7 Ear Pain Causes From Toothaches Explained
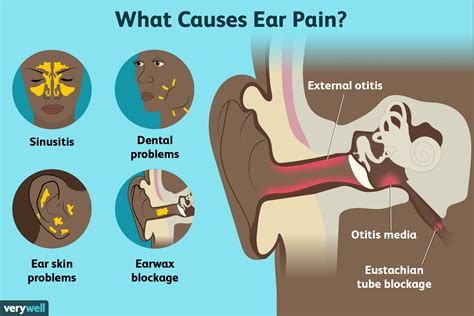
Ear pain can be a debilitating and frustrating experience, especially when it seems to come out of nowhere. While many people assume that ear pain is always related to issues within the ear itself, such as infections or blockages, it can also be referred pain from other areas of the body. One common and often overlooked cause of ear pain is toothaches. The connection between toothaches and ear pain might seem obscure at first, but understanding the anatomical and neurological links between the teeth, jaw, and ears can provide valuable insights into why toothaches can cause ear pain.
The Anatomical Connection
The ears, teeth, and jaw are closely interconnected through a complex system of nerves and bones. The temporomandibular joint (TMJ), located just in front of the ear, connects the jawbone to the skull. This joint plays a crucial role in facilitating movements such as chewing, talking, and yawning. The nerves that supply the TMJ and the surrounding areas also have branches that extend to the ears. As a result, pain or discomfort in the teeth or jaw can be referred to the ear due to the shared nerve pathways.
1. Tooth Decay and Infection
Tooth decay, if left untreated, can lead to infections that reach the pulp of the tooth, causing significant pain. This pain can radiate to the ear, especially if the affected tooth is in the upper jaw, due to the proximity and shared nerve supply. The infection can irritate the nerves, leading to referred pain in the ear.
2. Abscesses
A dental abscess is a collection of pus that can form in the teeth or gums as a result of a bacterial infection. An abscess can cause severe, throbbing pain, and if it’s located near the back teeth, this pain can easily radiate to the ear. The pressure and inflammation from the abscess can irritate the trigeminal nerve, one of the main nerves responsible for facial sensation, including parts of the ear.
3. Impacted Wisdom Teeth
Impacted wisdom teeth are those that do not have enough room to come in normally or develop normally. This can lead to pain, swelling, and infection, especially if the wisdom tooth pushes against the surrounding teeth or becomes impacted. The pain from an impacted wisdom tooth can be felt in the ear due to the close proximity of the wisdom teeth to the temporomandibular joint and the ear.
4. Gum Disease
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is an infection of the gums that can cause pain, swelling, and bad breath. Advanced gum disease can lead to the formation of abscesses and significant pain, which can refer to the ear. The inflammation and infection associated with gum disease can irritate the nerves, causing pain that feels like it’s coming from the ear.
5. Dental Work
Sometimes, the process of dental work itself can lead to ear pain. Procedures like root canals, extractions, or planting dental implants can cause temporary pain and discomfort. If the dental work irritates the nerves or causes inflammation near the jaw or TMJ, it can lead to referred pain in the ear.
6. TMJ Disorders
The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) plays a critical role in the functioning of the jaw. Disorders of the TMJ can cause pain in the jaw, face, and ear. Activities like chewing gum, grinding teeth, or clenching the jaw can exacerbate TMJ disorders, leading to significant discomfort and pain that feels like it’s coming from the ear.
7. Bruxism
Bruxism is the habit of grinding, gnashing, or clenching the teeth, often unknowingly while sleeping. This can put excessive strain on the jaw muscles and the TMJ, leading to pain and discomfort. The repeated stress on the jaw and the nerves can cause pain that is referred to the ear, making it feel like the ear is the source of the discomfort.
Conclusion
The connection between toothaches and ear pain highlights the complex interplay between different parts of the body. Understanding that toothaches can cause referred pain in the ear can lead to more accurate diagnoses and effective treatments. If you’re experiencing unexplained ear pain, it’s crucial to consider dental issues as a potential cause. Consulting both a dentist and an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist can help pinpoint the exact cause of the pain and provide the appropriate treatment.
Can toothaches always cause ear pain?
+No, not all toothaches cause ear pain. However, toothaches, especially those involving the upper teeth or the back molars, can cause referred pain in the ear due to shared nerve pathways.
How can I differentiate between ear pain caused by toothaches and other ear issues?
+Differentiating between the two requires a thorough examination by both a dentist and an ENT specialist. They can perform specific tests and examinations to determine the source of the pain.
Can treating toothaches resolve ear pain caused by them?
+Yes, in many cases, treating the underlying dental issue can resolve the referred ear pain. However, the specific treatment depends on the cause of the toothache and may involve dental procedures, medication for pain and infection, or orthodontic treatments for issues like TMJ disorders.