Dental Check-Ups: Visit your dentist regularly for cleanings and to catch any oral health issues early.
- Quit Tobacco: Smoking and tobacco use significantly increase the risk of gum disease.
- Manage Stress: Find healthy ways to manage stress to avoid teeth grinding and clenching.
FAQ Section
What are the signs of receding gums?
+Signs include sensitivity of the teeth, especially to hot and cold temperatures, visible roots of the teeth, and changes in the fit of dentures or other oral appliances.
Can receding gums be reversed?
+While some treatments can restore the appearance of the gum line and prevent further recession, the term "reversal" might be misleading. The goal of treatment is often to halt the progression of the condition and improve the health and appearance of the gums.
What is the cost of treating receding gums?
+The cost can vary widely depending on the severity of the condition, the treatment options chosen, and the dental professional's fees. Insurance coverage also plays a significant role in the out-of-pocket costs.
In conclusion, while receding gums and deep pockets present a challenge, they are not irreversible. With the right combination of professional treatment and preventive measures, it’s possible to restore the health and appearance of the gums, preventing further complications and ensuring a healthy, confident smile for years to come.
