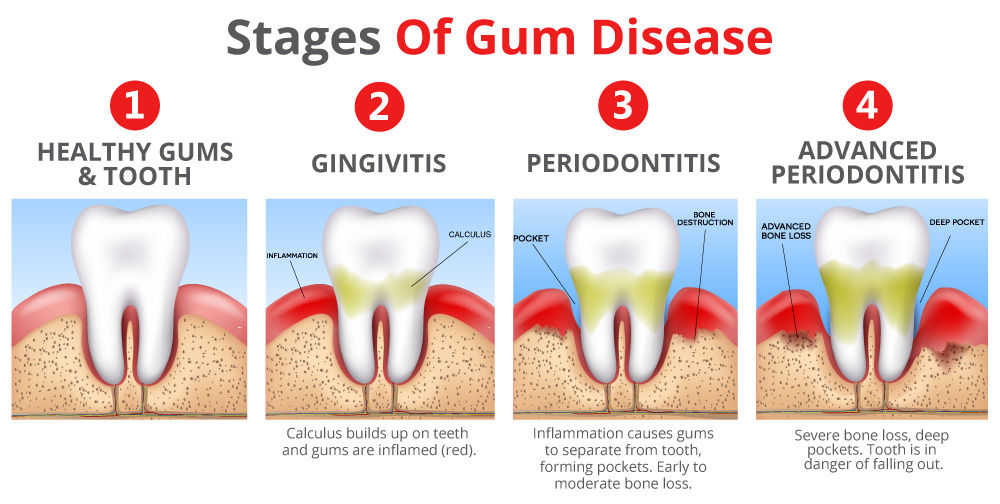
Can Gums Bruise
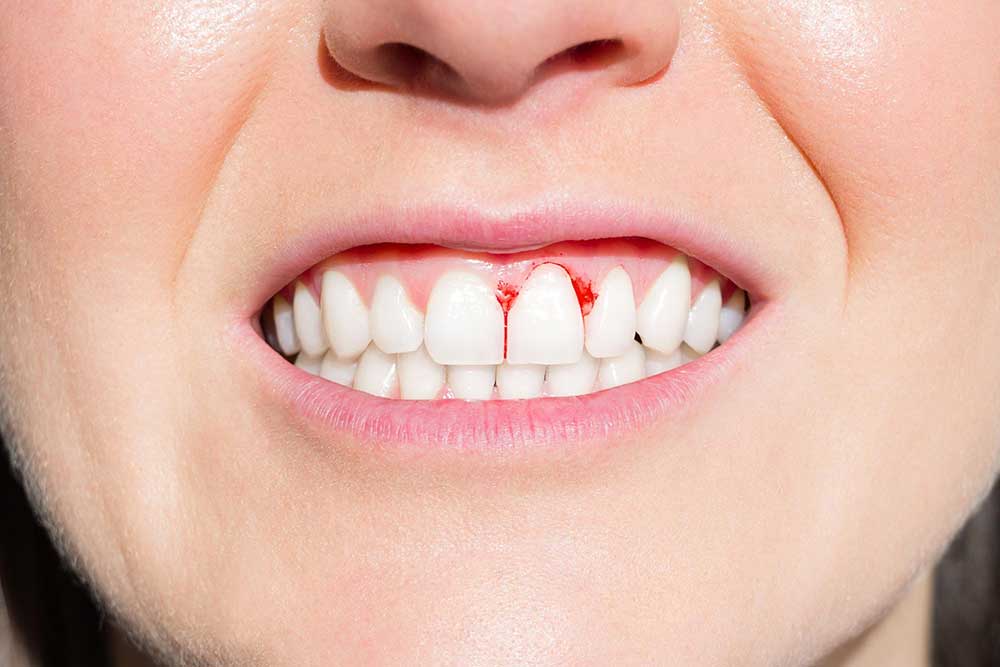
Gums, being a soft tissue, can indeed suffer from bruising, although it’s not as common or visible as bruising on the skin. The condition is often referred to as a gum bruise or a hematoma. A bruise on the gums occurs when blood vessels in the gum tissue are damaged, causing blood to leak into the surrounding tissues. This can result from various factors, including trauma, infection, or certain medical conditions.
The manifestation of a bruise on the gums can vary. It may appear as a small, localized discoloration, typically blue or purple, which can be tender to the touch. In some cases, the bruise might be accompanied by swelling or inflammation of the gum tissue. The pain associated with a gum bruise can range from mild to severe and may be exacerbated by factors such as eating, drinking, or even breathing through the mouth.
One of the primary concerns with gum bruising is the potential for it to be a sign of an underlying issue. For instance, if the bruising is due to trauma, such as a blow to the mouth, it’s essential to assess whether there are any other injuries, such as cracked teeth or damage to the jaw. Furthermore, recurring or severe gum bruising could indicate a problem with blood clotting or a condition affecting the blood vessels, such as diabetes or hypertension.
In terms of treatment, minor gum bruises often resolve on their own with time and do not require specific medical intervention. However, applying a cold compress to the affected area can help reduce swelling and alleviate pain. Additionally, maintaining good oral hygiene is crucial to prevent infection, which could complicate the healing process.
For more severe cases or when the bruising is symptomatic of an underlying condition, seeking professional dental or medical advice is advisable. A healthcare provider can assess the bruise, determine its cause, and provide appropriate treatment. This might include antibiotics if there’s an infection, pain management strategies, or even surgical intervention in rare cases where the bruise is very large or does not heal.
Preventing gum bruising involves a combination of avoiding direct trauma to the mouth and gums, practicing good oral hygiene to prevent infections, and managing any underlying health conditions that could increase the risk of bruising. Regular dental check-ups are also essential for early detection and treatment of any issues that could lead to gum bruising.
FAQ Section
What causes gum bruising?
+Gum bruising can be caused by trauma to the mouth, infection, or certain medical conditions that affect blood vessels or clotting. It's essential to determine the cause to provide appropriate treatment.
How long does it take for a gum bruise to heal?
+The healing time for a gum bruise can vary depending on the severity of the injury and the overall health of the individual. Minor bruises may resolve within a few days to a week, while more severe cases could take longer to heal.
Can gum bruising be a sign of an underlying health issue?
+In conclusion, while gum bruising is not a common topic of discussion, it is a condition that can occur due to various reasons. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and knowing when to seek professional advice are key to managing gum bruising effectively. By taking proactive steps in oral health care and being mindful of overall health, individuals can minimize the risk of gum bruising and ensure prompt treatment when it does occur.