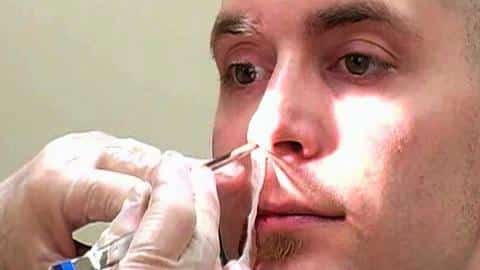
Bottom Lip Tie
The concept of a bottom lip tie, also known as an inferior labial tie, has gained significant attention in recent years, particularly among parents and healthcare professionals. This condition, which affects the tissue that connects the bottom lip to the gums, can have a profound impact on an individual’s oral function, speech, and overall quality of life. In this article, we will delve into the world of bottom lip ties, exploring their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options, as well as the potential effects on daily life and the importance of proper care.
Understanding the Anatomy
To comprehend the implications of a bottom lip tie, it’s essential to understand the anatomy of the oral cavity. The labial frenulum, a small fold of tissue, connects the bottom lip to the gums. In a normal anatomical setup, this tissue is relatively thin and flexible, allowing for a full range of motion. However, in individuals with a bottom lip tie, this tissue is often thicker, tighter, or more prominent, restricting the movement of the bottom lip.
Causes and Risk Factors
Research suggests that bottom lip ties can be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some potential causes include:
- Genetic predisposition: Family history can play a significant role in the development of a bottom lip tie.
- Oral habits: Prolonged thumb sucking or pacifier use can contribute to the formation of a bottom lip tie.
- Trauma: Injury to the oral cavity, such as a fall or a blow to the mouth, can cause the labial frenulum to become scarred or tight.
- Infection: Certain infections, like oral thrush, can lead to inflammation and scarring of the labial frenulum.
Symptoms and Effects
The symptoms of a bottom lip tie can vary widely, depending on the severity of the condition. Some common effects include:
- Restricted lip movement: A bottom lip tie can limit the range of motion of the bottom lip, making it difficult to speak, eat, or smile.
- Speech difficulties: The restricted lip movement can lead to speech impediments, such as a lisp or difficulty articulating certain sounds.
- Oral hygiene issues: A bottom lip tie can make it challenging to clean the teeth and gums properly, increasing the risk of oral infections and decay.
- Dental problems: The altered oral anatomy can lead to issues like misaligned teeth, gum recession, or an increased risk of tooth decay.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing a bottom lip tie typically involves a visual examination and a review of the individual’s medical history. Healthcare professionals may use various diagnostic tools, such as:
- Visual inspection: A thorough examination of the oral cavity to assess the appearance and movement of the bottom lip.
- Palpation: A gentle probing of the labial frenulum to evaluate its thickness and flexibility.
- Imaging studies: X-rays or other imaging tests may be used to rule out underlying conditions that could be contributing to the bottom lip tie.
Treatment options for a bottom lip tie vary depending on the severity of the condition and the individual’s overall health. Some common treatments include:
- Frenectomy: A surgical procedure to release the labial frenulum, allowing for improved lip movement and oral function.
- Orthodontic treatment: Braces or other orthodontic appliances can help correct misaligned teeth and improve the overall appearance of the smile.
- Speech therapy: Targeted exercises and techniques can help individuals with a bottom lip tie improve their speech and articulation.
Living with a Bottom Lip Tie
For individuals with a bottom lip tie, daily life can present unique challenges. Simple tasks like eating, speaking, or smiling can become difficult and frustrating. However, with proper care and attention, it’s possible to manage the condition and improve overall quality of life.
Some practical tips for living with a bottom lip tie include:
- Practicing good oral hygiene: Regular brushing and flossing can help prevent oral infections and decay.
- Avoiding irritants: Steer clear of foods or substances that can irritate the labial frenulum, such as spicy or acidic foods.
- Exercising the lips: Gentle stretching and exercises can help improve lip movement and flexibility.
What are the symptoms of a bottom lip tie in infants?
+Symptoms of a bottom lip tie in infants can include difficulty latching during breastfeeding, excessive drooling, and clicking or smacking sounds while feeding.
Can a bottom lip tie cause speech problems in children?
+Yes, a bottom lip tie can contribute to speech difficulties in children, particularly with sounds that require precise lip movement, such as the "b" or "p" sounds.
How can I prevent a bottom lip tie in my child?
+While it's not possible to completely prevent a bottom lip tie, encouraging good oral habits, such as avoiding prolonged thumb sucking or pacifier use, can help reduce the risk of developing the condition.
In conclusion, a bottom lip tie is a complex condition that requires careful diagnosis and treatment. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and effects of this condition, individuals can take the first steps towards improving their oral function, speech, and overall quality of life. With the right care and attention, it’s possible to manage the challenges of a bottom lip tie and achieve a healthier, happier smile.