Cephalometric X Ray
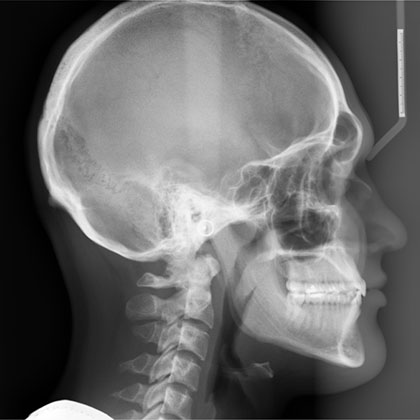
The cephalometric X-ray, a crucial diagnostic tool in the fields of orthodontics and oral surgery, has been a cornerstone in the assessment and treatment planning of dental and skeletal abnormalities for decades. This specialized X-ray technique provides a comprehensive, two-dimensional representation of the craniofacial structure, enabling practitioners to analyze the intricate relationships between the teeth, jaw, and facial bones with unparalleled precision.
Historical Evolution of Cephalometric X-Rays
The concept of cephalometric analysis dates back to the 1930s, when Broadbent introduced the first cephalometric X-ray apparatus. This pioneering work laid the foundation for the development of standardized techniques and analysis methods, which would later become indispensable in orthodontic diagnosis and treatment planning. Over the years, advancements in technology have led to the development of digital cephalometric X-ray systems, offering enhanced image quality, reduced radiation exposure, and streamlined analysis processes.
Technical Breakdown: How Cephalometric X-Rays Work
Cephalometric X-rays are typically taken with the patient standing or sitting in a specialized unit, with their head positioned against a cephalostat to ensure precise alignment. The X-ray beam is then directed through the patient’s head, capturing a lateral or posteroanterior (PA) view of the craniofacial structure. The resultant image provides a detailed representation of the skeletal and dental relationships, including the position of the teeth, jaw, and facial bones.
Expert Insight: Interpreting Cephalometric X-Rays
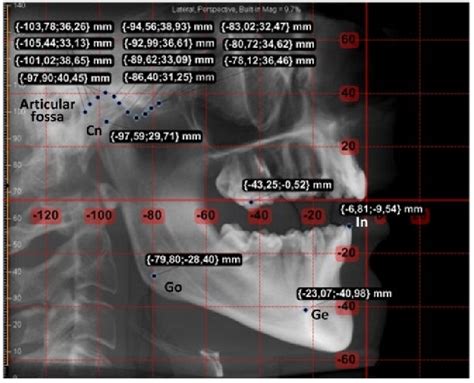
Interpreting cephalometric X-rays requires a deep understanding of craniofacial anatomy and orthodontic principles. Practitioners must carefully analyze the X-ray image, taking into account various landmarks, such as the sella turcica, nasion, and gonion, to assess the patient’s skeletal and dental relationships. This information is then used to identify potential abnormalities, such as teeth crowding, overbites, or underbites, and to develop an effective treatment plan.
When analyzing cephalometric X-rays, it's essential to consider the patient's overall facial aesthetics, as well as their dental and skeletal relationships. This comprehensive approach enables practitioners to develop treatment plans that not only address the patient's orthodontic needs but also enhance their overall facial harmony.
Problem-Solution Framework: Common Applications of Cephalometric X-Rays
Cephalometric X-rays have a wide range of applications in orthodontics and oral surgery, including:
- Orthodontic diagnosis and treatment planning: Cephalometric X-rays help practitioners identify skeletal and dental abnormalities, such as Class II or Class III malocclusions, and develop targeted treatment plans.
- Surgical planning: Cephalometric X-rays are used to assess the patient’s craniofacial structure and plan surgical interventions, such as orthognathic surgery.
- Growth and development analysis: Cephalometric X-rays can be used to monitor the growth and development of the craniofacial structure in children and adolescents, enabling practitioners to anticipate and address potential orthodontic issues.
Comparative Analysis: Digital vs. Traditional Cephalometric X-Rays
The advent of digital cephalometric X-ray systems has revolutionized the field of orthodontics, offering several advantages over traditional film-based systems. Digital X-rays provide enhanced image quality, reduced radiation exposure, and streamlined analysis processes. Additionally, digital X-rays can be easily stored, shared, and retrieved, facilitating communication between practitioners and improving patient care.
| Characteristic | Digital Cephalometric X-Rays | Traditional Cephalometric X-Rays |
|---|---|---|
| Image Quality | High-resolution, digital images | Lower-resolution, film-based images |
| Radiation Exposure | Reduced radiation exposure | Higher radiation exposure |
| Analysis Process | Streamlined, automated analysis | Manual, time-consuming analysis |
Future Trends Projection: Advances in Cephalometric X-Ray Technology
As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see significant advancements in cephalometric X-ray technology. Some potential developments on the horizon include:
- 3D imaging capabilities: The integration of 3D imaging technology into cephalometric X-ray systems, enabling practitioners to analyze the craniofacial structure with unprecedented precision.
- Artificial intelligence (AI) analysis tools: The development of AI-powered analysis tools, which can help practitioners identify potential abnormalities and develop personalized treatment plans.
- Increased accessibility: The expansion of cephalometric X-ray technology to more remote or underserved areas, enabling greater access to orthodontic care and improving overall oral health outcomes.
What is the primary purpose of a cephalometric X-ray?
+The primary purpose of a cephalometric X-ray is to provide a detailed, two-dimensional representation of the craniofacial structure, enabling practitioners to diagnose and treat orthodontic and oral surgery conditions.
How do digital cephalometric X-rays differ from traditional X-rays?
+Digital cephalometric X-rays offer enhanced image quality, reduced radiation exposure, and streamlined analysis processes compared to traditional film-based X-rays.
What are some common applications of cephalometric X-rays in orthodontics?
+Cephalometric X-rays are commonly used for orthodontic diagnosis and treatment planning, surgical planning, and growth and development analysis.
In conclusion, cephalometric X-rays have revolutionized the field of orthodontics, providing a valuable diagnostic tool for practitioners to assess and treat craniofacial abnormalities. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see significant advancements in cephalometric X-ray technology, enabling even more precise and effective orthodontic care.
