12 Ms Causes To Understand Peripheral Neuropathy
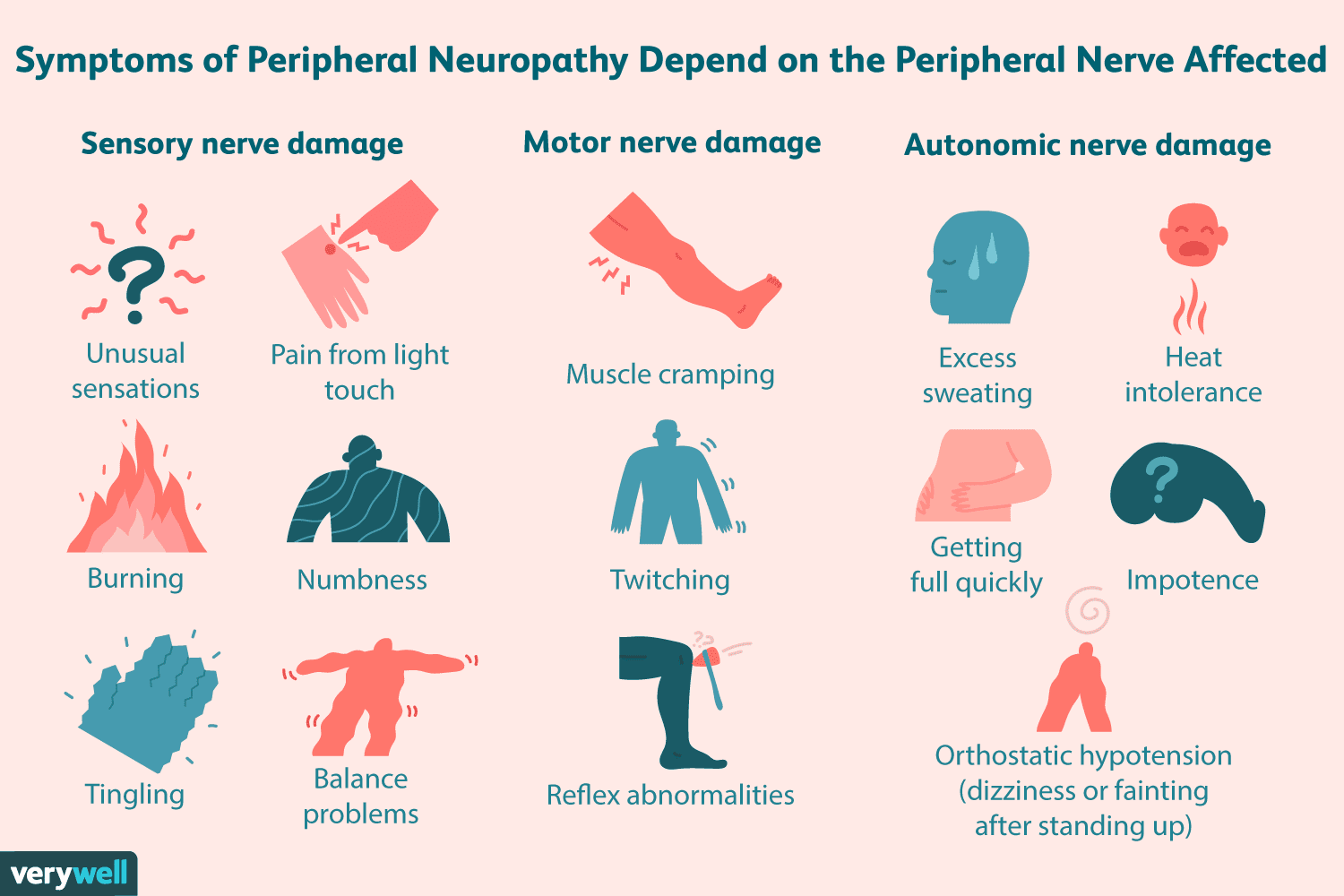
Peripheral neuropathy, a condition affecting millions worldwide, is characterized by damage to the peripheral nerves, which are responsible for transmitting information between the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the rest of the body. This damage can lead to a wide range of symptoms, including numbness, weakness, and pain, typically in the hands and feet. Understanding the causes of peripheral neuropathy is crucial for developing effective treatment strategies and preventive measures. Here are 12 key causes to grasp the complexities of this condition:
Diabetes Mellitus: Diabetes is one of the leading causes of peripheral neuropathy. High blood sugar levels over a long period can damage the nerves, leading to diabetic neuropathy. This condition can manifest as pain, numbness, or tingling in the feet and hands.
Trauma or Injury: Physical injury from accidents, falls, or sports can cause peripheral neuropathy. The trauma can directly damage the nerves, leading to symptoms such as pain, weakness, or numbness, depending on the severity and location of the injury.
Infections: Certain infections, such as Lyme disease, shingles, and HIV, can cause peripheral neuropathy. These infections can directly damage the nerves or trigger an immune response that leads to nerve damage.
Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and Guillain-Barré Syndrome can lead to peripheral neuropathy. In these disorders, the immune system mistakenly attacks the nerves, causing inflammation and damage.
Nutritional Deficiencies: Lack of vitamins, particularly B vitamins (including B1, B6, and B12), can cause peripheral neuropathy. These vitamins are crucial for nerve health, and deficiencies can lead to nerve damage over time.
Exposure to Toxins: Exposure to certain toxins, such as heavy metals (arsenic, lead, mercury) and industrial chemicals, can damage peripheral nerves. These toxins can be found in the environment, in certain jobs, or in products.
Genetic Predisposition: Some people are born with genetic disorders that affect the nerves, leading to peripheral neuropathy. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease is one such inherited disorder that damages the peripheral nerves.
Tumors: Both benign and malignant tumors can compress or damage nerves, leading to peripheral neuropathy. The pressure exerted by the tumor on the nerves can cause a range of symptoms, including pain, numbness, and weakness.
Medications: Certain medications, including some used to treat cancer, infections, and high blood pressure, can have peripheral neuropathy as a side effect. The mechanism often involves interfering with nerve function or damaging the nerves directly.
Vitamin Deficiency Due to Alcoholism: Chronic alcohol abuse can lead to a deficiency in thiamine (vitamin B1) and other nutrients, contributing to peripheral neuropathy. Alcohol itself can also be toxic to nerves.
Kidney or Liver Diseases: These conditions can lead to the accumulation of toxins in the body, which can damage the nerves.Peripheral neuropathy is a known complication of end-stage kidney disease and liver failure.
Aging: As people age, they are more likely to develop peripheral neuropathy. Age-related wear and tear on the nerves, combined with other health issues that become more common with age, can contribute to the development of peripheral neuropathy.
Understanding these causes is essential for healthcare providers to diagnose and treat peripheral neuropathy effectively. Treatment often involves addressing the underlying cause, managing symptoms, and preventing further nerve damage. Lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy diet, quitting smoking, and limiting alcohol consumption, can also help manage the condition and prevent its progression.
In practical terms, managing peripheral neuropathy requires a multifaceted approach. For individuals with diabetes, closely monitoring blood sugar levels and maintaining good foot care can prevent complications. For those with a history of trauma or exposure to toxins, seeking immediate medical attention and following up with rehabilitation can mitigate long-term effects.
Furthermore, recognizing the interplay between peripheral neuropathy and broader systemic health is crucial. Conditions that affect the peripheral nerves often reflect or contribute to other health issues, such as cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, or autoimmune conditions. Thus, a holistic approach to health, focusing on prevention, early detection, and comprehensive management, is key to living with peripheral neuropathy and improving quality of life.
Peripheral neuropathy is not just a condition to be managed; it's a symptom of broader health dynamics. Understanding its causes and addressing them can lead to substantial improvements in patient outcomes and quality of life.
Given the complexity and variability of peripheral neuropathy, personalized care plans are essential. These plans should consider the individual’s specific symptoms, underlying causes, lifestyle, and other health conditions. By taking a tailored approach, healthcare providers can offer more effective support and guidance, empowering individuals to manage their condition proactively.
For instance, incorporating natural therapies and lifestyle adjustments can complement medical treatments. Exercise, physical therapy, and dietary changes have been shown to improve nerve function and reduce symptoms in some individuals. Moreover, stress management techniques, such as meditation and yoga, can help cope with the emotional and psychological aspects of living with peripheral neuropathy.
In conclusion, peripheral neuropathy is a multifaceted condition with a wide range of causes and symptoms. By understanding these causes, individuals and healthcare providers can work together to develop effective treatment plans, manage symptoms, and improve quality of life. Whether through medical intervention, lifestyle changes, or a combination of both, there are pathways to mitigating the effects of peripheral neuropathy and promoting overall well-being.
What are the first steps in managing peripheral neuropathy?
+The first steps include identifying and treating the underlying cause, managing symptoms, and adopting lifestyle changes to prevent further nerve damage. Consultation with a healthcare provider is essential for personalized advice.
Can peripheral neuropathy be reversible?
+Some forms of peripheral neuropathy can be reversible or significantly improved with proper treatment of the underlying cause. Early intervention is key to preventing permanent nerve damage.
How can I reduce my risk of developing peripheral neuropathy?
+Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, not smoking, and limiting alcohol consumption, can reduce the risk. Regular health check-ups can also help in early detection and management of conditions that may lead to peripheral neuropathy.
