10+ Prophylaxis Definition Secrets For Better Care

Prophylaxis, a term often misunderstood, yet crucial in the realm of healthcare, refers to measures designed to preserve health and prevent the spread of diseases. The essence of prophylaxis lies in its proactive approach, emphasizing the importance of early intervention and prevention over treatment after the fact. This concept is broad, encompassing a wide range of practices from personal hygiene and vaccination to the use of protective gear in medical settings. Understanding the nuances of prophylaxis is key to better care, as it not only protects individuals but also contributes to public health by reducing the incidence of diseases.
1. Understanding the Basics of Prophylaxis
At its core, prophylaxis is about adopting strategies to avoid disease. This includes practices such as regular dental check-ups for oral health, exercising and dieting for cardiovascular health, and using condoms to prevent sexually transmitted infections. The foundational principle of prophylaxis is that prevention is more effective, less costly, and generally easier than treatment. This principle guides healthcare policies, personal health choices, and public health initiatives.
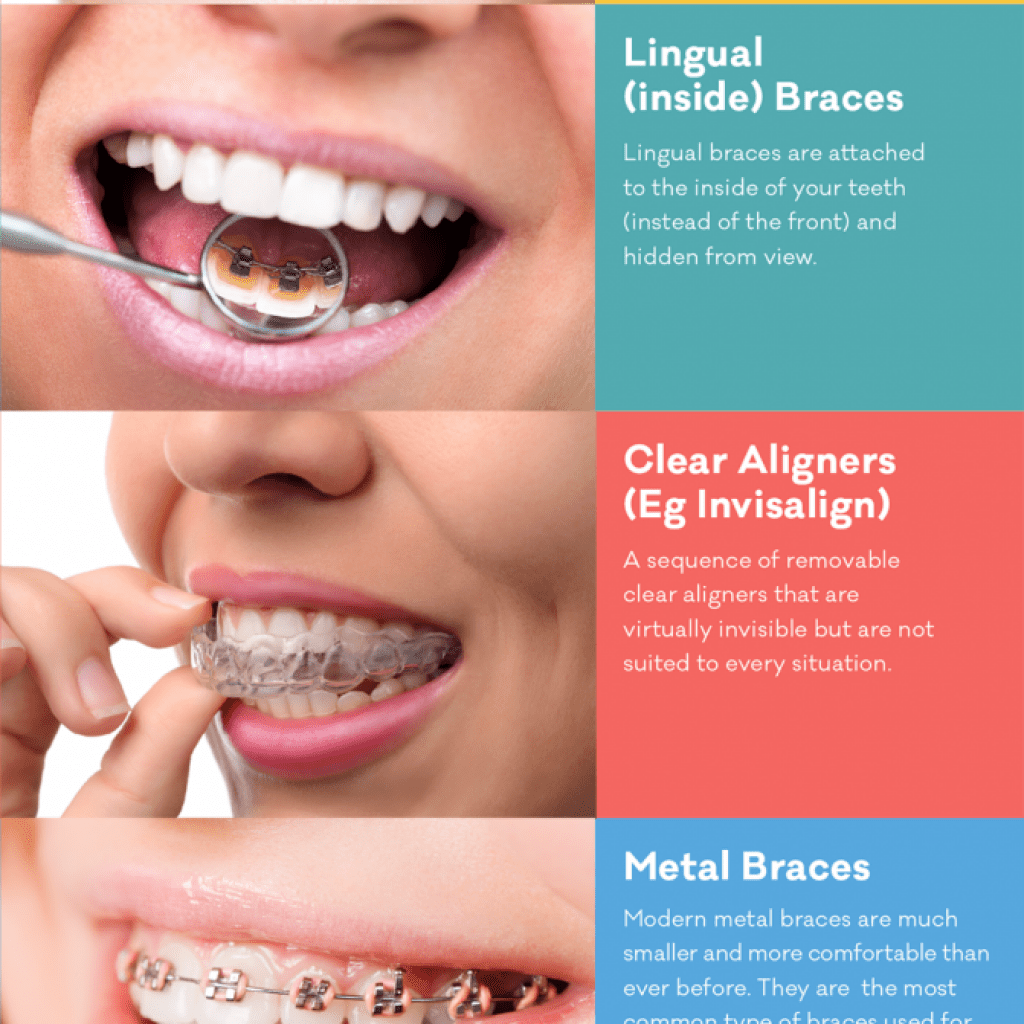
2. Prophylaxis in Dentistry
In dentistry, prophylaxis refers specifically to the measures taken to prevent dental diseases. This includes professional teeth cleaning to remove plaque and tartar, which are primary causes of cavities and gum diseases. Regular dental prophylaxis not only ensures a healthy mouth but also has broader implications for overall health, as research links gum diseases to increased risks of heart disease, diabetes, and other systemic conditions.
3. Pharmacological Prophylaxis
Pharmacological prophylaxis involves the use of drugs to prevent diseases. This can range from taking antibiotics before surgery to prevent infections to using antimalarial drugs when traveling to areas where malaria is common. Vaccination, a form of pharmacological prophylaxis, is one of the most effective ways to prevent infectious diseases. Vaccines work by stimulating the body’s immune system to recognize and fight pathogens without causing the disease itself.
4. Prophylaxis in Surgery
In the context of surgery, prophylaxis is crucial for preventing surgical site infections (SSIs), which are a significant cause of morbidity and mortality. Preoperative prophylaxis includes measures such as skin preparation, appropriate use of antimicrobial agents, and maintaining a sterile environment during surgery. Postoperative care also involves prophylactic measures to monitor for signs of infection and manage pain effectively.
5. Nutritional Prophylaxis
Nutritional prophylaxis emphasizes the role of diet in preventing diseases. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help prevent chronic diseases like heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. Specific nutrients have been identified for their prophylactic benefits, such as omega-3 fatty acids for heart health and calcium for bone health.
6. Psychological Prophylaxis
Psychological prophylaxis focuses on mental health and stress management as preventive measures. Techniques such as meditation, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and mindfulness can prevent or mitigate the effects of mental health disorders like depression and anxiety. Recognizing the interplay between mental and physical health, psychological prophylaxis is increasingly acknowledged as a critical component of overall health.
7. Prophylaxis in Public Health
On a larger scale, prophylaxis plays a vital role in public health policy and practice. This includes initiatives like water fluoridation to prevent tooth decay, campaigns to promote the use of sunscreen to prevent skin cancer, and programs aimed at reducing the incidence of infectious diseases through vaccination and vector control. Public health prophylaxis measures are designed to protect populations and prevent outbreaks.
8. Technological Advances in Prophylaxis
Technological advancements have significantly enhanced prophylactic measures. For example, the development of personal protective equipment (PPE) like masks, gloves, and suits has been crucial in preventing the spread of infectious diseases among healthcare workers. Telemedicine and digital health platforms have also expanded access to preventive care services, enabling more people to engage in prophylactic practices.
9. Economic Benefits of Prophylaxis
The economic benefits of prophylaxis are substantial. Preventing diseases reduces the financial burden on healthcare systems, decreases lost productivity due to illness, and minimizes the economic impact of public health crises. Investing in prophylaxis can yield long-term savings and contribute to economic stability, especially in the context of chronic and infectious diseases.
10. Future Directions in Prophylaxis
The future of prophylaxis is promising, with ongoing research into new preventive technologies, treatments, and strategies. The integration of genetic and genomic information into preventive care holds great potential, as does the development of personalized medicine approaches to prophylaxis. Additionally, advancements in materials science and biotechnology are expected to lead to innovative solutions for disease prevention.
Conclusion
In conclusion, prophylaxis is a multifaceted concept that underpins the foundation of healthcare and public health. By understanding and adopting prophylactic measures, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of disease, and societies can work towards better health outcomes. As our understanding of health and disease evolves, so too will the strategies and technologies used in prophylaxis, offering a promising future for the prevention of diseases and the promotion of global health.
What is the primary goal of prophylaxis in healthcare?
+The primary goal of prophylaxis is to prevent diseases and promote health through early intervention and the adoption of preventive measures.
How does nutritional prophylaxis contribute to overall health?
+Nutritional prophylaxis plays a critical role in preventing chronic diseases by providing the body with the necessary nutrients to function optimally, thereby reducing the risk of conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers.
What are some examples of pharmacological prophylaxis?
+Examples of pharmacological prophylaxis include the use of antibiotics before surgery, antimalarial drugs for travelers, and vaccines to prevent infectious diseases.