7 Hpv Wart Symptoms Explained
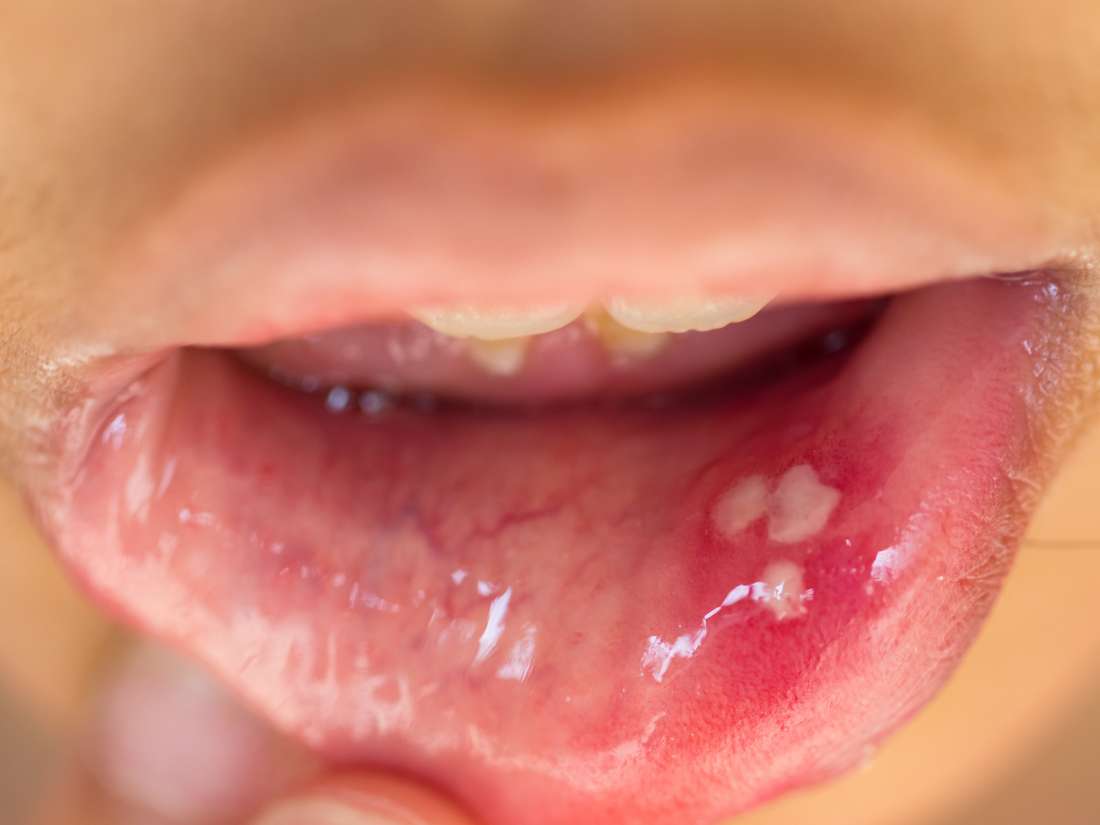
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is a widespread virus that can lead to the development of warts, which are benign growths on the skin or mucous membranes. There are over 100 types of HPV, and some strains are more likely to cause warts than others. Understanding the symptoms of HPV warts is crucial for early detection, diagnosis, and treatment. In this article, we will delve into the seven key HPV wart symptoms, exploring their characteristics, and what they might indicate about the underlying condition.
1. Appearance of Warts
One of the most common symptoms of HPV warts is the appearance of small, rough, or flat growths on the skin. These warts can appear anywhere on the body but are most commonly found on the hands, feet, face, or genital area. The appearance of warts can vary significantly; they might be: - Common Warts: These are usually rough to the touch and appear as small, grainy bumps, often on the hands or fingers. - Plantar Warts: Found on the bottom of the feet, these warts can be painful and may appear as small holes or patches. - Flat Warts: Smaller and smoother than common warts, these can appear anywhere and are often numerous. - Genital Warts: These appear in the genital area and can be itchy, uncomfortable, and sometimes painful.
2. Itchiness or Irritation
Many people with HPV warts experience itchiness or irritation around the affected area. This symptom can be particularly bothersome with genital warts, as the location can make the irritation feel more pronounced. Itchiness is a response to the body’s reaction to the virus and the wart itself, which can sometimes cause discomfort and annoyance.
3. Bleeding
In some cases, especially with genital warts, there might be bleeding during sexual intercourse or other activities that cause friction. This is due to the friable nature of the warts, which can bleed easily. Bleeding is a symptom that should prompt immediate medical evaluation to rule out other, potentially more serious conditions.
4. Discomfort or Pain
While many warts are painless, some, especially those on the soles of the feet (plantar warts) or in the genital area, can cause discomfort or pain. The pain is usually a result of pressure on the wart or due to the location of the wart, which can be subjected to friction or pressure.
5. Changes in Skin Color
In some instances, the skin around the wart may exhibit changes in color, becoming lighter or darker than the surrounding skin. This can be due to the viral infection influencing the skin’s pigmentation or the body’s immune response to the wart.
6. Multiple Warts Appearing
HPV can cause multiple warts to appear in the same area or in different parts of the body. The appearance of multiple warts can indicate a more significant viral load and may suggest that the immune system is having difficulty clearing the virus.
7. Respiratory Symptoms (Rare)
Although rare, some types of HPV, particularly those that cause warts in the throat (recurrent respiratory papillomatosis), can lead to respiratory symptoms. These might include hoarseness, voice changes, or difficulty breathing in severe cases. This condition requires immediate medical attention due to the potential for airway obstruction.
Understanding and Addressing HPV Wart Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of HPV warts is crucial for managing the condition effectively. While many warts will resolve on their own, some may require treatment to alleviate symptoms, prevent the spread of the virus, and address any related discomfort or complications. It’s also important to note that some strains of HPV are associated with a higher risk of certain cancers, emphasizing the need for regular health check-ups and discussions with healthcare providers about HPV prevention, screening, and treatment options.
What are the most common types of HPV warts?
+The most common types include common warts, plantar warts, flat warts, and genital warts. Each type has distinct characteristics and appears in different locations on the body.
Can HPV warts be treated?
+How can I prevent getting HPV warts?
+Prevention measures include practicing good hygiene, avoiding skin-to-skin contact with someone who has warts, not sharing personal items, and getting vaccinated against certain strains of HPV. For genital warts, using condoms can reduce the risk of transmission.
In conclusion, being aware of the symptoms of HPV warts is the first step in managing and treating the condition. Understanding that HPV warts can manifest differently in various individuals highlights the importance of seeking medical advice for any new or suspicious growths. Early detection and appropriate treatment not only alleviate discomfort and cosmetic concerns but also play a critical role in preventing the spread of the virus and addressing any potential long-term health implications associated with certain strains of HPV.