Anterior Tibial Tendonitis: Strengthen Ankles Fast
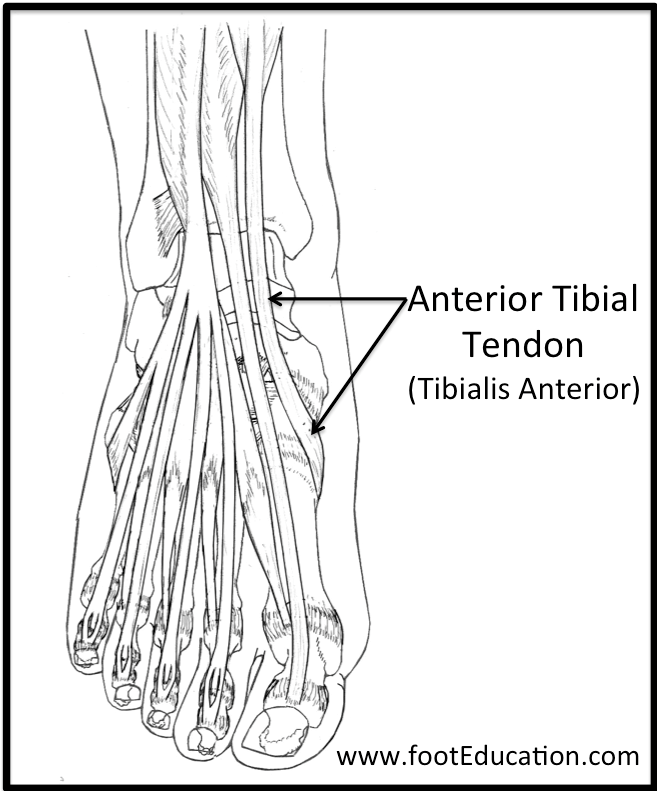
Anterior tibial tendonitis is a common overuse injury that affects the tendons in the front of the ankle, leading to pain, swelling, and limited mobility. This condition is particularly prevalent among athletes and individuals who engage in activities that involve repetitive ankle movements, such as running, hiking, or dancing. The anterior tibial tendon plays a crucial role in supporting the ankle joint and facilitating movements like dorsiflexion (lifting the foot upwards) and inversion (turning the foot inwards). When this tendon becomes inflamed or damaged, it can significantly impact an individual’s ability to perform daily activities, let alone maintain an active lifestyle.
To address anterior tibial tendonitis effectively, it’s essential to adopt a comprehensive approach that incorporates rest, rehabilitation, and strengthening exercises. While rest and ice are critical components of the initial treatment phase, targeted exercises can help strengthen the ankle, promote healing, and prevent future injuries.
Understanding the Anatomy and Function
The anterior tibial tendon is one of the primary tendons in the ankle, connecting the tibialis anterior muscle to the bones in the foot. This tendon is responsible for transmitting the forces generated by the muscle to the foot, enabling movements that are essential for walking, running, and balance. When the tendon becomes inflamed due to overuse, poor biomechanics, or direct trauma, it can lead to anterior tibial tendonitis. Understanding the anatomy and function of the anterior tibial tendon is vital for developing effective treatment and prevention strategies.
Symptom Identification and Diagnosis
Identifying the symptoms of anterior tibial tendonitis is the first step towards seeking appropriate treatment. Common symptoms include pain and swelling in the front of the ankle, particularly during activities that involve ankle movement. Individuals may also experience stiffness, especially after periods of rest, and limited mobility of the ankle joint. In severe cases, the pain can become chronic, affecting daily activities and quality of life. Diagnosis typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history review, and potentially, imaging studies like ultrasound or MRI to rule out other conditions and assess the extent of tendon damage.
Rest and Rehabilitation
The initial phase of treating anterior tibial tendonitis involves rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) to reduce pain and inflammation. This is followed by a rehabilitation program that aims to restore strength, flexibility, and function to the ankle. Rehabilitation exercises are progressively introduced, starting with gentle mobilization and strengthening of the foot and ankle muscles. It’s crucial to avoid activities that aggravate the condition during this phase, allowing the tendon time to heal.
Strengthening Exercises for the Ankles
Strengthening the muscles around the ankle, particularly the tibialis anterior, is critical for recovering from anterior tibial tendonitis and preventing future injuries. Here are some exercises that can be incorporated into a rehabilitation program:
- Ankle Alphabet: This exercise involves drawing the alphabet with the toes, starting from A to Z. It helps improve ankle mobility and strength.
- Toe Raises: Standing on the edge of a stair or curb with the heels hanging off, raise up onto the toes and then lower back down. This exercise targets the calf muscles and helps strengthen the ankle.
- Ankle Circles: Sit on the floor with the legs straight out in front. Lift one foot off the ground and draw circles with the ankle, starting from small circles and gradually increasing in size. Repeat with the other foot.
- Resistance Band Exercises: Using a resistance band, perform ankle movements like dorsiflexion, plantarflexion, inversion, and eversion. These exercises help strengthen the muscles around the ankle.
It's essential to start these exercises gently and progress gradually, as overexertion can exacerbate the condition. Consultation with a healthcare provider or a physical therapist can provide personalized guidance on the appropriate exercises and intensity level.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing anterior tibial tendonitis involves a combination of proper training techniques, footwear selection, and regular strengthening exercises. Athletes and individuals with a high risk of overuse injuries should incorporate ankle strengthening exercises into their routine training programs. Additionally, wearing appropriate footwear that supports the ankle and provides adequate cushioning can reduce the risk of injury.
How to Integrate Strengthening Exercises into Daily Routine
Incorporating ankle strengthening exercises into a daily routine can be straightforward. Here are some tips: - Start with short sessions (5-10 minutes) and gradually increase duration and intensity. - Perform exercises during commercial breaks while watching TV or during other downtimes. - Incorporate exercises into a daily warm-up routine before engaging in physical activities. - Use reminders or schedule exercises into a daily planner to maintain consistency.
Step-by-Step Guide to Ankle Strengthening
- Begin with ankle mobility exercises to improve range of motion.
- Progress to strengthening exercises like toe raises and resistance band workouts.
- Incorporate balance and proprioception exercises to enhance ankle stability.
- Gradually increase the intensity and duration of exercises based on comfort and progress.
Balanced Approach to Recovery
Recovery from anterior tibial tendonitis requires a balanced approach that includes rest, rehabilitation, and strengthening exercises. It’s crucial to avoid rushing back into activities too quickly, as this can lead to further injury and prolonged recovery times. A healthcare provider or physical therapist can offer personalized advice and create a tailored rehabilitation program to ensure a safe and effective recovery.
Future Trends in Treatment and Prevention
Emerging trends in the treatment and prevention of anterior tibial tendonitis include the use of advanced rehabilitation technologies, such as electromyography (EMG) biofeedback, to enhance muscle strengthening and neuromuscular control. Additionally, there is growing interest in the application of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy and other biologic treatments to promote tendon healing and reduce inflammation. As research continues to evolve, it’s likely that novel approaches to treating and preventing anterior tibial tendonitis will become available, offering improved outcomes for affected individuals.
FAQs
What are the primary causes of anterior tibial tendonitis?
+The primary causes of anterior tibial tendonitis include overuse injuries, poor biomechanics, and direct trauma to the tendon. It's also common among athletes who engage in sports that involve repetitive ankle movements.
How long does it take to recover from anterior tibial tendonitis?
+Recovery time from anterior tibial tendonitis can vary significantly depending on the severity of the injury and the effectiveness of the treatment plan. Mild cases may resolve within a few weeks, while more severe cases can take several months to heal completely.
Can anterior tibial tendonitis be prevented?
+Yes, anterior tibial tendonitis can be prevented or the risk can be significantly reduced by incorporating ankle strengthening exercises into a regular training program, wearing appropriate footwear, and avoiding overuse injuries through proper training techniques and gradual progression of activity levels.
In conclusion, anterior tibial tendonitis is a treatable condition that requires a comprehensive approach to recovery. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps towards healing and preventing future injuries. Incorporating strengthening exercises, adopting preventive strategies, and seeking professional advice when needed are key components of managing anterior tibial tendonitis effectively. With patience, persistence, and the right guidance, it’s possible to overcome this condition and maintain strong, healthy ankles.

