10+ Tooth Resorption Symptoms To Know
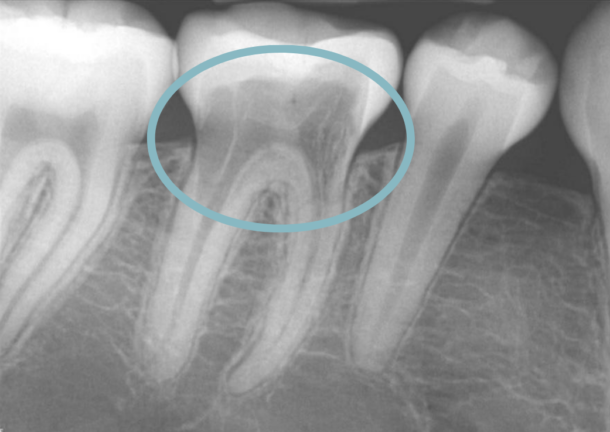
Tooth resorption is a dental condition characterized by the breakdown or dissolution of the tooth structure, which can be caused by various factors such as trauma, infection, or orthodontic treatment. The symptoms of tooth resorption can vary depending on the severity and location of the condition, but here are 10+ common symptoms to look out for:
- Tooth sensitivity: One of the earliest symptoms of tooth resorption is tooth sensitivity, which can range from mild to severe. You may experience pain or discomfort when consuming hot or cold foods and drinks, or when biting down on hard objects.
- Tooth discoloration: As the tooth structure breaks down, the tooth may become discolored, turning gray, brown, or yellow. This discoloration can be noticeable and may affect the appearance of your smile.
- Tooth mobility: In advanced cases of tooth resorption, the tooth may become loose or mobile, making it difficult to chew or bite down on food.
- Pain or tenderness: Tooth resorption can cause pain or tenderness in the affected tooth, which can be constant or intermittent. The pain may be sharp or dull, and can radiate to other areas of the mouth or face.
- Swelling or inflammation: If the tooth resorption is caused by an infection, you may experience swelling or inflammation in the surrounding tissues, including the gums, cheeks, or lips.
- Bad taste or odor: In some cases, tooth resorption can cause a bad taste or odor in the mouth, which can be embarrassing and affect your self-confidence.
- Gum recession: Tooth resorption can cause the gums to recede, exposing more of the tooth root and making the tooth appear longer than normal.
- Tooth fracture: If the tooth resorption is severe, the tooth may fracture or break, which can be painful and require emergency dental treatment.
- Abscess or cyst formation: In rare cases, tooth resorption can lead to the formation of an abscess or cyst in the surrounding tissues, which can be painful and require surgical intervention.
- Limited mouth opening: If the tooth resorption is caused by an infection or inflammation, you may experience limited mouth opening or difficulty chewing, which can affect your ability to eat and speak.
- Clicking or popping sound: In some cases, tooth resorption can cause a clicking or popping sound when you bite down or chew, which can be annoying and affect your quality of life.
- Tooth worn down: Tooth resorption can cause the tooth to wear down, making it shorter than normal and affecting the appearance of your smile.
It is essential to seek dental care if you experience any of these symptoms, as tooth resorption can progress quickly and lead to more severe consequences if left untreated.
According to the American Association of Endodontists, tooth resorption is a common condition that can affect up to 40% of the population. However, with prompt and proper treatment, it is possible to prevent further progression of the condition and save the affected tooth.
Causes of Tooth Resorption
Tooth resorption can be caused by various factors, including:
- Trauma: A blow to the mouth or a fall can cause tooth resorption, especially if the tooth is knocked out of position or suffers a severe crack.
- Infection: Bacterial infections, such as periodontal disease, can cause tooth resorption by breaking down the tooth structure.
- Orthodontic treatment: Orthodontic treatment, such as braces or Invisalign, can cause tooth resorption if the teeth are moved too quickly or if the treatment is not properly monitored.
- Genetic predisposition: Some people may be more prone to tooth resorption due to their genetic background.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing tooth resorption typically involves a combination of:
- Clinical examination: A dentist will examine your mouth and teeth to look for signs of tooth resorption, such as tooth discoloration or mobility.
- Radiographs: X-rays or other imaging tests may be used to visualize the tooth structure and detect any signs of resorption.
- CBCT scans: Cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) scans may be used to create a 3D image of the tooth and surrounding tissues.
Treatment for tooth resorption depends on the severity of the condition and may involve:
- Root canal therapy: If the tooth resorption is caused by an infection, root canal therapy may be necessary to remove the infected tissue and save the tooth.
- Tooth extraction: In severe cases of tooth resorption, the tooth may need to be extracted to prevent further complications.
- Dental restoration: If the tooth resorption is mild, a dental restoration, such as a crown or filling, may be used to repair the tooth and prevent further breakdown.
What are the common causes of tooth resorption?
+Tooth resorption can be caused by trauma, infection, orthodontic treatment, and genetic predisposition. It is essential to seek dental care if you experience any symptoms of tooth resorption to prevent further progression of the condition.
How is tooth resorption diagnosed?
+Diagnosing tooth resorption typically involves a combination of clinical examination, radiographs, and CBCT scans. A dentist will examine your mouth and teeth to look for signs of tooth resorption and use imaging tests to visualize the tooth structure and detect any signs of resorption.
What are the treatment options for tooth resorption?
+Treatment for tooth resorption depends on the severity of the condition and may involve root canal therapy, tooth extraction, or dental restoration. It is essential to seek dental care promptly to prevent further progression of the condition and save the affected tooth.
In conclusion, tooth resorption is a dental condition that can cause a range of symptoms, from tooth sensitivity and discoloration to tooth mobility and pain. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is essential to seek dental care promptly to prevent further progression of the condition and save the affected tooth. With proper treatment and care, it is possible to prevent tooth resorption and maintain good oral health.

